Python 的 type() 和 isinstance() 函数
type()、isinstance()都是对象类型操作函数,用于判定 Python 对象类型,用哪个函数更好哩?
-
Python 官网:https://www.python.org/
-
Free:大咖免费“圣经”教程《 python 完全自学教程》,不仅仅是基础那么简单……
地址:https://lqpybook.readthedocs.io/
自学并不是什么神秘的东西,一个人一辈子自学的时间总是比在学校学习的时间长,没有老师的时候总是比有老师的时候多。
—— 华罗庚
- My CSDN主页、My HOT博、My Python 学习个人备忘录
- 好文力荐、 老齐教室
本文质量分:
CSDN质量分查询入口:http://www.csdn.net/qc
- ◆ type() & isinstance() —— Python
-
- 1、初识 type()、isinstance() 函数
-
- 1.1 help() 函数
- 1.2 type()
- 1.3 isinstance()
- 2、判定 Python 基本类型
-
- 2.1 type() 查看数据类型
- 2.2 type() 判定数据类型
- 2.3 isinstance() 判定数据类型
- 3、type() 快速生成新 class
-
- 3.1 type() 创建 class
- 3.2 type()、 isinstance() 判定自定义 class
- 4、isinstance() 的类型参数可以是多个类型联合的元组
- 5、isinstance() 与 type() 区别
- 6、完整源码
◆ type() & isinstance() —— Python
1、初识 type()、isinstance() 函数
1.1 help() 函数
我们先来认识下 type()、 isinstance() 这两个函数——
对于认识 Python 内置对象,Python 为我们准备了多快好省的内置函数 help() 。把想要查看的对象当其参数放入圆括号就行,函数对象作参数对象时不写圆括号。例如——
- help(type)、help(isinstance)
help(type)
help(isinstance)
其次就是 Python 官方文档,更权威详尽。但对于英文不太好的我来说,虽然祭出词霸大杀器,大多依旧不能很好理解。我学习 Python 的一般路数就是在基本会用时,再探索其官方文档,以资用得正统。
- Python 最新官方文档
Python 3.12.07a 内建函数文档地址:
https://docs.python.org/3.12/library/functions.html
1.2 type()
- help(type)
help(type)
Help on class type in module builtins:
class type(object)
type(object) -> the object’s type
type(name, bases, dict, **kwds) -> a new type
…
Data and other attributes defined here:
base =
The base class of the class hierarchy.
When called, it accepts no arguments and returns a new featureless instance that has no instance attributes and cannot be given any.
…
- Python 3.12.0a7 的 type() 文档
class type(object)
class type(name, bases, dict, **kwds)
With one argument, return the type of an object. The return value is a type object and generally the same object as returned by object.class.
The isinstance() built-in function is recommended for testing the type of an object, because it takes subclasses into account.
With three arguments, return a new type object. This is essentially a dynamic form of the class statement. The name string is the class name and becomes the name attribute. The bases tuple contains the base classes and becomes the bases attribute; if empty, object, the ultimate base of all classes, is added. The dict dictionary contains attribute and method definitions for the class body; it may be copied or wrapped before becoming the dict attribute. The following two statements create identical type objects:
>>>
>>> class X:
... a = 1
...
>>> X = type('X', (), dict(a=1))
See also Type Objects.
Keyword arguments provided to the three argument form are passed to the appropriate metaclass machinery (usually init_subclass()) in the same way that keywords in a class definition (besides metaclass) would.
See also Customizing class creation.
Changed in version 3.6: Subclasses of type which don’t override type.new may no longer use the one-argument form to get the type of an object.
- type() 最新官方文档地址:https://docs.python.org/3.12/library/functions.html#type
- type() 语法
type(object) -> the object's type
type(name, bases, dict, **kwds) -> a new type
一个参数查看参数对象类型,返回类型字符串;三个参数(字符串 str、基类元组 (int,)、字典 {} ——字典可以为空——,三个参数不可缺省),快速新建类。新建一个基类元组参数的子类,没有返回值。
1.3 isinstance()
- help(isinstance)
help(isinstance)
Help on built-in function isinstance in module builtins:
isinstance(obj, class_or_tuple, /)
Return whether an object is an instance of a class or of a subclass thereof.
A tuple, as inisinstance(x, (A, B, ...)), may be given as the target to check against. This is equivalent toisinstance(x, A) or isinstance(x, B) or ...etc.
- Python 3.12.0a7 的 isinstance() 文档
isinstance(object, classinfo)
Return True if the object argument is an instance of the classinfo argument, or of a (direct, indirect, or virtual) subclass thereof. If object is not an object of the given type, the function always returns False. If classinfo is a tuple of type objects (or recursively, other such tuples) or a Union Type of multiple types, return True if object is an instance of any of the types. If classinfo is not a type or tuple of types and such tuples, a TypeError exception is raised. TypeError may not be raised for an invalid type if an earlier check succeeds.
Changed in version 3.10: classinfo can be a Union Type.
-
isinstance() 最新官方文档地址:https://docs.python.org/3.12/library/functions.html#isinstance
-
语法
isinstance(obj, class_or_tuple, /)
isinstance(object, classinfo)
isinstance() 返回的是 bool 值 ( True or Flase ),参数1是参数2的类型,返回 True ;反之返回 Flase 。
译文,总是有译者理解和观点的影子。对一段语言的多个译文,就是一棵树上的叶子,不会有相同的两片。为不让别人的“经验”对大家造成影响,我在这里直接贴出最新的官方文档。帮助文档也是直接 cv 的 help()输出。
如果您跟我一样,英文“大字不识一箩筐”,也不用着急。下面有例子代码、运行效果截屏,您跟我一样,可以慢慢理解,渐渐会用的。type()、isinstance() 难不住您!
2、判定 Python 基本类型
我们分别用 type()、isinstance()对 Python 数字、字符串、列表、元组、集合、字典六种基本类型判定试炼。
2.1 type() 查看数据类型
data = 6, 4.5, 'ok', [4, 'ok'], {4: 'ok'}, (4, 'ok'), {4, 'ok'}
print(f"{clear}\n用 type() 查看下面这些对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n") # 对 data 字符串格式化,并插值字符串格式化输出结果。
for i in data:
print(f"{i} = {type(i)}")
2.2 type() 判定数据类型
用示例数据对象,生成类型列表,配伍类型字符串打造类型字符字典。随机打乱类型列表与示例数据比对类型,据所得 bool 值输出 True or False。
print(f"{clear}\n用 type() 判定 Python 基本类型对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n")
types = [type(i) for i in data]
type_dict = {mytype: name for mytype,name in zip(types, ['Int', 'Float', 'Str', 'List', 'Dict', 'Tuple', 'Set'])}
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱 Python 基本类型字符串列表。
for k,i in zip(types, data):
print(f"{str(i):>21} is {type_dict[k]}: {type(i) == k}")
print('~'*50)
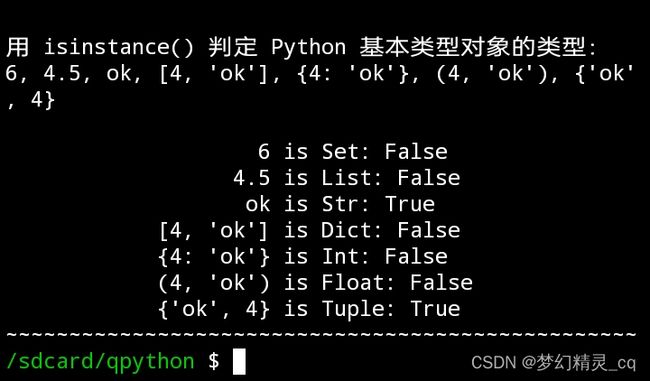
2.3 isinstance() 判定数据类型
print(f"{clear}\n用 isinstance() 判定 Python 基本类型对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n")
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱类型函数列表。
for k,i in zip(types, data):
print(f"{str(i):>21} is {type_dict[k]}: {isinstance(i, k)}")
print('~'*50)
如您所见,用 isinstance() 判定 Python 对象类型,更优雅,代码更有“意义”,更易读。
3、type() 快速生成新 class
3.1 type() 创建 class
myclass = type('DreamElf', (str,), {'name': '梦幻精灵_cq', 'live': '重庆'})
m = myclass()
print(f"{clear}\n type() 生成的新 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n类型:{type(m)}\n name 属性:{m.name}\n live 属性:{m.live}\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
用 type () 生成 Python 简单的 class 对象,方便快捷,感觉超爽。
3.2 type()、 isinstance() 判定自定义 class
如例子代码运行效果所见,type() 也是可以显示子类的。我们也用 type()、 isinstance() 来试炼下自定义类的判定——
- type() 判定
print(f"{clear}\n type() 判定自定义 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类:{type(m) == myclass }\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类的父类 str :{type(m) == str }\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
- isinstance() 判定
print(f"{clear}\n isinstance() 判定自定义 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类:{isinstance(m, myclass)}\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类的父类 str :{isinstance(m, str)}\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
4、isinstance() 的类型参数可以是多个类型联合的元组
print(f"{clear}\n用类型元组作 isinstance() 第二个参数:\n{'':~^50}\n\n")
type_dict[myclass] = 'DreamElf'
types += [myclass]
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱类型列表。
one = ' '
for i in data + [m]:
type3 = sample(types, k=3) # 随机从类型列表中取三个类型。
type3_str = (type_dict[i] for i in type3) # 生成器解析类型名字符串。
print(f"{'':>4} {i} 的类型是 “{', '.join(type3_str)}”:\n{f'{one+str(isinstance(i, tuple(type3)))+one:~^42}':^50}\n")
print(f"\n{'':~^50}\n")
- 代码运行效果截屏图片

从试炼效果截屏图片可以看到,isinstance() 的类型参数,确实是可以用多个类型的元组的,第一个参数对象的实际类型,只要在第二个参数元组中,就是 True ;反之是 Flase 。
最后一行的是自定义类实例 m ,由于实例化时没有传入字符参数,Python 默认是空白字符串 ‘’,所以是空白。
如果实例化时传入参数——
myclass = type('DreamElf', (str,), {'name': '梦幻精灵_cq', 'live': '重庆'})
m = myclass('梦幻精灵_cq')
myclass = type('DreamElf', (str,), {'name': '梦幻精灵_cq', 'live': '重庆'})
m = myclass(666)
5、isinstance() 与 type() 区别
- type()
1、返回参数对象的类型。
2、不会认为子类是一种父类类型,不考虑继承关系。
3、可以用三个参数轻松创建简单类。
- isinstance()
1、返回 bool 类型—— True or Flase 。
2、会认为子类是一种父类类型,考虑继承关系。
3、第二个类型参数可以是类型组合的元组。(第一个参数对象的实际类型,只要在第二个参数元组中,就是 True ;反之是 Flase 。)
判断两个类型是否相同,强烈推荐使 用 Python 的内置函数 isinstance() 。 以上是关于对 Python 怎么判断数据类型的详细介绍。欢迎大家在本文评论区,对 Python 怎么判断数据类型内容提出宝贵意见。
参考资料:
- Python 3.12.0a7 内建函数官方文档(最新版本)
CSDN 博文——
- 怎么判断数据类型,python怎么判断数据类型
- Python 中 isinstance() 用法详解
- Python 中 type() 函数
- The type () function of the Python
6、完整源码
(源码较长,点此跳过源码)
#!/sur/bin/nve python
# coding: utf-8
from random import shuffle
from random import sample
clear = '\033[2J' # Linux 下的清屏字符串。
data = [6, 4.5, 'ok', [4, 'ok'], {4: 'ok'}, (4, 'ok'), {4, 'ok'}]
print(f"{clear}\n用 type() 查看下面这些对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n") # 对 data 字符串格式化,并插值字符串格式化输出结果。
for i in data:
print(f"{i} = {type(i)}")
# 判定对象类型
print(f"{clear}\n用 type() 判定 Python 基本类型对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n")
types = [int, float, str, list, tuple, set, dict]
type_dict = {mytype: name for mytype,name in zip(types, ['Int', 'Float', 'Str', 'List', 'Dict', 'Tuple', 'Set'])}
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱 Python 基本类型字符串列表。
for k,i in zip(types, data):
print(f"{str(i):>21} is {type_dict[k]}: {type(i) == k}")
print('~'*50)
print(f"{clear}\n用 isinstance() 判定 Python 基本类型对象的类型:\n{', '.join(map(str, data))}\n")
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱类型函数列表。
for k,i in zip(types, data):
print(f"{str(i):>21} is {type_dict[k]}: {isinstance(i, k)}")
print('~'*50)
# type() 创建简单类
myclass = type('DreamElf', (str,), {'name': '梦幻精灵_cq', 'live': '重庆'})
m = myclass(666)
print(f"{clear}\n type() 生成的新 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n类型:{type(m)}\n name 属性:{m.name}\n live 属性:{m.live}\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
# 判定自定义类
print(f"{clear}\n type() 判定自定义 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类:{type(m) == myclass }\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类的父类 str :{type(m) == str }\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
print(f"{clear}\n isinstance() 判定自定义 class:\n{'':~^50}\n\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类:{isinstance(m, myclass)}\n自定义类实例 m 是 myclass 类的父类 str :{isinstance(m, str)}\n\n{'':~^50}\n")
# 用类型元组作 isinstance() 第二个参数。
print(f"{clear}\n用类型元组作 isinstance() 第二个参数:\n{'':~^50}\n\n")
type_dict[myclass] = 'DreamElf'
types += [myclass]
shuffle(types) # 随机打乱类型列表。
one = ' '
for i in data + [m]:
type3 = sample(types, k=3) # 随机从类型列表中取三个类型。
type3_str = (type_dict[i] for i in type3) # 生成器解析类型名字符串。
print(f"{'':>4} {i} 的类型是 “{', '.join(type3_str)}”:\n{f'{one+str(isinstance(i, tuple(type3)))+one:~^42}':^50}\n")
print(f"\n{'':~^50}\n")
上一篇: 统计单词长度-列表(输入一段英文计算每个单词长度,统计不含非英文字符,列表输出)
下一篇:
我的HOT博:
本次共计收集 210 篇博文笔记信息,总阅读量 33.91w,平均阅读量 1614。已生成 22 篇阅读量不小于 3000 的博文笔记索引链接。数据采集于 2023-05-22 05:29:13 完成,用时 4 分 49.29 秒。
- 让QQ群昵称色变的神奇代码
( 54591 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122566500
点赞:24 踩 :0 收藏:80 打赏:0 评论:17
本篇博文笔记于 2022-01-18 19:15:08 首发,最晚于 2022-01-20 07:56:47 修改。 - ChatGPT国内镜像站初体验:聊天、Python代码生成等
( 52131 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/129035387
点赞:123 踩 :0 收藏:788 打赏:0 评论:75
本篇博文笔记于 2023-02-14 23:46:33 首发,最晚于 2023-03-22 00:03:44 修改。 - pandas 数据类型之 DataFrame
( 8313 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/124525814
点赞:6 踩 :0 收藏:25 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-05-01 13:20:17 首发,最晚于 2022-05-08 08:46:13 修改。 - 罗马数字转换器|罗马数字生成器
( 6457 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122592047
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:1 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-01-19 23:26:42 首发,最晚于 2022-01-21 18:37:46 修改。 - Python字符串居中显示
( 6277 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122163023
点赞:1 踩 :0 收藏:5 打赏:0 评论:1
本篇博文笔记于 2021-12-26 23:35:29 发布。 - 个人信息提取(字符串)
( 5886 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/124244618
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:9 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-04-18 11:07:12 首发,最晚于 2022-04-20 13:17:54 修改。 - 斐波那契数列的递归实现和for实现
( 5308 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122355295
点赞:4 踩 :0 收藏:2 打赏:0 评论:8
本篇博文笔记于 2022-01-06 23:27:40 发布。 - 练习:字符串统计(坑:f‘string‘报错)
( 4892 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/121723096
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:1 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-12-04 22:54:29 发布。 - 练习:尼姆游戏(聪明版/傻瓜式•人机对战)
( 4632 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/121645399
点赞:14 踩 :0 收藏:42 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-11-30 23:43:17 发布。 - 回车符、换行符和回车换行符
( 4427 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/123109488
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:2 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-02-24 13:10:02 首发,最晚于 2022-02-25 20:07:40 修改。 - python清屏
( 4406 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/120762101
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:5 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-10-14 13:47:21 发布。 - Python列表(list)反序(降序)的7种实现方式
( 4268 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/128271700
点赞:4 踩 :0 收藏:14 打赏:0 评论:8
本篇博文笔记于 2022-12-11 23:54:15 首发,最晚于 2023-03-20 18:13:55 修改。 - 密码强度检测器
( 3924 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/121739694
点赞:1 踩 :0 收藏:4 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-12-06 09:08:25 首发,最晚于 2022-11-27 09:39:39 修改。 - 罗马数字转换器(用罗马数字构造元素的值取模实现)
( 3840 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122608526
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:0 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-01-20 19:38:12 首发,最晚于 2022-01-21 18:32:02 修改。 - 练习:生成100个随机正整数
( 3740 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/122558220
点赞:1 踩 :0 收藏:4 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-01-18 13:31:36 首发,最晚于 2022-01-20 07:58:12 修改。 - 练习:班里有人和我同生日难吗?(概率probability、蒙特卡洛随机模拟法)
( 3588 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/124424935
点赞:1 踩 :0 收藏:2 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-04-26 12:46:25 首发,最晚于 2022-04-27 21:22:07 修改。 - 我的 Python.color() (Python 色彩打印控制)
( 3470 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/123194259
点赞:2 踩 :0 收藏:7 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2022-02-28 22:46:21 首发,最晚于 2022-03-03 10:30:03 修改。 - 练习:仿真模拟福彩双色球——中500w巨奖到底有多难?跑跑代码就晓得了。
( 3258 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/125415626
点赞:3 踩 :0 收藏:4 打赏:0 评论:3
本篇博文笔记于 2022-06-22 19:54:20 首发,最晚于 2022-06-23 22:41:33 修改。 - 聊天消息敏感词屏蔽系统(字符串替换 str.replace(str1, *) )
( 3125 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/124539589
点赞:3 踩 :0 收藏:2 打赏:0 评论:3
本篇博文笔记于 2022-05-02 13:02:39 首发,最晚于 2022-05-21 06:10:42 修改。 - Linux 脚本文件第一行的特殊注释符(井号和感叹号组合)的含义
( 3089 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/123087606
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:4 打赏:0 评论:3
本篇博文笔记于 2022-02-23 13:08:07 首发,最晚于 2022-04-04 23:52:38 修改。 - 练习:求列表(整数列表)平衡点
( 3034 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/121737612
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:0 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-12-05 23:28:10 发布。 - random.sample()将在python 3.9x后续版本中被弃用
( 3000 阅读)
博文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57158496/article/details/120657230
点赞:0 踩 :0 收藏:0 打赏:0 评论:0
本篇博文笔记于 2021-10-08 18:35:09 发布。
精品文章:
- 好文力荐:齐伟书稿 《python 完全自学教程》 Free连载(已完稿并集结成书,还有PDF版本百度网盘永久分享,点击跳转免费下载。)
- OPP三大特性:封装中的property
- 通过内置对象理解python'
- 正则表达式
- python中“*”的作用
- Python 完全自学手册
- 海象运算符
- Python中的 `!=`与`is not`不同
- 学习编程的正确方法
来源:老齐教室
◆ Python 入门指南【Python 3.6.3】
好文力荐:
- 全栈领域优质创作者——[寒佬](还是国内某高校学生)博文“非技术文—关于英语和如何正确的提问”,“英语”和“会提问”是编程学习的两大利器。
- 【8大编程语言的适用领域】先别着急选语言学编程,先看它们能干嘛
- 靠谱程序员的好习惯
- 大佬帅地的优质好文“函数功能、结束条件、函数等价式”三大要素让您认清递归
CSDN实用技巧博文:
- 8个好用到爆的Python实用技巧
- python忽略警告
- Python代码编写规范
- Python的docstring规范(说明文档的规范写法)