spring boot利用redis作为缓存
一、缓存介绍
在 Spring Boot 中,可以使用 Spring Cache abstraction 来实现缓存功能。Spring Cache abstraction 是 Spring 框架提供的一个抽象层,它对底层缓存实现(如 Redis、Ehcache、Caffeine 等)进行了封装,使得在不同的缓存实现之间切换变得更加方便。
Spring Cache Abstraction 的实现原理主要是通过在运行时动态创建代理对象来实现的。当一个带有缓存注解的方法被调用时,代理对象首先检查指定的缓存中是否已有方法的返回值,如果缓存中有,则直接返回缓存中的值,否则调用原方法获取返回值,并将返回值存入缓存中,再返回给调用者。
在具体实现上,Spring Cache Abstraction 依赖于 CacheManager 和 Cache 两个接口来实现对缓存的管理和操作。CacheManager 接口提供了获取特定缓存的实例的能力,而 Cache 接口则提供了实际的缓存操作,如 get、put 和 evict 等。
同时,在 Spring Boot 中,我们可以通过配置来指定使用的缓存类型以及其他相关属性,比如缓存的过期时间、最大缓存数量等。
二、利用redis实现缓存
spring boot的整体的设计思路是约定大于配置,约定俗成,第一步,我们需要引入redis和cache的相关的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
注意:commons-pool2必须引入,不然可能会报java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/commons/pool2/impl/GenericObjectPoolConfig错误
第二步,配置spring boot配置文件application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
password:
database: 0
port: 6379
lettuce:
pool:
max-idle: 8
max-active: 8
max-wait: 3000ms
min-idle: 0
cache:
# 指定Redis作为缓存实现
type: redis
# 指定项目中的cacheNames
cache-names:
- USERS
redis:
# 缓存过期时间为10分钟,单位为毫秒
time-to-live: 600000
# 是否允许缓存空数据,当查询到的结果为空时缓存空数据到redis中
cache-null-values: true
# 为Redis的KEY拼接前缀
key-prefix: "BOOT_CACHE:"
# 是否拼接KEY前缀
use-key-prefix: true
# 是否开启缓存统计
enable-statistics: false第三步,配置序列化器
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
// 获取Properties中Redis的配置信息
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
// 获取RedisCacheConfiguration的默认配置对象
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// 指定序列化器为GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer
config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
// 过期时间设置
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
// KEY前缀配置
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixCacheNameWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
// 缓存空值配置
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
// 是否启用前缀
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}第四步,开启缓存-@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication springApplication=new SpringApplication(Application.class);
springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
springApplication.run(args);
}
}到此,我们利用redis作为spring boot的缓存已经搭建好了,下面我们来做个测试,这里就不使用数据库了,我们使用数据来自己模拟数据库数据查询,模拟数据访问层
@Repository
@Slf4j
public class UserMapper {
public final Map map = new HashMap<>();
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
SystemPermissions permissions1 = new SystemPermissions("1", "query");
SystemPermissions permissions2 = new SystemPermissions("2", "add");
Set permissionsSet = new HashSet<>();
permissionsSet.add(permissions1);
permissionsSet.add(permissions2);
SystemRole role = new SystemRole("1", "admin", permissionsSet);
Set roleSet = new HashSet<>();
roleSet.add(role);
SystemUser user = new SystemUser();
user.setUserName("test");
user.setUserId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
user.setUserPwd("123456");
user.setSystemRoles(roleSet);
map.put(user.getUserName(), user);
Set permissionsSet1 = new HashSet<>();
permissionsSet1.add(permissions1);
SystemRole role1 = new SystemRole("2", "user", permissionsSet1);
Set roleSet1 = new HashSet<>();
roleSet1.add(role1);
SystemUser user1 = new SystemUser();
user1.setUserName("test1");
user1.setUserId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
user1.setUserPwd("123456");
user1.setSystemRoles(roleSet1);
map.put(user1.getUserName(), user1);
}
public SystemUser queryUser(String userName){
log.error("queryUser_没有走缓存:"+userName);
return map.get(userName);
}
} 以上类是自己的类,自己实现时可以换成自己的,编写service
public interface UserService {
SystemUser getUserByName(String userName);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private final UserMapper userMapper;
public UserServiceImpl(UserMapper userMapper) {
this.userMapper = userMapper;
}
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "USERS",key = "#userName")
@Override
public SystemUser getUserByName(String userName) {
return userMapper.queryUser(userName);
}
}
编写controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
private final UserService userService;
public UserController(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@GetMapping("queryUser")
public JsonResult getUser(String userName){
SystemUser user=userService.getUserByName(userName);
return new JsonResult<>("0", "查询成功", user);
}
}
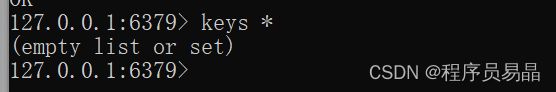
测试,可以看到,此时我们的redis中没有数据
第一次,请求没有走缓存,我们再看redis,已经有了数据,第二次请求直接拿了redis缓存中的数据