STM32 Cube 发送和接收485数据
1.说明
发送485数据和串口数据是不同的,刚入行一直以为是相同的只是电平的信号可能不同
发送485数据,需要对发送和接收的RE和DE进行使能操作,来决定发送有效,还是接收有效,也就是需要单片机的IO来控制数据的流向!
发送串口数据(TTL), 直接RX和TX反接线即可
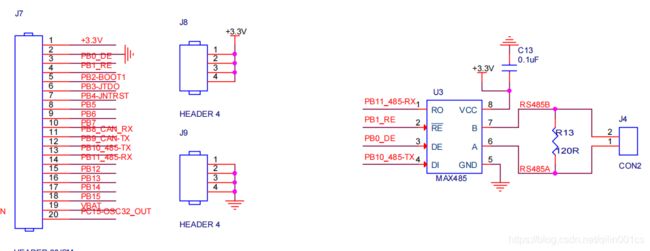
这里既然知道了485和串口的区别,那么发送485之前一定要看下电路的原理图是怎么接线的
例如:这里PB0 - DE ,PB1 - RE , PB10 和PB11 接的TX和RX
2.看原理图
那么我们分析下, 当DE和RE为1时,则发送有效,DE和RE为0时,则接收有效
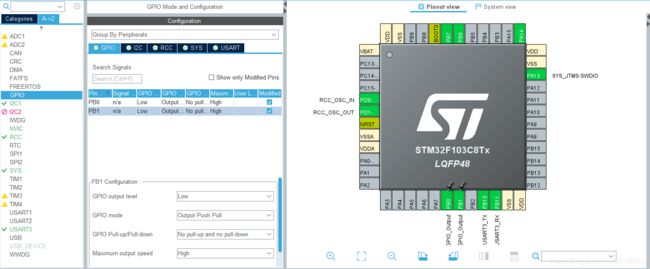
3.单片机引脚配置
串口引脚配置如下:
1.打开UART3 , 设置波特率为:9600,同时打开中断
2.设置GPIO口, GPIOB PIN_0 为低电平,PIN_1为低电平
4. 源码如下:
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* 485串口发送和接收
*
******************************************************************************
*/
#include "main.h"
#include "i2c.h"
#include "usart.h"
#include "gpio.h"
#include "stdio.h"
uint8_t UART1_len=1; //1次只收1个
uint8_t UART1_arr[1]={0};
uint8_t UART1_buf[2]={0};//最大收多少
uint8_t UART1_buf_i=0;
void SystemClock_Config(void);
void send485(uint8_t *pData,uint8_t len);
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_I2C1_Init();
MX_USART3_UART_Init();
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, (uint8_t *)UART1_arr, UART1_len);
while (1)
{
}
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSI_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLMUL = RCC_PLL_MUL4;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_0) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
//485发送
void send485(uint8_t *pData,uint8_t len){
// 485
//接收:DE为0,RE为0,设置为接收
//发送:DE为1,RE为 1,设置为发送
//设置为发送
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_SET); //PB0 = DE = 1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_SET); //PB1 = RE = 1
//发送内容
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart3, pData, len, 1000);
//重置为接收
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_RESET); //PB0 = DE = 0
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET); //PB1 = RE = 0
}
//crc modbus485 声明
uint8_t crc16_1 =0;
uint8_t crc16_2 =0;
uint16_t crc_table[] = {
0x0000, 0xcc01, 0xd801, 0x1400,
0xf001, 0x3c00, 0x2800, 0xe401,
0xa001, 0x6c00, 0x7800, 0xb401,
0x5000, 0x9c01, 0x8801, 0x4400
};
void rs485_crc16(uint8_t *arr,uint8_t len)
{
uint16_t crc = 0xffff;
uint8_t i;
uint8_t temp;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++) {
temp = *arr++;
crc = crc_table[(temp ^ crc) & 15] ^ (crc >> 4);
crc = crc_table[((temp >> 4) ^ crc) & 15] ^ (crc >> 4);
}
crc16_1 = (uint8_t)(crc & 0xff ); //高8位
crc16_2 = (uint8_t)(crc >> 8); //低8位
}
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){
if(huart->Instance == USART3){ //uart3 端口
UART1_buf[UART1_buf_i] = UART1_arr[0];
UART1_buf_i++;
if(0x0a == UART1_arr[0]){ //检测到结束符 是 0A
//简单业务逻辑处理
if(0x01==UART1_buf[0] && 0x0A==UART1_buf[1] ){ //如果发送的是 01 0A 则返回,发送的内容,其他的不返回
//我们返回485
uint8_t return_arr[6] = {0x01,0x0A,0x02,0x00,0x00,0x00};
rs485_crc16(return_arr, 4);
return_arr[4] = crc16_1;
return_arr[5] = crc16_2;
send485((uint8_t *)return_arr,6);
}
//i置0
UART1_buf_i = 0;
}
//再次开启打印
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, (uint8_t *)UART1_arr, UART1_len);
}
}
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
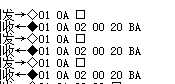
5.演示结果
感谢您的支持,写的文章如对您有所帮助,开源不易,请您打赏,谢谢啦~
![]()