Spring源码系列-第3章-后置处理器和Bean生命周期
文章目录
- 第3章-后置处理器和Bean生命周期
-
- 再来看一下我们的测试类
-
- MyBeanPostProcessor
- MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
- MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor
- MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- Cat
- beans2.xml
- MainTest
- 继续Bean生命周期
-
- 流程图-Bean生命周期与后置处理器
- BeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors()注册Bean后置处理器
- PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors()
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行无参构造
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行predictBeanType方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
- DefaultListableBeanFactory#doGetBeanNamesForType()获取某一个组件在容器中的名字
- AbstractBeanFactory#isTypeMatch()
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#predictBeanType()
- 此方法能做什么?
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()完成BeanFactory初始化
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()创建Bean
- 此方法能做什么?
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行determineCandidateConstructors方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()无参构造创建Bean,属性赋值,初始化等
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance()使用构造器创建Bean
- 此方法能做什么?
- Cat-执行无参构造方法
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- 此方法能做什么?
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean()属性赋值
- BeanWrapperImpl#setValue()
- 此方法能做什么?
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessProperties方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties()
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata()找到自动装配的元信息,比如@Autowired,@Value
- 此方法能做什么?
- Cat-执行setName-@Autowire注入原理
-
- Debug调用栈
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- BeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean()初始化Bean
- 此方法能做什么?
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
- Cat-调用afterPropertiesSet方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods()
- BeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法
-
- Debug调用栈
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法
- 文章优先发布在Github,其它平台会晚一段时间,文章纠错与更新内容只在Github:https://github.com/youthlql/JavaYouth
- 转载须知:转载请注明GitHub出处,让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境。
- 如果你要提交 issue 或者 pr 的话建议到 Github 提交。笔者会陆续更新,如果对你有所帮助,不妨Github点个Star~。你的Star是我创作的动力。
第3章-后置处理器和Bean生命周期
再来看一下我们的测试类
为了分析后面的,测试类有些许变动
MyBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...");
}
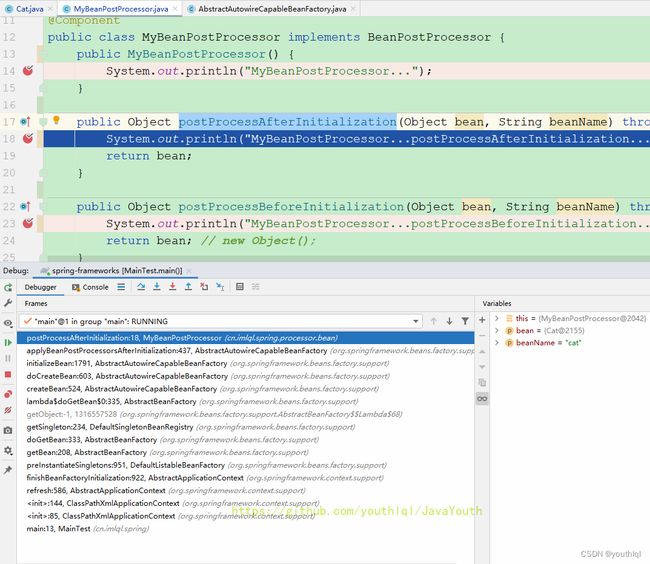
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInitialization..." + bean + "==>" + beanName);
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization..." + bean + "==>" + beanName);
return bean; // new Object();
}
}
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...");
} //初始化之前进行后置处理,Spring留给我们给这个组件创建对象的回调。
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInstantiation=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName); //if(class.isAssFrom(Cat.class)){return new Dog()}
return null; //如果我们自己创建了对象返回。Spring则不会帮我们创建对象,用我们自己创建的对象? 我们创建的这个对象,Spring会保存单实例?还是每次getBean都调到我们这里创建一个新的?
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInstantiation=>" + bean + "--" + beanName); //提前改变一些Spring不管的bean里面的属性
return true; //返回false则bean的赋值全部结束
} //解析自定义注解进行属性值注入;pvs 封装了所有的属性信息。
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessProperties=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return null;
}
}
MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
public MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization...=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return bean; //null
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInitialization..=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return null;
}
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessMergedBeanDefinition..=>" + beanName + "--" + beanType + "---" + beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void resetBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...resetBeanDefinition.." + beanName);
}
}
MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Component //bean进行代理增强期间进行使用
public class MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...");
} //预测bean的类型,最后一次改变组件类型。
public Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...predictBeanType=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName);
return null;
}
//返回我们要使用的构造器候选列表
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...determineCandidateConstructors=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName);
//返回一个我们指定的构造器
return null;
}
//返回早期的bean引用
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...getEarlyBeanReference=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor
/**
* BeanFactory的后置处理器
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor...");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor....postProcessBeanFactory==>"+beanFactory);
}
}
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor");
}
@Override //紧接着执行
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor....postProcessBeanFactory...");
}
@Override //先执行的
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor...postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry...");
//增强bean定义信息的注册中心,比如自己注册组件
}
}
Cat
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean {
public Cat() {
System.out.println("cat被创建了...");
}
private String name;
@Value("${JAVA_HOME}") //自动赋值功能
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("cat....setName正在赋值调用....");
this.name = name;
}
//注解怎么定义这个是初始化方法?
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("CatInitializingBean..afterPropertiesSet...");
}
}
beans2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.imlql.spring.processor"/>
<bean class="cn.imlql.spring.bean.Cat" id="cat"/>
</beans>
MainTest
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
继续Bean生命周期
流程图-Bean生命周期与后置处理器
BeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
前面两个工厂后置处理器执行完之后,接下来就是我们的Bean后置处理器,第一个执行的就是BeanPostProcessor
Debug调用栈
AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors()注册Bean后置处理器
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors()
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
//获取到容器中所有的 BeanPostProcessor; Bean的后置处理器
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { //获取所有实现了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
//首先,注册所有的实现了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor ; First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
//接下来,注册所有的实现了 Ordered 的 BeanPostProcessor Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// 最后,注册所有普通的 BeanPostProcessor ;Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); //从容器中获取这个组件
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);//所谓的注册其实就是保存到一个Map里面,后续用的时候可以直接拿
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
- Bean工厂后置处理器调用的是
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory , List) - Bean后置处理器调用的是
registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory , AbstractApplicationContext )
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
- BeanPostProcessor执行顺序和BeanFactoryPostProcessor有点不一样
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor是先执行完每一个的无参构造和实现的几个方法,再去执行下一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- BeanPostProcessor是先执行所有BeanPostProcessor的无参构造,再执行所有BeanPostProcessor实现的方法。
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行无参构造
同上
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行无参构造
同上
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行predictBeanType方法
Debug调用栈
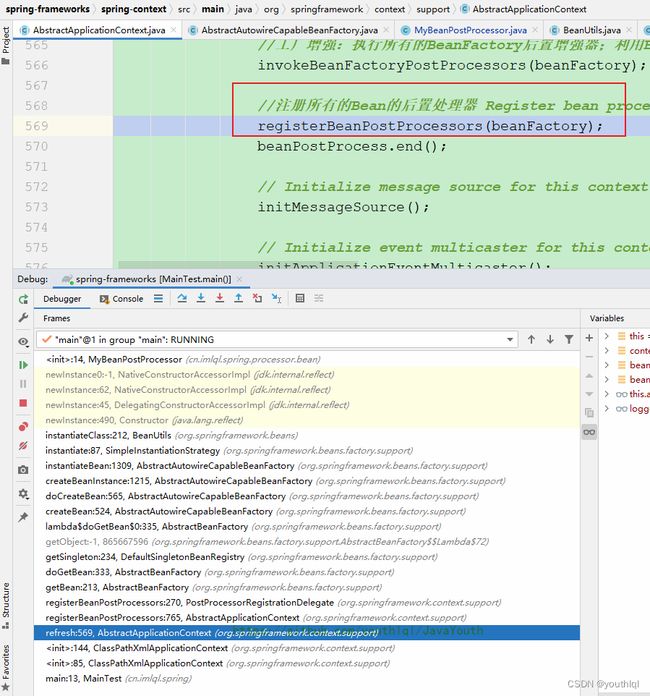
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
@Override //容器刷新的十二大步。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 工厂创建:BeanFactory第一次开始创建的时候,有xml解析逻辑。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
//工厂增强:执行所有的BeanFactory后置增强器;利用BeanFactory后置增强器对工厂进行修改或者增强,配置类会在这里进行解析。 Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册所有的Bean的后置处理器 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
//注册监听器,从容器中获取所有的ApplicationListener; Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//bean创建;完成 BeanFactory 初始化。(工厂里面所有的组件都好了)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! 获取ApplicationListener在ioc容器中注册的bean的名字
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); //获取所有的容器中的监听器,并保存他们的名字
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
在调用registerListeners()的时候,竟然进入到了我们的后置处理器逻辑,我们接着往后看
DefaultListableBeanFactory#doGetBeanNamesForType()获取某一个组件在容器中的名字
调过一些不重要的调用,逻辑到了这里
//获取某一个组件在容器中的名字。
private String[] doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
// Check all bean definitions. 因为Spring没有直接保存class--bean名字的对应信息,只能遍历所有的beanname,拿出他们beanname的定义信息,再看是否我指定的类型。
for (String beanName : this.beanDefinitionNames) {
// Only consider bean as eligible if the bean name is not defined as alias for some other bean.
if (!isAlias(beanName)) { //判断是否别名
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// Only check bean definition if it is complete.
if (!mbd.isAbstract() && (allowEagerInit ||
(mbd.hasBeanClass() || !mbd.isLazyInit() || isAllowEagerClassLoading()) &&
!requiresEagerInitForType(mbd.getFactoryBeanName()))) {
boolean isFactoryBean = isFactoryBean(beanName, mbd); //是否FactoryBean
BeanDefinitionHolder dbd = mbd.getDecoratedDefinition();
boolean matchFound = false;
boolean allowFactoryBeanInit = (allowEagerInit || containsSingleton(beanName));
boolean isNonLazyDecorated = (dbd != null && !mbd.isLazyInit());
if (!isFactoryBean) {
if (includeNonSingletons || isSingleton(beanName, mbd, dbd)) {
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit); //是否类型匹配?
}
}
else {
if (includeNonSingletons || isNonLazyDecorated ||
(allowFactoryBeanInit && isSingleton(beanName, mbd, dbd))) {
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit);
}
if (!matchFound) {
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean instance itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit);
}
}
if (matchFound) {
result.add(beanName);
}
}
}
// ......
}
}
// ......
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
- 下面是容器中现在有的bean定义信息,但是这些bean不一定都创建好了。
- Spring在这里是想要按照类型去容器中去找组件,在这里就是想找ApplicationListener.class类型的组件。但是Spring中只存储了BeanName=>BeanType的对应关系(BeanDefinitions),没有存BeanType=>BeanName的对应关系。
- 所以在这里只能遍历循环beanDefinitionNames
- 通过beanName再去BeanDefinitions拿beanType
- 判断是不是想要的类型。
- 这里有没有优化空间,再存一个BeanType=>BeanName的对应关系?但是这样的关系是一对多的,同一个BeanType下可能有多个beanName,Spring可能是考虑到空间成本,没有这样弄。
AbstractBeanFactory#isTypeMatch()
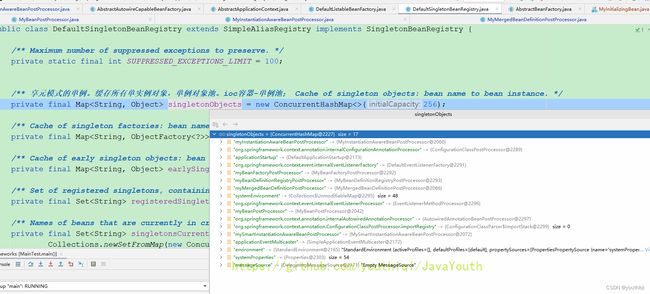
- 有一个小细节,在debug的时候我们发现这里,只有Cat类进入到了后续判断,为什么上面的其它9个类没有进入后续逻辑呢?
这里是因为其它9个对象都已经在之前创建好了对象,只有Cat还没有创建对象。Spring在这里给我们一个机会,在对象创建之前,我们可以最后一次决定Cat的类型。什么意思?往后看
- 我们来看看此时单例池里有哪些对象
protected boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
boolean isFactoryDereference = BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name);
// 检查是否已经有这个beanName的单例对象,有了直接用对象的Class,没有可以最后一次决定这个组件的类型;SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.predictBeanType() Check manually registered singletons.
Object beanInstance = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (beanInstance != null && beanInstance.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
if (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) {
if (!isFactoryDereference) {
Class<?> type = getTypeForFactoryBean((FactoryBean<?>) beanInstance);
return (type != null && typeToMatch.isAssignableFrom(type));
}
else {
return typeToMatch.isInstance(beanInstance);
}
}
else if (!isFactoryDereference) {
if (typeToMatch.isInstance(beanInstance)) {
// Direct match for exposed instance?
return true;
}
else if (typeToMatch.hasGenerics() && containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// ......
return (resolvableType != null && typeToMatch.isAssignableFrom(resolvableType));
}
}
return false;
}
else if (containsSingleton(beanName) && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// null instance registered
return false;
}
// No singleton instance found -> check bean definition.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// No bean definition found in this factory -> delegate to parent.
return parentBeanFactory.isTypeMatch(originalBeanName(name), typeToMatch);
}
// Retrieve corresponding bean definition.
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
BeanDefinitionHolder dbd = mbd.getDecoratedDefinition();
// Setup the types that we want to match against
Class<?> classToMatch = typeToMatch.resolve();
if (classToMatch == null) {
classToMatch = FactoryBean.class;
}
Class<?>[] typesToMatch = (FactoryBean.class == classToMatch ?
new Class<?>[] {classToMatch} : new Class<?>[] {FactoryBean.class, classToMatch});
// Attempt to predict the bean type
Class<?> predictedType = null;
if (!isFactoryDereference && dbd != null && isFactoryBean(beanName, mbd)) {
// ...
}
// 通过后置处理器,可以返回自定义的类型 If we couldn't use the target type, try regular prediction.
if (predictedType == null) {
predictedType = predictBeanType(beanName, mbd, typesToMatch);
if (predictedType == null) {
return false;
}
}
//......
// If we don't have a bean type, fallback to the predicted type
return typeToMatch.isAssignableFrom(predictedType);
}
预测BeanType是什么意思呢?因为每个组件都会经过我们自定义的方法,假设你现在有个Cat类,你可以在这里写个if判断。你可以让猫变成狗,有点类似于指鹿为马
public Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...predictBeanType=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName);
if(beanClass == Cat.class){
return Dog.class;
}
return null;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#predictBeanType()
protected Class<?> predictBeanType(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd, typesToMatch);
// Apply SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors to predict the
// eventual type after a before-instantiation shortcut.
if (targetType != null && !mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
boolean matchingOnlyFactoryBean = typesToMatch.length == 1 && typesToMatch[0] == FactoryBean.class;
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
// 在这里调用我们自定义的predictBeanType,也就是MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#predictBeanType
Class<?> predicted = bp.predictBeanType(targetType, beanName);//还是可以理解为模板模式
if (predicted != null &&
(!matchingOnlyFactoryBean || FactoryBean.class.isAssignableFrom(predicted))) {
return predicted;
}
}
}
return targetType;
}
此方法能做什么?
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor起名为智能实例化感知后置处理器,smart也是聪明的意思,表示这是一个聪明的后置处理器
- 之所以这样起名,意思是我们可以实现这个接口然后实现它的方法,就可以告诉Spring:我们要使用的构造器候选列表。我们期望它是什么BeanType,甚至可以返回早期的bean引用(后面说)
- 那应用场景什么呢?
- 当一个组件需要代理对象的时候,你如果返回原来的BeanType肯定是不对的,这时候这个功能就起作用了
- 还有我们可以在这里强制Spring全部使用有参构造器创建我们自己的Bean
- bean进行代理增强期间这个接口用的比较多
- 在Spring中只要调用了
doGetBeanNamesForType方法或者getBeanNamesForType方法,就一定会经过SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的处理
在此方法里为什么Cat会进来两次呢?往后面看
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
Debug调用栈
AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()完成BeanFactory初始化
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 给工厂设置好 ConversionService【负责类型转换的组件服务】, Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// 注册一个默认的值解析器("${}") ;Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// LoadTimeWeaverAware;aspectj:加载时织入功能【aop】。 Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName); //从容器中获取组件,有则直接获取,没则进行创建
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化所有的非懒加载的单实例Bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
- 前面刚说过只要调用
getBeanNamesForType,就会经过SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的处理。
//注册监听器,从容器中获取所有的ApplicationListener; Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//bean创建;完成 BeanFactory 初始化。(工厂里面所有的组件都好了)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
这两方法都调用了getBeanNamesForType,所以上面Cat会打印两次
- 上面我们也看了只有Cat的对象还没创建,还没初始化,所以下面就开始创建对象了。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()创建Bean
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// 提前给我们一个机会,去返回组件的代理对象。 Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try { //Spring真正自己创建对象
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
@Nullable
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
@Nullable
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
Object result = bp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName); //还是老样子,调用我们自己写的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
此方法能做什么?
后置处理器在此处提前给我们一个机会,去返回组件的代理对象
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInstantiation=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName); //if(class.isAssFrom(Cat.class)){return new Dog()}
return null; //如果我们自己创建了对象返回。Spring则不会帮我们创建对象,用我们自己创建的对象(可以是代理对象)
}
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行determineCandidateConstructors方法
Debug调用栈
前面还是一样的执行逻辑,直接来到下面
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()无参构造创建Bean,属性赋值,初始化等
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) { //是否单例的
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建Bean的实例,默认使用无参构造器创建的对象,组件的原始对象就创建了
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
//允许 后置处理器 再来修改下beanDefinition;MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition;; Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
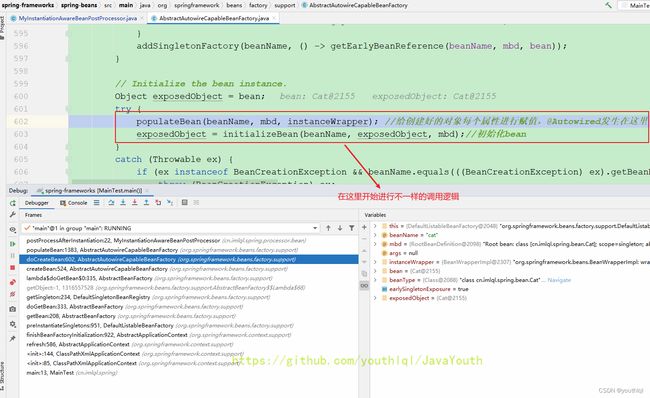
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //给创建好的对象每个属性进行赋值,@Autowired发生在这里
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//初始化bean
}
// ......
return exposedObject;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance()使用构造器创建Bean
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
//获取Bean的类型 Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
//定义Bean的实例提供者
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
//@Bean注解等可能会调用此方法进行创建出来,Spring把@Bean标注的方法理解为工厂方法
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//快速创建? Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
//后置处理器有机会在这里决定当前bean用哪个构造器?SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors() Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); //构造器方式的自动注入与对象创建
}
//使用默认的自己设置的高优先级的构造器 Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// 默认使用无参构造器为当前组件创建对象;No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
@Nullable
protected Constructor<?>[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
Constructor<?>[] ctors = bp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);// 一样的,调我们自定义的
if (ctors != null) {
return ctors;
}
}
}
return null;
}
- 实例提供者:
此方法能做什么?
后置处理器有机会在这里决定当前bean用哪个构造器
//返回我们要使用的构造器候选列表
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...determineCandidateConstructors=>" + beanClass + "--" + beanName);
//返回一个我们指定的构造器
return null;
}
Cat-执行无参构造方法
以前讲过。
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
Debug调用栈
此方法能做什么?
看这个传进来的参数,应该就是能修改下beanDefinition
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessMergedBeanDefinition..=>" + beanName + "--" + beanType + "---" + beanDefinition);
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
Debug调用栈
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean()属性赋值
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// @Autowired赋值也在这里(但是没做事)。可以中断初始化行为; 在属性赋值之前,后置处理器可以提前准备些东西 Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
} //以上的后置处理器可以中断以下的行为
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); //xml中property标签指定的
} //使用后置处理器处理属性
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse; //封装了当前bean的所有属性名和值,可以由后置处理器处理得到
}
// 在这里设置过的属性,在后面就不用处理了
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) { //把以前处理好的PropertyValues给bean里面设置一下。主要是上面步骤没有给bean里面设置的属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); //xml版的所有配置会来到这里给属性赋值
}
}
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理@Autowire)也在这里,但是直接返回了true,相当于没做事。
BeanWrapperImpl#setValue()
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);最终也是用下面的反射进行赋值
@Override //利用set方法反射赋值
public void setValue(@Nullable Object value) throws Exception { //name setName
Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
此方法能做什么?
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//提前改变一些你不想让Spring管理的bean里面的属性
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInstantiation=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return true; //返回false则bean的赋值全部结束
}
这个有点类似于拦截器链,可以中断后面的行为。我感觉也没干啥事,可能我没用到过。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessProperties方法
Debug调用栈
和上面一样
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties()
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);//找到自动装配的元信息
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata()找到自动装配的元信息,比如@Autowired,@Value
自动装配处理器在这里开始真正做事
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}//下面是分析当前类方法或者属性有没有标注@Autowired等自动赋值的注解
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//找所有属性中标注了@Autowired\@Value\@Inject注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//拿到所有方法,看有没有@Autowired注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
此方法能做什么?
这里是真正的控制属性赋值的地方
//可以在这里解析自定义注解进行属性值注入;pvs 封装了所有的属性信息。
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessProperties=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return null;
}
Cat-执行setName-@Autowire注入原理
Debug调用栈
这也说明了,@Autowire,@Value赋值的时候会去找setXXX,这也是@Autowire的原理
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);//找到自动装配的元信息
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
BeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
Debug调用栈
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean()初始化Bean
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); //组件有Aware接口,先Aware;BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {//执行后置处理器的BeforeInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); //这里是真正初始化
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //执行后置处理器的AfterInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);//这里又是一样的逻辑,调用我们自定义的
if (current == null) { //不管null的东西
return result;
}
result = current; //新Bean会替换以前的Bean
}
return result;
}
此方法能做什么?
这里根据参数很明显可以看到又是一个可以改变Bean的地方
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization..." + bean + "==>" + beanName);
return bean; // new Object();
}
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
因为MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor是继承自BeanPostProcessor,所以这里的效果和BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization效果一样
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization...=>" + bean + "--" + beanName);
return bean; //null
}
Cat-调用afterPropertiesSet方法
Debug调用栈
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods()
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
//如果组件实现了 InitializingBean 接口,就调用组件自己的afterPropertiesSet
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); //调自定义的
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); //调自定义的
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); //如果有自定义的初始化方法,就是那个init-method,这里也会执行
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
BeanPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法
Debug调用栈
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor-执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法
同上
- 至此,后置处理器处理完成了。
- Spring内部所有的功能增强都是由后置处理器完成。例如事务,AOP,代理等等