SpringAop源码解析
SpringAop源码解析(基于springBoot)
要读懂SpringAop,首先需要看springIoc,否则连入口代码都找不到。
首先我们先看一下一个bean被初始化的过程

一个简单的bean会通过反射被实例化出来,然后进行属性的填充,执行init方法,然后bean放到sinletonObjects里面,能通过getBean方法拿出来。但需要创建代理的bean在执行完init方法后,会经过一个特殊的beanPostProcess把bean变成一个代理类,放到sinletonObjects里面。
在springboot工程中,假如我们要使用AOP,只需要加上一个注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy。
首先点进去EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,可以看到,这里使用了@Import
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
Import的是AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) {
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
}
然后我们看一下注册的beanDefinition是什么,点进去
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);就是把AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator变成了beanDefinition,注册进了容器中。
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
我们看一下注册到容器中的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是什么东西,打开AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的继承树,原来是一个beanPostProcess。
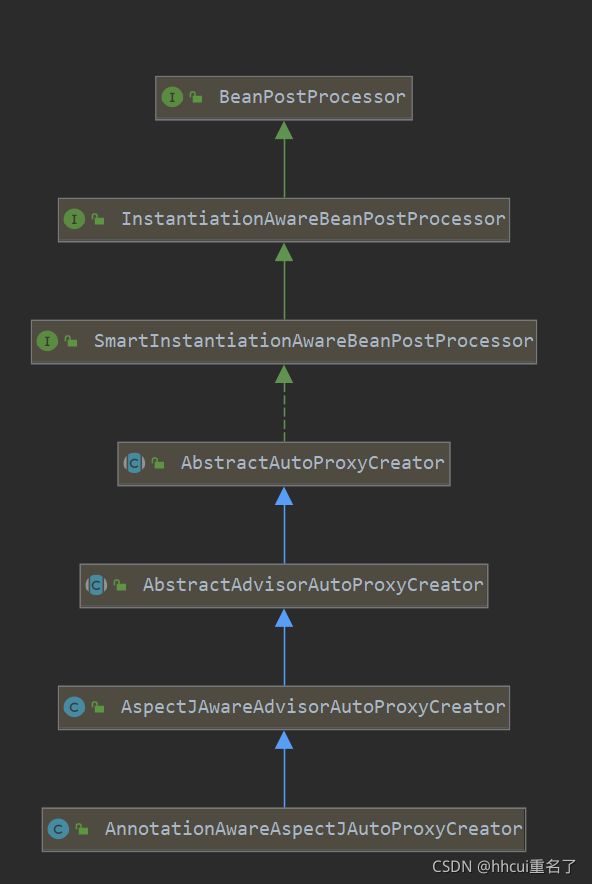
可以看到实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,对着上面的图,我们知道会执行postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法。AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
然后我们看一下这个方法做了什么
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//第一次进来,cache肯定没东西
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
//重点在shouldSkip,这里就是解析aop的代码
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
}
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
return null;
}
里面有一个重点方法shouldSkip,里面就是解析aop的
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//找出advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&
((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}
直接进入关键代码,org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation。BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder#buildAspectJAdvisors
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
//拿到容器中的beanNames
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
//判断当前遍历的bean是不是一个Aspect
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//解析aspect类,把所有的通知都转化成一个Advistor
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
如何判断一个bean是不是Aspect,就看他是否带了@Aspect注解并且不是ajc$开头
this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)
@Override
public boolean isAspect(Class<?> clazz) {
return (hasAspectAnnotation(clazz) && !compiledByAjc(clazz));
}
然后就是通知转化成Advisor
首先是遍历Aspect的所有的method,执行getAdvisor方法
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
进入getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName)
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
//拿到切点表达式
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
进入getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
其实就是在方法上看看是否有Pointcut.class, Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class这些注解
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
然后就执行new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl继承了Advistor,就这样Advistor就创建出来了。
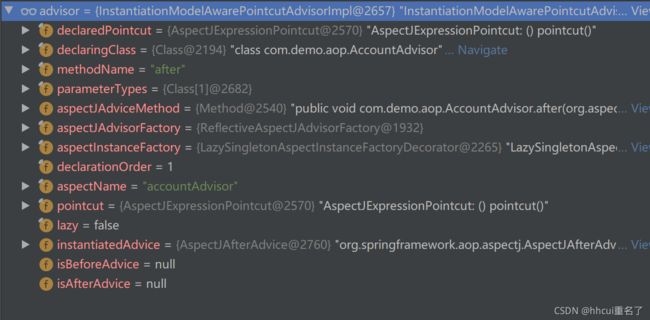
其中InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的构造方法中有this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
就为不同的通知创建成了不同类型的advice
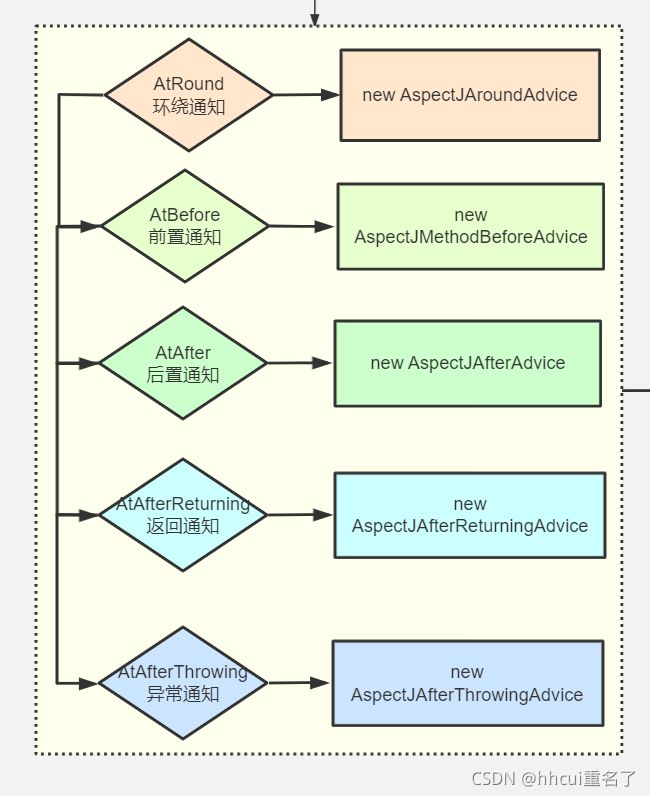
最后就会把所有的通知都解析成Advistor
解析切面已经完成了,后面就是如何把一个bean变成动态代理类。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator还继承了beanPostProcess,我们就去看找他的postProcessAfterInitialization,这就是把创建动态代理类,把本来的bean替换的代码。
在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator找到了postProcessAfterInitialization方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
可以看到,进来的还是AccountServiceImpl

所以创建动态代理并返回的就在wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey)代码里面了
wrapIfNecessary的关键代码有两行,一个是判断是否有合适的Advisors,另一个就是创建动态代理
//判断是否有合适的Advisors,而且给advices排序
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
//创建动态代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
怎么判断是合适的Advisors,前面解析的Advisors都是带有pointCutExpression,
使用experssion去匹配。
给Advisors排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
createProxy,这里面就是创建动态代理的方法,假如没有指定使用cglib,有接口的就用jdk动态代理,没有接口的就使用cglib创建代理类。
由于我的是一个接口,所以会创建jdk动态代理,this就是JdkDynamicAopProxy。
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
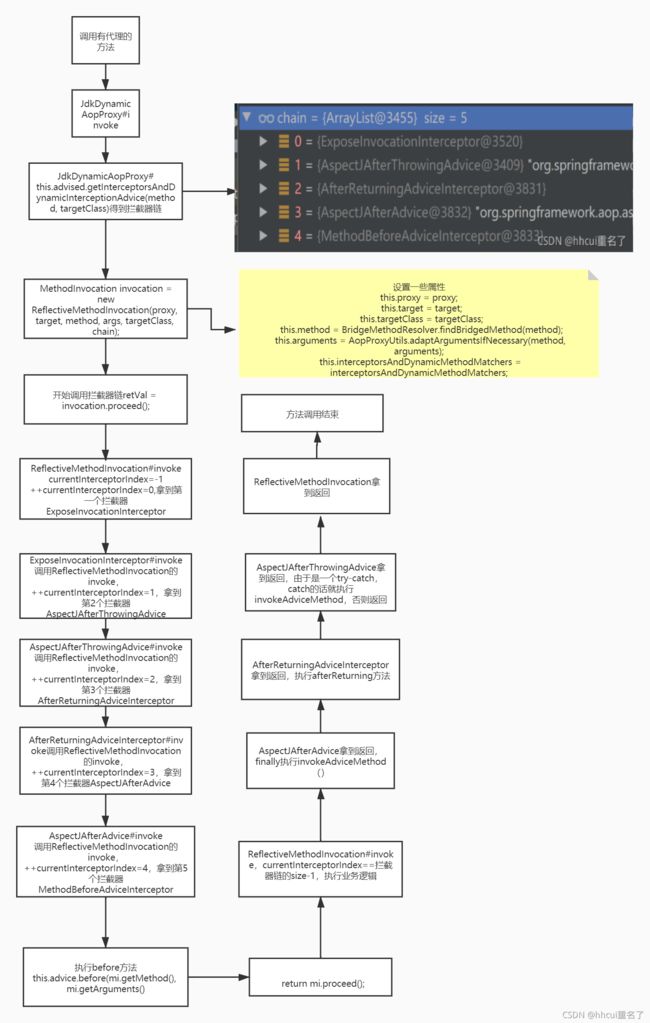
现在看方法是怎么调用的,因为为service创建了动态代理,而invocationHandler是JdkDynamicAopProxy,所以当调用service的方法时,首先会进入JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法
首先会创建一条拦截器链,会遍历advistor,看看哪些advistor匹配成功,由于advistor前面排过序,所以生成的interceptor拦截链也会有顺序。
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);

接下来就会生成MethodInvocation,调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed方法
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
//currentInterceptorIndex 初始值为-1,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers就是刚刚的5个chain的size
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
//currentInterceptorIndex++,其实就是拿到下一个interceptors
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
//第一个Interceptor是ExposeInvocationInterceptor,所以直接走else
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
return proceed();
}
}
else {
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
首先this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++currentInterceptorIndex),就拿到了第一个interceptor,是ExposeInvocationInterceptor,ExposeInvocationInterceptor不是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher,所以直接走else,((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
ExposeInvocationInterceptor的invoke方法
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
//mi就是刚刚创建的ReflectiveMethodInvocation
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
可以看到会调用mi.proceed(),mi方法传进来的ReflectiveMethodInvocation,所以又会回到
ReflectiveMethodInvocation的invoke方法,++currentInterceptorIndex,所以拿到的会是inteceptor的下一个AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice,又会调用AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.invoke
然后我们看AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice的invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
//在catch里面,所以有异常就会执行afterThrowing方法
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
又会回去调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation的invoke方法,拿到下一个inteceptor,AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor,调用他的invoke方法
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
//执行aterReturning方法
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
然后又会回去调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation的invoke方法,拿到下一个inteceptor,
AspectJAfterAdvice的invoke方法,
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
//执行after方法,因为在finally,出现异常也会执行
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
然后又会回去调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation的invoke方法,拿到下一个inteceptor,MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//执行before方法
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
//
return mi.proceed();
}
然后又回到了ReflectiveMethodInvocation,这时候currentInterceptorIndex 就等于interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size-1,所以就执行真正的业务逻辑去了。
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}