Seata入门系列【12】AT模式源码分析之开启全局事务和数据源代理
1 开启全局事务
在之前,我们分析了TransactionalTemplate会进行全局事务的开启、提交或者回滚,接下来分析下,是如何开启全局事务的。
开始全局事务调用的是beginTransaction方法:
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
// 开启全局事务之前钩子
triggerBeforeBegin();
// 开始全局事务
tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName());
// 开启全局事务之后钩子
triggerAfterBegin();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.BeginFailure);
}
}
1.1 事务钩子TransactionHook
在开始全局事务会调用triggerBeforeBegin和triggerAfterBegin方法,会从ThreadLocal中获取当前事务的TransactionHook事务钩子,执行其钩子方法:
private void triggerBeforeBegin() {
for (TransactionHook hook : getCurrentHooks()) {
try {
// 钩子中的beforeBegin
hook.beforeBegin();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed execute beforeBegin in hook {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
private void triggerAfterBegin() {
for (TransactionHook hook : getCurrentHooks()) {
try {
// 钩子中的afterBegin
hook.afterBegin();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed execute afterBegin in hook {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
TransactionHook 接口就是事务钩子,可以在事务的各个状态中添加钩子,比如在事务回滚之后记录全局事务失败日志。
public interface TransactionHook {
/**
* before tx begin
*/
void beforeBegin();
/**
* after tx begin
*/
void afterBegin();
/**
* before tx commit
*/
void beforeCommit();
/**
* after tx commit
*/
void afterCommit();
/**
* before tx rollback
*/
void beforeRollback();
/**
* after tx rollback
*/
void afterRollback();
/**
* after tx all Completed
*/
void afterCompletion();
}
1.2 事务角色
TransactionalTemplate.beginTransaction方法传入了TransactionInfo和GlobalTransaction参数,TransactionInfo封装了@GlobalTransactional注解的配置信息,而GlobalTransaction就是全局事务。

在GlobalTransaction实例对象有,有一个全局事务角色枚举类,源码如下:
public enum GlobalTransactionRole {
/**
* 发起者,开启全局事务
*/
Launcher,
/**
* 参与者,加入已存在的全局事务
*/
Participant
}
TM 开启事务时,在线程中是没有xid的,所以会创建一个全局事务,直接创建一个DefaultGlobalTransaction对象:
/**
* Try to create a new GlobalTransaction.
*
* @return the new global transaction
*/
public static GlobalTransaction createNew() {
return new DefaultGlobalTransaction();
}
在DefaultGlobalTransaction的构造方法中,可以看到这里设置事务角色为Launcher
DefaultGlobalTransaction() {
this(null, GlobalStatus.UnKnown, GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher);
}
在DefaultGlobalTransaction.begin开始方法中,首先就会判断角色
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
// 当前角色不是事务发起者
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
// 不是发起者,判断xid 是否存在,不存在抛出IllegalStateException异常
// 存在xid ,直接return,说明只能TC 开启全局事务。
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
// 省略....
1.3 全局事务管理器
DefaultGlobalTransaction.begin校验角色之后,就会调用事务管理器开始全局事务,这里有一个xid 的生成及传递。
// 开始全局事务之前xid 必须为空
assertXIDNull();
String currentXid = RootContext.getXID();
if (currentXid != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," +
" can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid);
}
// 调用事务管理器开始全局事务
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
// 标记事务状态为开始
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
// 绑定xid
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
TransactionManager接口用于定义并控制全局事务,全局事务的开启、提交、回滚、状态报告,都由该接口完成,其默认实现类为DefaultTransactionManager。
所以开启事务,会进入到了DefaultTransactionManager的begin 方法,该方法会创建开始全局事务请求对象,请求Seata 服务端,并获取响应回来的xid :
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 请求对象
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
// 请求并返回响应
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
// 返回响应中的xid
return response.getXid();
}
GlobalBeginRequest对象中,只传递了事务超时时间和当前执行的方法名:
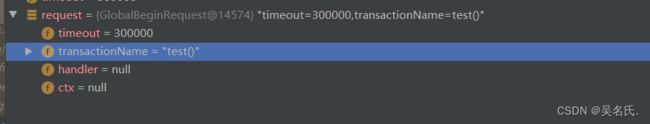
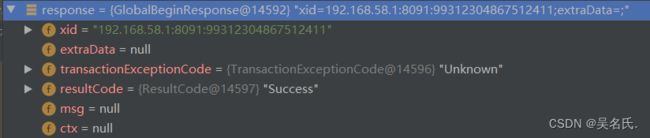
GlobalBeginResponse对象中,只返回了xid 和响应状态。
1.4 RPC 请求TC 服务端
TM 发送请求是基于Netty 框架,会获取TC 服务端地址,然后发送消息,具体源码就不分析了,内容太多。
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
return (AbstractTransactionResponse)TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException var3) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", var3);
}
}
在Seata 服务端,开启、提交、回滚全局事务,注册、提交、回滚分支事务都是由DefaultCoordinator(协调这)负责协调处理的。
TC开始全局事务时,就会进入到DefaultCoordinator的doGlobalBegin方法:
@Override
protected void doGlobalBegin(GlobalBeginRequest request, GlobalBeginResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
// 调用DefaultCore的 begin方法
response.setXid(core.begin(rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout()));
// 打印开始全局事务日志
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction applicationId: {},transactionServiceGroup: {}, transactionName: {},timeout:{},xid:{}",
rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(), request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout(), response.getXid());
}
}
在DefaultCore的 begin方法中,完成服务端整个开始全局事务的处理逻辑:
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 1. 创建全局事务Session
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
// 2. 将xid 绑定到日志Slf4j的MDC机制中,用于追踪全局日志
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, session.getXid());
//Session 中添加回调监听 ,Session 管理器(观察者模式)
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 会话开启
session.begin();
// 事务开始事件
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
// 响应XID 给TM端
return session.getXid();
}
在创建全局会话的代码中,可以看到xid 是使用服务端IP+端口+雪花ID 方式生成的:
public GlobalSession(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String transactionName, int timeout) {
this.transactionId = UUIDGenerator.generateUUID();
this.status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
this.applicationId = applicationId;
this.transactionServiceGroup = transactionServiceGroup;
this.transactionName = transactionName;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.xid = XID.generateXID(transactionId);
}
1.5 TC 服务端的事务会话管理器
服务端在开启全局事务时,会添加事务会话管理器,这里设置的是数据库存储,所以使用的是的DataBaseSessionManager:
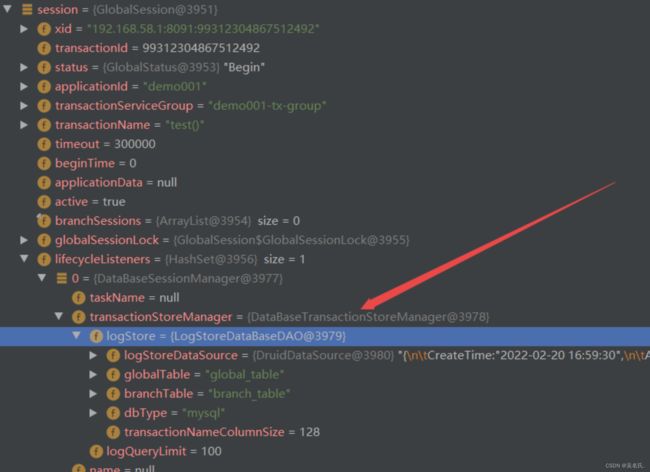
Seata 支持三种事务会话存储,分别为数据库、文件、Redis:
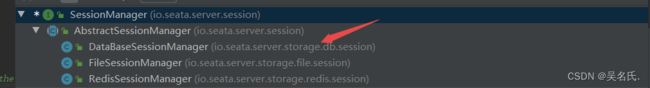
之后begin 方法就到了DataBaseSessionManager的addGlobalSession方法:
@Override
public void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(taskName)) {
// 写入会话
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
} else {
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
}
}
1.6 存储全局事务信息
在第五步写入Session 时,会将全局事务信息插入到global_table表中,并将xid 返回给TC,整个开始事务的流程就结束了
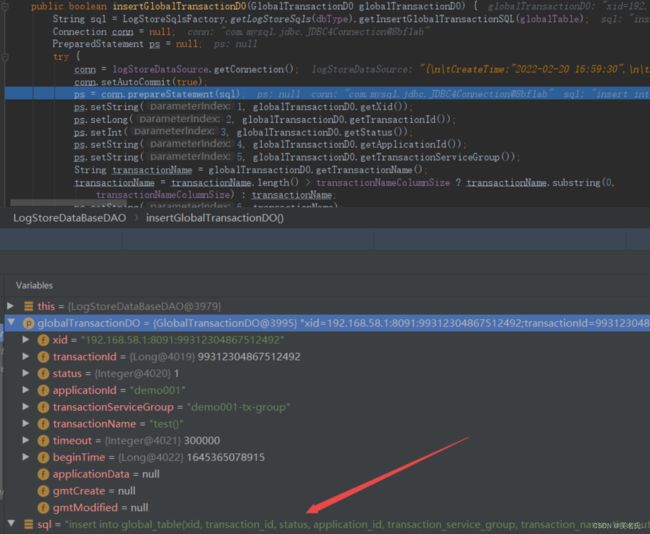
2 数据源代理
2.1 前言
在之前,我们了解到Seata 会对数据源进行代理,执行SQL时,会进入到Seata 的代理数据源中,接下来我们分析下是如何进行代理的?
2.2 数据源代理
2.2.1 自动代理配置类
在seata-spring-boot-starter模块的SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration配置类中,开启了seata数据源的自动代理,该准备主要是注入了SeataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor和SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator。
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnExpression("${seata.enable:true} && ${seata.enableAutoDataSourceProxy:true} && ${seata.enable-auto-data-source-proxy:true}")
public class SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean seataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor.
*/
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SEATA_DATA_SOURCE_BEAN_POST_PROCESSOR)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SeataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor.class)
public SeataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor seataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor(SeataProperties seataProperties) {
//
return new SeataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor(seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying(), seataProperties.getDataSourceProxyMode());
}
/**
* The bean seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.
*/
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SEATA_AUTO_DATA_SOURCE_PROXY_CREATOR)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class)
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(SeataProperties seataProperties) {
return new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(seataProperties.isUseJdkProxy(),
seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying(), seataProperties.getDataSourceProxyMode());
}
}
2.2.2 数据源后置处理器
SeataDataSourceBeanPostProcessor 实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,BeanPostProcessor是Spring 中的后置处理器,作用是在Bean对象在实例化和依赖注入完毕后,调用初始化方法时在其前后添加我们自己的逻辑。
主要是重写了其postProcessAfterInitialization方法,在Bean 初始化完成后会调用该方法,会进行数据源的代理。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof DataSource) {
//When not in the excludes, put and init proxy.
// 配置中没有忽略DataSource类的代理,则进行代理
if (!excludes.contains(bean.getClass().getName())) {
//Only put and init proxy, not return proxy.
// 初始化代理
DataSourceProxyHolder.get().putDataSource((DataSource) bean, dataSourceProxyMode);
}
//If is SeataDataSourceProxy, return the original data source.
// 如果Bean 已经是SeataDataSourceProxy,返回原来的数据源
if (bean instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy) {
LOGGER.info("Unwrap the bean of the data source," +
" and return the original data source to replace the data source proxy.");
return ((SeataDataSourceProxy) bean).getTargetDataSource();
}
}
return bean;
}
在上面的putDataSource方法中,会进行数据源代理类的创建:
/**
* Put dataSource
*
* @param dataSource 数据源
* @param dataSourceProxyMode 代理模式,AT模式
* @return dataSourceProxy
*/
public SeataDataSourceProxy putDataSource(DataSource dataSource, BranchType dataSourceProxyMode) {
DataSource originalDataSource;
// 1. 如果数据源是SeataDataSourceProxy,则直接返回
if (dataSource instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy) {
SeataDataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = (SeataDataSourceProxy) dataSource;
//If it's an right proxy, return it directly.
// 如果是正确的代理,请直接返回。
if (dataSourceProxyMode == dataSourceProxy.getBranchType()) {
return (SeataDataSourceProxy) dataSource;
}
//Get the original data source.
// 获取原始数据源。
originalDataSource = dataSourceProxy.getTargetDataSource();
} else {
originalDataSource = dataSource;
}
// 2. 从存放代理的集合中获取该数据源的代理数据源
SeataDataSourceProxy dsProxy = dataSourceProxyMap.get(originalDataSource);
if (dsProxy == null) {
// 3.如果没有则创建代理并放入集合中
synchronized (dataSourceProxyMap) {
dsProxy = dataSourceProxyMap.get(originalDataSource);
if (dsProxy == null) {
dsProxy = createDsProxyByMode(dataSourceProxyMode, originalDataSource);
dataSourceProxyMap.put(originalDataSource, dsProxy);
}
}
}
//4. 返回
return dsProxy;
}
createDsProxyByMode方法用于创建数据源代理,如果是XA 模式,创建DataSourceProxyXA,其他模式(AT模式)创建DataSourceProxy:
private SeataDataSourceProxy createDsProxyByMode(BranchType mode, DataSource originDs) {
return (SeataDataSourceProxy)(BranchType.XA == mode ? new DataSourceProxyXA(originDs) : new DataSourceProxy(originDs));
}
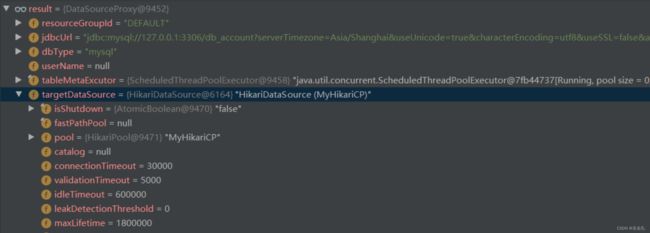
DataSourceProxy就是代理数据源类,直接通过New 创建数据源代理:
public DataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
if (targetDataSource instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy) {
LOGGER.info("Unwrap the target data source, because the type is: {}", targetDataSource.getClass().getName());
targetDataSource = ((SeataDataSourceProxy) targetDataSource).getTargetDataSource();
}
this.targetDataSource = targetDataSource;
init(targetDataSource, resourceGroupId);
}
在数据源代理的构造方法中,会调用init 初始化方法,获取原来数据源的属性信息,设置到当前代理类中,并开启一个定时任务,每分钟查询一次数据源的表结构信息并缓存,在需要查询数据库结构时会用到,不然每次去数据库查询结构效率会很低。
private void init(DataSource dataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
this.resourceGroupId = resourceGroupId;
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
// 数据库连接
jdbcUrl = connection.getMetaData().getURL();
// 数据库类型,MySql
dbType = JdbcUtils.getDbType(jdbcUrl);
if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType)) {
userName = connection.getMetaData().getUserName();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("can not init dataSource", e);
}
// 资源管理器管理注册本类
DefaultResourceManager.get().registerResource(this);
// 判断是否启动定时任务,定时任务的作用是缓存数据库表结构,表结构在RM保存数据快照的时候使用。如果内存中没有缓存,会实时查询数据库。
//默认1分钟运行一次。
if (ENABLE_TABLE_META_CHECKER_ENABLE) {
tableMetaExcutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(DataSourceProxy.this.getDbType())
.refresh(connection, DataSourceProxy.this.getResourceId());
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}, 0, TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
//Set the default branch type to 'AT' in the RootContext.
RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.getBranchType());
}
2.2.3 添加AOP
在上面的类中,生成了数据源的代理对象,那么执行数据增删改查时,是如何切换到代理数据源的呢?
SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator抽象类,Spring 通过 AbstractAutoProxyCreator来创建 AOP 代理,其实现了BeanPostProcessor 接口,用于在 bean 初始化完成之后创建它的代理。在Seata 中,该类目的是为数据源添加Advisor,当数据源执行操作时,会进入其SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice类中处理。
public class SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class);
private final List<String> excludes;
private final Advisor advisor;
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(boolean useJdkProxy, String[] excludes, String dataSourceProxyMode) {
this.excludes = Arrays.asList(excludes);
this.advisor = new DefaultIntroductionAdvisor(new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(dataSourceProxyMode));
setProxyTargetClass(!useJdkProxy);
}
// 为数据源Bean 添加 Advisor
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource customTargetSource) throws BeansException {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Auto proxy of [{}]", beanName);
}
return new Object[]{advisor};
}
// 不是DataSource 则跳过
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
return !DataSource.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
SeataProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
excludes.contains(beanClass.getName());
}
}
当数据源执行操作时,由于添加了AOP代理,最终会进入到SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice的invoke方法中:
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && dataSourceProxyMode != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
return invocation.proceed();
}
// 数据源执行的方法,比如获取连接的 getConnection()
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
// 查询代理数据源对应的方法 DataSourceProxy.getConnection()
Method m = BeanUtils.findDeclaredMethod(dataSourceProxyClazz, method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes());
if (m != null && DataSource.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
SeataDataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = DataSourceProxyHolder.get().putDataSource((DataSource) invocation.getThis(), dataSourceProxyMode);
// 执行代理数据源的方法
return m.invoke(dataSourceProxy, args);
} else {
return invocation.proceed();
}
}