【Spring容器初始化后实例化单例bean过程源码解析 5.1.3.RELEASE版本】
目录
前言
一、基本介绍
二、SpringBean生命周期
2.1 生命周期流程图
2.2 各个节点含义
三、SpringBean实例化源码解析
3.1 代码入口
3.2 refresh方法
3.3 finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法
3.4 preInstantiateSingletons方法
3.5 getMergedLocalBeanDefinition方法
3.6 getBean方法
3.7 createBean方法
3.8 doCreateBean方法
3.9 createBeanInstance方法
四、SpringBean实例化对象属性赋值源码解析
4.1 doCreateBean方法
4.2 populateBean方法
五、SpringBean实例化后对象前后置处理源码解析
5.1 doCreateBean方法
5.2 initializeBean方法
5.3 invokeAwareMethods方法
5.4 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法
5.5 invokeInitMethods方法
5.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法
六、SpringBean销毁源码解析
6.1 代码入口
6.2 registerShutdownHook方法
6.3 doClose方法
6.4 destroyBeans方法
6.5 destroySingletons方法
6.6 destroySingletons方法
6.7 destroySingleton方法
6.8 destroyBean方法
6.9 destroy方法
七、SpringBean的AOP代理源码解析
7.1 代码入口
7.2 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
7.3 wrapIfNecessary方法
7.4 createProxy方法
7.5 getProxy方法
7.6 getProxy方法
7.7 JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法
7.8 proceed方法
总结
前言
看这篇文章,需要了解Spring容器初始化的过程,可以参考我的上篇文章或者查看其他优秀的CSDN文章。了解xml文件的bean标签最后转为BeanDefinition对象的全过程。
这篇文章将对Spring容器初始化后,对非懒加载的单例bean实例化过程进行源码解析,首先对SpringBean的生命周期进行详细的解释,包含一些用到的方法及其所在类,然后再进行源码的解析。
我也是初学bean初始化的源码, 解析的有问题欢迎指出,相互学习。
一、基本介绍
当Spring容器初始化之后,会对非懒加载的单例bean进行实例化、属性赋值和AOP增强等等操作,最后将单例保存在singletonObjects集合中。方法入口:finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
二、SpringBean生命周期
Spring管理的bean的生命周期和普通的java bean是不一样的,Spring可以根据我们的配置对bean进行一系列的增强操作,常见的就是aop或者实现Spring规定的一些接口,就会在实例化之后对bean进行增强。
2.1 生命周期流程图
bean创建到使用,流程图
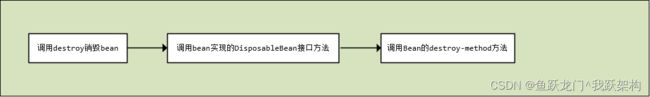
bean使用完销毁,流程图
2.2 各个节点含义
| beanDefinitionNames | 当前类.方法:DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons() List 遍历Spring容器初始化后,保存的所有beanName集合,进行实例化。 |
| Bean实例化 | 当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean() instanceWrapper = this.createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); 根据构造方法进行实例化 |
| Bean属性赋值 | 当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean() this.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); 对bean属性进行赋值,根据xml里面配置的property属性或者Autowired注解 |
| 调用Bean实现的Aware接口 | 当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean() this.invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 具体调用BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware和BeanFactoryAware接口的方法,可以进入invokeAwareMethods方法详细查看。 特殊的是ApplicationContextAware这个接口,它也是Aware的子类,但是没有在invokeAwareMethods这个方法调用,而是在applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法对bean进行的前置处理的时候调用的,由ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类的前置处理方法postProcessBeforeInitialization中进行调用。详细看方法invokeAwareInterfaces |
| 调用BeanPostProcessor接口的前置处理方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization |
当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean() wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization( bean, beanName); 这个方法很简单,就是获取所有BeanPostProcessor对象,依次调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 |
| 调用Bean实现的InitializingBean接口方法 | 当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean() this.invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 调用afterPropertiesSet方法,进入invokeInitMethods方法详细查看 |
| 调用Bean的init-method方法 | 当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean() this.invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 也是在这个invokeInitMethods方法里面,反射调用 |
| 调用BeanPostProcessor接口的后置处理方法 postProcessAfterInitialization |
当前类.方法:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean() wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization( wrappedBean, beanName); 获取所有BeanPostProcessor对象,依次调用postProcessAfterInitialization 方法。 aop也是在后置处理实现的,具体的处理类是AbstractAutoProxyCreator的wrapIfNecessary方法,在源码中详细解析。 |
| 调用destroy销毁bean | 当前类.方法:DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.destroyBean() bean.destroy(); |
| 调用bean实现的DisposableBean接口方法 | 当前类.方法:DisposableBeanAdapter.destroy() ((DisposableBean)this.bean).destroy(); |
| 调用Bean的destroy-method方法 | 当前类.方法:DisposableBeanAdapter.destroy() this.invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod); |
三、SpringBean实例化源码解析
3.1 代码入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
// new一个容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"classpath:*c/test*.xml","classpath:*c/s*/test*.xml");
applicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}// 当前类:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
// 进入重载的构造方法
this(configLocations, true, (ApplicationContext)null);
}// 当前类:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
// 设置xml路径
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 刷新容器
this.refresh();
}
}3.2 refresh方法
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext,初始化容器入口
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
// 初始化容器,加载xml数据转换为java对象,保存在容器里面,后面使用
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 容器的准备工作,对容器的一些属性赋值,以后使用
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 对于ClassPathXmlApplicationContext容器,这个是模板方法,没有实现,子类实现该
// 方法可以对容器进行一些后置处理,此时容器已经初始化了
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法
// 把当前容器传入,这个可以自己点开看看
// 这行currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName,
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册BeanPostProcessor对象,后面会画图解释,为什么要注册这个
// String[] postProcessorNames =
// beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 国际化
this.initMessageSource();
// 初始化事件管理类applicationEventMulticaster
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 模板方法,留给子类实现
this.onRefresh();
// 往事件管理类中注册事件类
this.registerListeners();
// bean实例化,属性赋值,前后置处理,aop代理
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
// 异常就destory容器中的所有单例bean
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}3.3 finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法
此处之后的代码都是Spring的源码
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext,下载的源码
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有的非懒加载的单例
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}3.4 preInstantiateSingletons方法
// 当前类:DefaultListableBeanFactory,下载的源码
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// 容器初始化之后保存的所有的beanName集合
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 得到该beanName的BeanDefinition和父BeanDefinition信息,包装在RootBeanDefinition里面
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 不是抽象的,而且是单例,非懒加载的,就实例化
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判断是不是工厂bean,这种bean的有特殊处理方式不同,
// 可以查看相关文章看看是不是FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction)
((SmartFactoryBean) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 其他单例bean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// bean初始化之后的回调,不讲解没研究过。。。
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction 3.5 getMergedLocalBeanDefinition方法
// 当前类:AbstractBeanFactory
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws BeansException {
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// 刚开始肯定为null
RootBeanDefinition mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
if (mbd != null) {
return mbd;
}
// getBeanDefinition(beanName)得到当前beanName的BeanDefinition
return getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName, getBeanDefinition(beanName));
}
// 当前类:DefaultListableBeanFactory
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
// 上一篇文章讲过,所有的bean标签都会保存在这个里面
BeanDefinition bd = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (bd == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No bean named '" + beanName + "' found in " + this);
}
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(beanName);
}
return bd;
}
// 当前类:AbstractBeanFactory
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(
String beanName, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
synchronized (this.mergedBeanDefinitions) {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = null;
// Check with full lock now in order to enforce the same merged instance.
if (containingBd == null) {
mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
}
if (mbd == null) {
// 看看有没有父beanName
if (bd.getParentName() == null) {
// Use copy of given root bean definition.
if (bd instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
mbd = ((RootBeanDefinition) bd).cloneBeanDefinition();
}
else {
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(bd);
}
}
else {
// Child bean definition: needs to be merged with parent.
// 有的话,那子类就可以覆盖父类的一些属性
BeanDefinition pbd;
try {
// 转换父beanName,去除&或者根据别名找到真正的beanName
String parentBeanName = transformedBeanName(bd.getParentName());
if (!beanName.equals(parentBeanName)) {
// 又递归查询了,看父beanName有没有父beanName
pbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
BeanFactory parent = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
pbd = ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) parent).getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(parentBeanName,
"Parent name '" + parentBeanName + "' is equal to bean name '" + beanName +
"': cannot be resolved without an AbstractBeanFactory parent");
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve parent bean definition '" + bd.getParentName() + "'", ex);
}
// Deep copy with overridden values.
// 在这里设置父beanName的BeanDefinition对象
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(pbd);
// 自己的BeanDefinition对象
mbd.overrideFrom(bd);
}
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(mbd.getScope())) {
mbd.setScope(RootBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON);
}
if (containingBd != null && !containingBd.isSingleton() && mbd.isSingleton()) {
mbd.setScope(containingBd.getScope());
}
if (containingBd == null && isCacheBeanMetadata()) {
this.mergedBeanDefinitions.put(beanName, mbd);
}
}
return mbd;
}
}3.6 getBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractBeanFactory
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
// 当前类:AbstractBeanFactory,删除好多代码,太长了
protected T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
// 已经加载的就不加载了
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
try {
// Create bean instance. 创建单例bean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 创建单例
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 多例的,先不讲解
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
3.7 createBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 给BeanPostProcessors一个机会返回一个代理而不是目标bean实例,自己研究,哈哈
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 创建bean
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}3.8 doCreateBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,删除很多代码
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例的话,创建之前肯定要删除缓存的bean
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建一个bean实例,既流程图的第二步,bean实例化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 流程图的第三步,属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 后面的几步,初始化bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}3.9 createBeanInstance方法
//
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
// 这里可以查看文章:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42213903/article/details/100513570
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
// 使用简单的无参构造方法创建实例AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}四、SpringBean实例化对象属性赋值源码解析
4.1 doCreateBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,删除很多代码
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例的话,创建之前肯定要删除缓存的bean
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建一个bean实例,既流程图的第二步,bean实例化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 流程图的第三步,属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 后面的几步,初始化bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}4.2 populateBean方法
populateBean方法很多源码特别的深奥,我目前有些还不会,不敢乱解析。。。只知道大概的流程。
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
// 属性注入的一个操作类
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// 根据beanName和beanType进行自动装配
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
// BeanPostProcessor对属性进行处理,循环依赖这种的情况,逻辑很复杂
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 给property属性赋值
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}五、SpringBean实例化后对象前后置处理源码解析
5.1 doCreateBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,删除很多代码
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例的话,创建之前肯定要删除缓存的bean
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建一个bean实例,既流程图的第二步,bean实例化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 流程图的第三步,属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 后面的几步,初始化bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}5.2 initializeBean方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 系统安全,这个很底层,不会
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction5.3 invokeAwareMethods方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
// 很简单,调用对应接口的方法
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}5.4 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
// 获取所有的处理器
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 执行postProcessBeforeInitialization,前置处理方法
// ApplicationContextAwareProcessor就是其中一个,调用ApplicationContextAware接口方法
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}5.5 invokeInitMethods方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
// bean实现了InitializingBean接口,就调用afterPropertiesSet方法
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction5.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
// 获取所有的处理器
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 调用后置处理方法postProcessAfterInitialization
// aop处理器AbstractAutoProxyCreator
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}到这就会把所有的beanName实例化完成了,可以使用了。
六、SpringBean销毁源码解析
6.1 代码入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"classpath:*c/test*.xml","classpath:*c/s*/test*.xml");
// shutdown容器会触发bean的销毁
applicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}6.2 registerShutdownHook方法
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext
public void registerShutdownHook() {
if (this.shutdownHook == null) {
// No shutdown hook registered yet.
this.shutdownHook = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 关闭容器
doClose();
}
}
};
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
}6.3 doClose方法
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing " + this);
}
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
// 销毁所有单例
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
onClose();
this.active.set(false);
}6.4 destroyBeans方法
// 当前类:AbstractApplicationContext
protected void destroyBeans() {
// 调用容器的方法,容器是DefaultListableBeanFactory
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
}6.5 destroySingletons方法
// 当前类:DefaultListableBeanFactory
public void destroySingletons() {
// 父类的方法
super.destroySingletons();
this.manualSingletonNames.clear();
clearByTypeCache();
}6.6 destroySingletons方法
// 当前类:DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void destroySingletons() {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Destroying singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true;
}
String[] disposableBeanNames;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());
}
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 销毁容器中所有单例
destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);
}
this.containedBeanMap.clear();
this.dependentBeanMap.clear();
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear();
// 清空所有的缓存
clearSingletonCache();
}
// 当前类:DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
protected void clearSingletonCache() {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.clear();
this.singletonFactories.clear();
this.earlySingletonObjects.clear();
this.registeredSingletons.clear();
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
}
}6.7 destroySingleton方法
// 当前类:DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void destroySingleton(String beanName) {
// Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any.
removeSingleton(beanName);
// Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance.
DisposableBean disposableBean;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
}
// 销毁bean
destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean);
}6.8 destroyBean方法
// 当前类:DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) {
// Trigger destruction of dependent beans first...
Set dependencies;
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
// Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set
dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
if (dependencies != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved dependent beans for bean '" + beanName + "': " + dependencies);
}
for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) {
destroySingleton(dependentBeanName);
}
}
// Actually destroy the bean now...
if (bean != null) {
try {
// 调用destroy方法
bean.destroy();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
// Trigger destruction of contained beans...
Set containedBeans;
synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) {
// Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set
containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
if (containedBeans != null) {
for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) {
destroySingleton(containedBeanName);
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean from other beans' dependencies.
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
for (Iterator>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry> entry = it.next();
Set dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue();
dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName);
if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean's prepared dependency information.
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName);
} 6.9 destroy方法
// 当前类:DisposableBeanAdapter
public void destroy() {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
// 实现了DisposableBean接口就调用destroy方法
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction七、SpringBean的AOP代理源码解析
7.1 代码入口
第5步的5.6步骤
// 当前类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 选择AbstractAutoProxyCreator处理器
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}7.2 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutoProxyCreator
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// 进行包装
return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}7.3 wrapIfNecessary方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutoProxyCreator
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
} else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
} else if (!this.isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) && !this.shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
// 得到当前bean对象,满足所有的通知Advisor对象
Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, (TargetSource)null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理对象
Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
} else {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
} else {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
}7.4 createProxy方法
// 当前类:AbstractAutoProxyCreator
protected Object createProxy(Class beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 代理工厂,spring支持CGLIB和JDK代理
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (this.shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
} else {
this.evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 所有的通知Advisor对象
Advisor[] advisors = this.buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
// 目标对象
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
this.customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (this.advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 创建代理
return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.getProxyClassLoader());
}7.5 getProxy方法
// 当前类:ProxyFactory
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// this.createAopProxy()方法会返回CGLIB或者JDK代理对象,具体的处理逻辑可以自己查看
return this.createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}7.6 getProxy方法
以JDK代理为例,CGLIB不会。。。。。
// 当前类:JdkDynamicAopProxy
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
this.findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
// java固定语法,返回jdk代理对象,JdkDynamicAopProxy实现了InvocationHandler方法
// 所以执行bean对象的方法时,会进入JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法
// 这是JDK代理知识,详细的自己搜文章学习
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}7.7 JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法
// 当前类:JdkDynamicAopProxy
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
Object retVal;
try {
if (this.advised.opaque || !method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() || !method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class targetClass = target != null ? target.getClass() : null;
// 把所有的aop通知类,转换为链,责任链模式
List7.8 proceed方法
// 当前类:ReflectiveMethodInvocation
// 看aop的代码要从invoke方法开始,仔细的阅读才能看懂,这个方法
// 多看几遍就可以了,我看了几遍有些地方还是忘了。。。。
// interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers所有通知包装类组成的集合
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return this.invokeJoinpoint();
} else {
// 相当于遍历的调用所有的通知,++this.currentInterceptorIndex,下标增加直到所有通知都代理完
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
// interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice通知包装的对象
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class targetClass = this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass();
// 判断该方法要不要被拦截,进行aop相关操作,不要就继续判断
return dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments) ? dm.interceptor.invoke(this) : this.proceed();
} else {
return ((MethodInterceptor)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}总结
AOP的可以多看几遍就会了,这个时间长不看,就会忘,我们只需要学习它的思想就行了。