【深度学习-吴恩达】L1-3 浅层神经网络 作业
L1 深度学习概论
3 浅层神经网络
作业链接:吴恩达《深度学习》 - Heywhale.com
0 作业任务
用1层隐藏层的神经网络分类二维数据
目标:
-
实现具有单个隐藏层的2分类神经网络
-
使用具有非线性激活函数的神经元
-
计算交叉熵损失
-
实现前向和后向传播
1 Logistic回归二分类的实现
1.1 导入安装包
- numpy是Python科学计算的基本包。
- sklearn提供了用于数据挖掘和分析的简单有效的工具。
- matplotlib是在Python中常用的绘制图形的库。
- testCases提供了一些测试示例用以评估函数的正确性
- planar_utils提供了此作业中使用的各种函数
# Package imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases import *
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(1) # set a seed so that the results are consistent
1.2 导入数据集
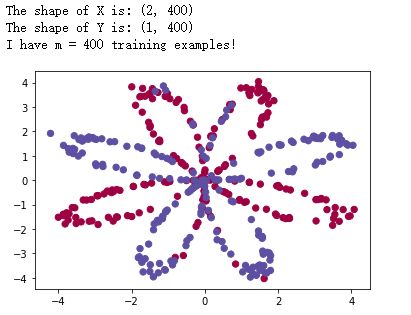
X, Y = load_planar_dataset()
# Visualize the data:
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=Y.reshape(X[0,:].shape), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
shape_X = X.shape
shape_Y = Y.shape
m = shape_X[1] # training set size
print ('The shape of X is: ' + str(shape_X))
print ('The shape of Y is: ' + str(shape_Y))
print ('I have m = %d training examples!' % (m))
得到数据集:
- X形状为(2, 400)
- Y形状为(1, 400)
- 一共有m个输入数据
如下图所示:
1.3 简单的Logistic回归
使用sklearn内置函数执行
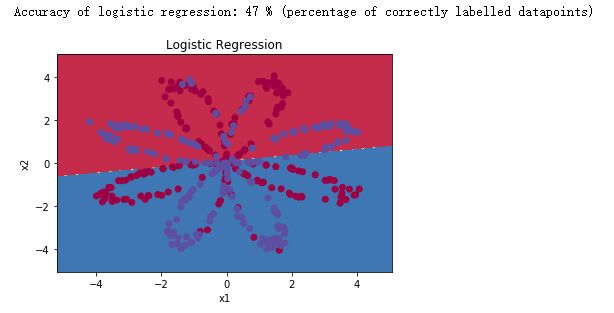
# Train the logistic regression classifier
clf = sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV();
clf.fit(X.T, Y.T);
# Plot the decision boundary for logistic regression
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: clf.predict(x), X, Y)
plt.title("Logistic Regression")
# Print accuracy
LR_predictions = clf.predict(X.T)
print ('Accuracy of logistic regression: %d ' % float((np.dot(Y,LR_predictions) + np.dot(1-Y,1-LR_predictions))/float(Y.size)*100) +
'% ' + "(percentage of correctly labelled datapoints)")
得到结果如下所示:
由于数据集不是线性可分的,因此逻辑回归效果不佳
-
注意这里出现bug,需要将planar_utils.py文件中的plt.scatter函数修改为:
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(y), cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
2 神经网络二分类的实现
2.1 定义神经网络结构
练习:定义三个变量:
- n_x:输入层的大小
- n_h:隐藏层的大小
- n_y:输出层的大小
# GRADED FUNCTION: layer_sizes
def layer_sizes(X, Y):
"""
Arguments:
X -- input dataset of shape (input size, number of examples)
Y -- labels of shape (output size, number of examples)
Returns:
n_x -- the size of the input layer
n_h -- the size of the hidden layer
n_y -- the size of the output layer
"""
n_x = X.shape[0] # size of input layer
n_h = 4
n_y = Y.shape[0] # size of output layer
return (n_x, n_h, n_y)
2.2 初始化模型的参数
练习:实现函数 initialize_parameters()。
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
params -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(2) # we set up a seed so that your output matches ours although the initialization is random.
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h,n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h,1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y,n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y,1))
assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
- 将权重矩阵初始化为随机数
- 将偏差向量初始化为0
2.3 循环
练习:实现forward_propagation()。
# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Argument:
X -- input data of size (n_x, m)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters (output of initialization function)
Returns:
A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation
cache -- a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2"
"""
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Implement Forward Propagation to calculate A2 (probabilities)
Z1 = np.dot(W1,X) + b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2,A1) + b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2)
assert(A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))
cache = {"Z1": Z1,
"A1": A1,
"Z2": Z2,
"A2": A2}
return A2, cache
- 第一层激活函数使用tanh函数
- 第二层激活函数使用sigmoid函数
练习:实现compute_cost()以计算损失 J J J的值。
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost
def compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters):
"""
Computes the cross-entropy cost given in equation (13)
Arguments:
A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation, of shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters W1, b1, W2 and b2
Returns:
cost -- cross-entropy cost given equation (13)
"""
m = Y.shape[1] # number of example
# Compute the cross-entropy cost
logprobs = Y*np.log(A2) + (1-Y)* np.log(1-A2)
cost = -1/m * np.sum(logprobs)
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
# makes sure cost is the dimension we expect.
# E.g., turns [[17]] into 17
assert(isinstance(cost, float))
return cost
练习:实现函数backward_propagation()
# GRADED FUNCTION: backward_propagation
def backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y):
"""
Implement the backward propagation using the instructions above.
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing our parameters
cache -- a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2".
X -- input data of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients with respect to different parameters
"""
m = X.shape[1]
# First, retrieve W1 and W2 from the dictionary "parameters".
W1 = parameters["W1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
# Retrieve also A1 and A2 from dictionary "cache".
A1 = cache["A1"]
A2 = cache["A2"]
# Backward propagation: calculate dW1, db1, dW2, db2.
dZ2= A2 - Y
dW2 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ2,A1.T)
db2 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ2,axis=1,keepdims=True)
dZ1 = np.dot(W2.T,dZ2) * (1-np.power(A1,2))
dW1 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ1,X.T)
db1 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ1,axis=1,keepdims=True)
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return grads
练习:实现参数更新。 使用梯度下降,你必须使用(dW1,db1,dW2,db2)才能更新(W1,b1,W2,b2)。
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 1.2):
"""
Updates parameters using the gradient descent update rule given above
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
"""
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Retrieve each gradient from the dictionary "grads"
dW1 = grads["dW1"]
db1 = grads["db1"]
dW2 = grads["dW2"]
db2 = grads["db2"]
# Update rule for each parameter
W1 = W1 - learning_rate * dW1
b1 = b1 - learning_rate * db1
W2 = W2 - learning_rate * dW2
b2 = b2 - learning_rate * db2
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
2.4 集成函数
练习:在nn_model()中建立你的神经网络模型。
def nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=False):
"""
Arguments:
X -- dataset of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- labels of shape (1, number of examples)
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
num_iterations -- Number of iterations in gradient descent loop
print_cost -- if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
np.random.seed(3)
n_x = layer_sizes(X, Y)[0]
n_y = layer_sizes(X, Y)[2]
# Initialize parameters, then retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2. Inputs: "n_x, n_h, n_y". Outputs = "W1, b1, W2, b2, parameters".
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation. Inputs: "X, parameters". Outputs: "A2, cache".
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Cost function. Inputs: "A2, Y, parameters". Outputs: "cost".
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters)
# Backpropagation. Inputs: "parameters, cache, X, Y". Outputs: "grads".
grads = backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y)
# Gradient descent parameter update. Inputs: "parameters, grads". Outputs: "parameters".
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)
# Print the cost every 1000 iterations
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
return parameters
2.5 进行预测
练习:使用你的模型通过构建predict()函数进行预测。
# GRADED FUNCTION: predict
def predict(parameters, X):
"""
Using the learned parameters, predicts a class for each example in X
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
X -- input data of size (n_x, m)
Returns
predictions -- vector of predictions of our model (red: 0 / blue: 1)
"""
# Computes probabilities using forward propagation, and classifies to 0/1 using 0.5 as the threshold.
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
predictions = np.round(A2)
return predictions
在二维数据集上运行模型
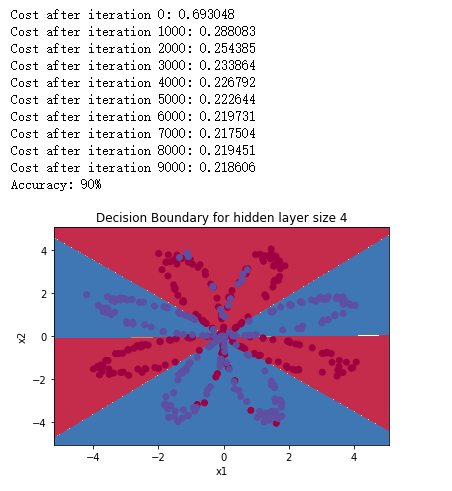
# Build a model with a n_h-dimensional hidden layer
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=True)
# Plot the decision boundary
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
plt.title("Decision Boundary for hidden layer size " + str(4))
# Print accuracy
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
print ('Accuracy: %d' % float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100) + '%')
得到如下运行结果:
准确率高于logistic回归
2.6 调整隐藏层大小
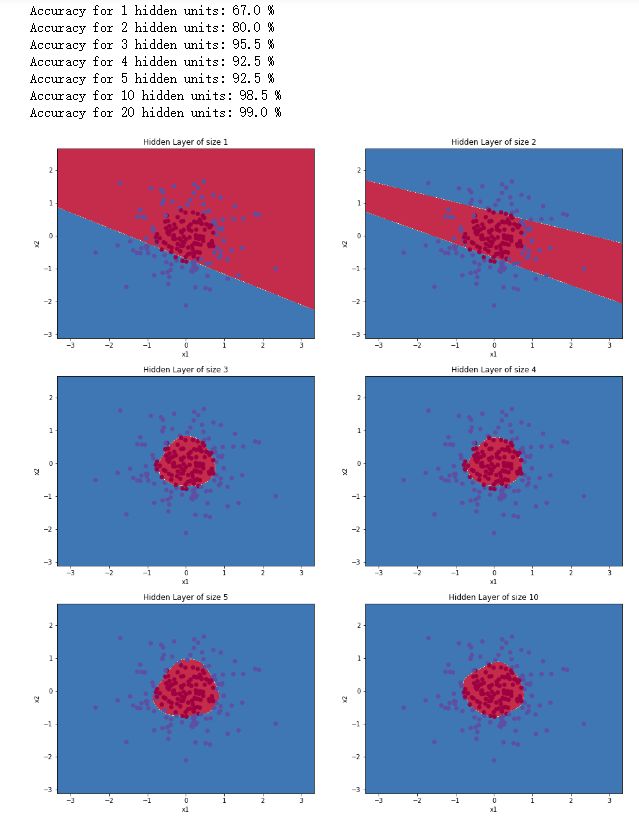
# This may take about 2 minutes to run
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 32))
hidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 20]
for i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes):
plt.subplot(5, 2, i+1)
plt.title('Hidden Layer of size %d' % n_h)
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 5000)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
accuracy = float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100)
print ("Accuracy for {} hidden units: {} %".format(n_h, accuracy))
得到如下运行结果:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-hN8BWS2u-1659012992274)(C:\Users\Jack London\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220727161738023.png)]
说明:
- 较大的模型能够更好地你和训练集
- 使用正则化可以防止过度拟合
2.7 使用其他数据集
# Datasets
noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structure = load_extra_datasets()
datasets = {"noisy_circles": noisy_circles,
"noisy_moons": noisy_moons,
"blobs": blobs,
"gaussian_quantiles": gaussian_quantiles}
### START CODE HERE ### (choose your dataset)
dataset = "gaussian_quantiles"
### END CODE HERE ###
X, Y = datasets[dataset]
X, Y = X.T, Y.reshape(1, Y.shape[0])
# make blobs binary
if dataset == "blobs":
Y = Y%2
# Visualize the data
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=Y.reshape(X[0,:].shape), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);
重新运行后得到如下结果: