Linux学习第24天:Linux 阻塞和非阻塞 IO 实验(一): 挂起
Linux版本号4.1.15 芯片I.MX6ULL 大叔学Linux 品人间百味 思文短情长
在正式开始今天的笔记之前谈一下工作中遇见的一个问题。
本篇笔记主要学习Linux 阻塞和非阻塞 IO 实验,主要包括阻塞和非阻塞简介、等待队列、轮询、poll操作、阻塞和非阻塞实验。其中重点内容为阻塞和非阻塞实验。
本笔记的思维导图如下:
一、阻塞和非阻塞IO
1.阻塞和非阻塞简介
1)阻塞
1 int fd;
2 int data = 0;
3 4
fd = open("/dev/xxx_dev", O_RDWR); /* 阻塞方式打开 */
5 ret = read(fd, &data, sizeof(data)); /* 读取数据 */2)非阻塞
1 int fd;
2 int data = 0;
3 4
fd = open("/dev/xxx_dev", O_RDWR); /* 阻塞方式打开 */
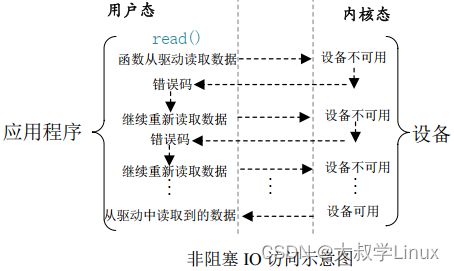
5 ret = read(fd, &data, sizeof(data)); /* 读取数据 */参数“O_NONBLOCK”,表示以非阻塞方式打开设备,这样从设备中读取数据的时候就是非阻塞方式的了。
2.等待队列
1)等待队列头
等待队列头使用结构体wait_queue_head_t 表示:
39 struct __wait_queue_head {
40 spinlock_t lock;
41 struct list_head task_list;
42 };
43 typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t;init_waitqueue_head 函数初始化等待队列头
void init_waitqueue_head(wait_queue_head_t *q)//参数 q 就是要初始化的等待队列头。也可以使用宏 DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD 来一次性完成等待队列头的定义的初始化。
2)等待队列项
结构体 wait_queue_t 表示等待队列项,结构体内容如下:
struct __wait_queue {
unsigned int flags;
void *private;
wait_queue_func_t func;
struct list_head task_list;
};
typedef struct __wait_queue wait_queue_t;宏DECLARE_WAITQUEUE 就是给当前正在运行的进程创建并初始化了一个等待队列项。
DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(name, tsk) name 就是等待队列项的名字, tsk 表示这个等待队列项属于哪个任务(进程),一般设置为
current , 在 Linux 内 核 中 current 相 当 于 一 个 全 局 变 量 , 表 示 当 前 进 程 。
3)将队列项添加/删除队列头
只有添加到等待队列头中以后进程才能进入休眠态。等待队列项添加 API 函数如下:
void add_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *q,
wait_queue_t *wait)等待队列项移除 API 函数如下:
void remove_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *q,
wait_queue_t *wait)4)等待唤醒
void wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *q)
void wake_up_interruptible(wait_queue_head_t *q)wake_up_interruptible 函数只能唤醒处于 TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 状态的进程。
5)等待事件
| 函数 | 描述 | |||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
3.轮询【非阻塞】
1)select函数
int select(int nfds,
fd_set *readfds,
fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds,
struct timeval *timeout)fd_set 类型变量的每一个位都代表了一个文件描述符。
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set)
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set)
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set)
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set)2)poll函数
没有最大文件描述符限制。
int poll(struct pollfd *fds,
nfds_t nfds,
int timeout)3)epoll函数
epoll 就是为处理大并发而准备的。
int epoll_create(int size)返回值: epoll 句柄,如果为-1 的话表示创建失败。
epoll_ctl 函数向其中添加要监视的文件描述符以及监视的事件, epoll_ctl 函数原型如下所示:
int epoll_ctl(int epfd,
int op,
int fd,
struct epoll_event *event)epoll_wait 函数来等待事件的发生:
int epoll_wait(int epfd,
struct epoll_event *events,
int maxevents,
int timeout)4.poll操作
poll 函数原型如下所示:
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *wait)poll_wait 函数不会引起阻塞,只是将应用程序添加到 poll_table 中, poll_wait 函数原型如下:
void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p) 参数 wait_address 是要添加到 poll_table 中的等待队列头,参数 p 就是 poll_table,就是
file_operations 中 poll 函数的 wait 参数。
四、总结
本篇笔记主要学习Linux 阻塞和非阻塞 IO 实验,主要包括阻塞和非阻塞简介、等待队列、轮询、poll操作。
以下内容将在下一篇笔记中进行学习:
二、阻塞IO实验
1.硬件原理图分析
2.实验程序
3.运行测试
三、非阻塞IO实验
1.硬件原理图分析
2.实验程序
3.运行测试
本文为参考正点原子开发板配套教程整理而得,仅用于学习交流使用,不得用于商业用途。