Pytorch(二) --梯度下降法
针对y=wx+b,利用梯度下降法求得相对应的w和b,此时,w和b是一个近似解,而不是确切解。

上图是针对y=wx的梯度下降法的步骤,y=w*x+b的步骤与之类似,只不过分为两步,w和b。
代码如下所示:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#y = 2*x+3
x_data = [1.0,2.0,3.0]
y_data = [5.0,7.0,9.0]
#随机初始化w和b
w=1.0
b=1.0
lr = 0.01
def forward(x):
return w*x+b
#损失函数
def cost(xs,ys):
cost = 0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
y_pred = forward(x)
cost+=(y_pred-y)**2
return cost/len(xs)
#梯度降函数
def gradient(xs,ys):
gradw=0
gradb=0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
gradw+=2*x*(x*w+b-y)
gradb+=2*(x*w+b-y)
return gradw/len(xs),gradb/len(xs)
epoch_list = []
cost_list = []
print('predict (before training)',4,forward(4))
for epoch in range(10000):#迭代10000次
cost_val = cost(x_data,y_data)
gradw,gradb = gradient(x_data,y_data)
w-=lr*gradw
b-=lr*gradb
print('epoch:',epoch,'w=',w,'b=',b,'loss=',cost_val)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(cost_val)
print('predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
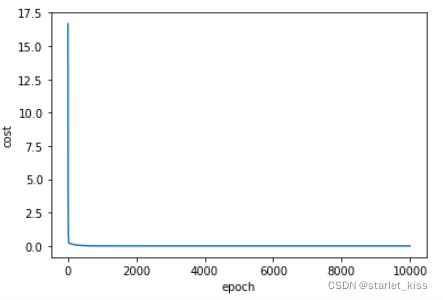
plt.plot(epoch_list,cost_list)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
最终的结果如下所示:
epoch: 9999 w= 2.0000000000202744 b= 2.9999999999539115 loss= 3.061922477666832e-22
SGD(随机梯度下降法)
上面求梯度的方法是利用了所有的样本求梯度,而在面对大量的样本时,这样做耗时严重,而且样本中所掺杂的噪声样本会影响最终的结果,因此,随机梯度下降法是很好的选择,每次只选择一个样本求梯度,然后更新梯度,最终也会获得很好的结果。
两种求梯度方法的优缺点:
1)
优点:可以并行计算,计算效率高。
缺点:最终的结果误差较大。
2)
优点:最终的结果较为准确。
缺点:不能并行计算,计算效率比较低。
采取折中的办法------Mini batch
SGD代码如下所示:
def SGD(x,y):
return 2*x*(x*w+b-y),2*(x*w+b-y)
epoch_list = []
cost_list = []
print('predict (before training)',4,forward(4))
for epoch in range(10000):
cost_val = cost(x_data,y_data)
gradw,gradb = gradient(x_data,y_data)
w-=lr*gradw
b-=lr*gradb
print('epoch:',epoch,'w=',w,'b=',b,'loss=',cost_val)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(cost_val)
print('predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
plt.plot(epoch_list,cost_list)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
结果如下:
epoch: 9999 w= 2.0000000000202744 b= 2.9999999999539115 loss= 3.061922477666832e-22