Springboot 自动配置
SpringBoot
1. SpringBoot自动配置
@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class})}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication{}
1.1 @SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
@Configuration:代表当前是一个配置类
1.2 @EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
1.2.1 @AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
@Import:给容器中导入一个组件(Registrar.class),利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件;
registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)方法中metadata代表注解的元信息,我们这个这个注解是
@AutoConfigurationPackage;registerBeanDefinitions方法体的内部有一行代码getPackageNames()代表获取元注解的包信息,所以我们拿到的包信息就是Springboot的main方法的包路径;
public class AutoConfigurationPackages{
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
Registrar() {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (String[])(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata)).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
}
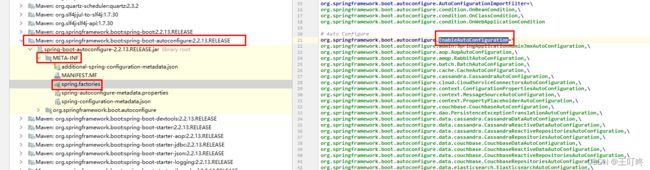
所以,@Import 注解最终实现的结果就是将启动类路径下的包和子包,全部扫描进容器中;(全部扫描不意味着全部加载,能够被加载需要满足加载所需的条件)
1.2.2 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
step1:
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector{
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
}
step2:
利用 this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector{
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//获取所有候选的配置
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//移除重复的配置
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//校验不符合要求的配置
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
//返回符合条件的配置
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
step3:
getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取所有导入到容器中的配置类,(全部导入不意味着全部加载,能够被加载需要满足加载所需的条件)
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector{
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
protected ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader;
}
}
step4:
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
getOrDefault()
public class LinkedMultiValueMap<K, V> implements MultiValueMap<K, V>{}
public interface MultiValueMap<K, V> extends Map<K, List<V>> {}
public class Map{
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
}
}
step5:
loadSpringFactories()
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
//.........
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
step6:加载到全部需加载的配置后,回到step2,对配置进行条件判断,判断是否能够成功加载;
1.3 @ComponentScan
@ComponentScan:指定扫描的包路径
2. SpringBoot对于MVC的自动配置
2.1 静态资源
官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/web.html#web.servlet.spring-mvc.static-content
默认情况下,Spring Boot 从类路径中名为
/static(或/public或/resources或/META-INF/resources)的目录或从ServletContext. 它使用ResourceHttpRequestHandler来自 Spring MVC 的方法,因此您可以通过添加自己的方法WebMvcConfigurer并覆盖该addResourceHandlers方法来修改该行为。在独立的 Web 应用程序中,容器中的默认 servlet 也被启用并充当后备,
ServletContext如果 Spring 决定不处理它,则从根目录提供内容。大多数情况下,这不会发生(除非你修改了默认的 MVC 配置),因为 Spring 总是可以通过DispatcherServlet.默认情况下,资源映射在 上
/**,但您可以使用该spring.mvc.static-path-pattern属性对其进行调整。例如,将所有资源重新定位到/resources/**可以实现如下:spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/**您还可以使用该
spring.web.resources.static-locations属性自定义静态资源位置(将默认值替换为目录位置列表)。根 servlet 上下文路径"/"也会自动添加为位置。
2.1.1 静态资源的访问原理
Q:静态资源的访问和Controller层的调用顺序是怎么样的?(当Controller层有和静态资源同名的路径,会访问Controller 还是静态资源?)先访问Controller,然后再访问静态资源;
Q:如何修改默认的静态资源访问路径?spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/wddong
2.1.2 静态资源的访问前缀
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/** # 访问方式为 当前项目+ `/resources` + 静态资源名 = 静态资源
2.1.3 静态资源的配置原理
类的包路径:\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-autoconfigure\2.2.13.RELEASE\spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.13.RELEASE-sources.jar!\org\springframework\boot\autoconfigure\web\servlet\WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {}
}
WebMvcProperties与配置文件中的spring.mvc进行了绑定;
ResourceProperties与配置文件中的spring.resources进行了绑定;
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /wddong/**
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/wddong
cache:
period: 100
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.mvc")
public class WebMvcProperties {
private String staticPathPattern = "/**";
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
}
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中的静态内部类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter只有一个有参构造器;并且为
@Configuration 被Spring管理,意味着方法的形参值都是从Spring中获取;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties;
private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider;
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(WebMvcProperties mvcProperties, ListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider) {
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
}
}
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中的静态内部类EnableWebMvcConfiguration只有一个有参构造器;同理如上;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware {
//有参构造方法
public EnableWebMvcConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ObjectProvider<WebMvcProperties> mvcPropertiesProvider,
ObjectProvider<WebMvcRegistrations> mvcRegistrationsProvider,
ObjectProvider<ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.mvcProperties = mvcPropertiesProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.mvcRegistrations = mvcRegistrationsProvider.getIfUnique();
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
//资源处理的方法
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(),
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
}
}
2.1.4 静态资源的处理规则
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration {
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//调用父类方法,添加资源处理器
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
//resourceProperties为上文中,提到的映射 配置文件中的spring.resources属性
//判断配置文件中的isAddMappings,当配置文件中配置isAddMappings=false;下面的代码不执行
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
//webjars的相关规则
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
//mvcProperties为上文中,提到的映射 配置文件中的spring.mvc属性
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(),
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
//resourceProperties为上文中,提到的映射 配置文件中的spring.resources属性
}
private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, String... locations) {
if (registry.hasMappingForPattern(pattern)) {
return;
}
ResourceHandlerRegistration registration = registry.addResourceHandler(pattern);
registration.addResourceLocations(locations);
//设置缓存时间
registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod()));
registration.setCacheControl(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl());
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registration);
this.autoConfiguredResourceHandlers.add(pattern);
}
}
addResourceHandlers()解析:
step1:调用父类方法,添加资源处理器
step2:resourceProperties对应为ResourceProperties类,ResourceProperties从配置文件spring.resources中获取属性;判断配置文件中的isAddMappings,当配置文件中配置isAddMappings=false;下面的代码不执行
step3:配置webjars的相关规则;
step4:获取mvcProperties的相关配置;mvcProperties对应为WebMvcProperties类,WebMvcProperties从配置文件spring.mvc中获取属性getStaticLocations();当配置文件中没有配置static-locations的相关信息时,加载的即为系统默认的配置,如下图;
step5:当配置文件中配置有static-locations的相关信息时,加载的配置的文件信息,替换系统默认的配置;
2.1.5 欢迎页配置
SpringBoot如何自动配置欢迎页为index.html
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration{
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
}
final class WelcomePageHandlerMapping{
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext, Resource welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage != null && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage);
setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
}
else if (welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
setRootViewName("index");
}
}
}
3. SpringBoot中配置文件的加载位置及顺序
3.1 配置文件的加载位置
- classpath 根路径
- classpath 根路径下的 config 目录
- jar 包当前目录
- jar 包当前目录的 config 目录
- /config 子目录的直接子目录
3.2 配置文件的加载顺序
- 当前 jar 包内部的 application.properties 和 application.yml
- 当前 jar 包内部的 application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
- 引用的外部 jar 包的 application.properties 和 application.yml
- 引用的外部 jar 包的 application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
同一种类型的.yml的配置文件加载顺序优先于.properties的配置文件
3.3 bootstrap和application的比较
bootstrap (.yml 或者 .properties),application (.yml 或者 .properties);
在 Spring Boot 中有两种上下文,一种是 bootstrap, 另外一种是 application, bootstrap 是应用程序的父上下文,也就是说 bootstrap 加载优先于 applicaton。
加载位置和加载顺序均为数字编号,先被加载的配置会被后续加载的同名配置所覆盖
4. SpringBoot内嵌Tomcat的流程
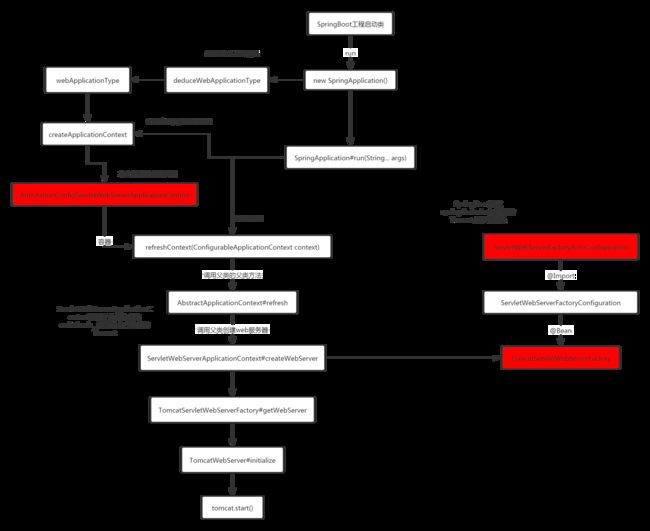
SpringBoot与Tomcat的启动(内嵌Tomcat)
通过代码详细分析上图的流程
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
//根据run方法得到以下
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
//再次跟进run方法得到以下
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
分为了两部分part1:(new SpringApplication(primarySources))
``part2:.run(args),首先看part1`
//part1部分
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this((ResourceLoader)null, primarySources);
}
//本方法内部推断了当前Web应用类型以及启动类
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
....
//推断当前web容器类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
....
// 推断当前工程主启动类
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
//可以看到SpringApplication构造方法通过 WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath 方法确定Web容器的类型webApplicationType(NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE;最终会得到这三种类型其中一种)
接下来看part2:.run(args)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
.....
try {
...
//创建ApplicationContext容器
context = this.createApplicationContext();
...
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新容器
this.refreshContext(context);
....
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
.....
}
注意看refreshContext(刷新容器的方法)
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
里面调用的refresh(),如果对Spring的启动流程有了解的话,应该知道Spring启动过程中,最重要的就是AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()过程,在这个方法中Spring执行了BeanFactory的初始化,Bean的实例化、属性填充、初始化操作等等重要的操作
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
....
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
....
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
....
} catch (BeansException ex) {
...
} finally {
...
}
}
}
}
//两个方法在spring中均是空实现。
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
}
如上spring的refresh方法,其他的模板方法已省略,保留了两个spring交给子类个性化定制的方法。
在step2中。构造SpringApplicaton时,已经推断出当前Web工程类型,当开始执行#run方法时,会根据不同类型的Web项目创建不同类型的ApplicationContext。然后接着会执行 this.refreshContext(context);刷新容器的方法,所以上面模板方法,会调用子类中个性化定制的方法。所以确定好子类,找到子类的实现方法就好了。
//part2中创建ApplicationContext容器
// context = this.createApplicationContext();
// 根据deduceWebApplicationType推断出来的webApplicationType
// 选择不同类型的ApplicationContext创建
public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext";
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
//根据前面得到的webApplicationType创建ApplicationContext类型、
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
// 本文将会根据此行代码创建容器对象
// 类型:AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
// 继承自:ServletWebServerApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// ... 省略异常处理
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
接着执行refreshContext方法,来到前面根据webApplicationType创建的容器类ServletWebServerApplicationContext。找到对应的实现。
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext
extends GenericWebApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext {
// 重点是这里,它重写了AbstractApplicationContext的onRefresh
// 并且在这类创建了一个web服务器
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 通过Spring.factories配置自动装配类
// ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
// 该类通过Import引入ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration#EmbeddedTomcat
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException ex) {
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
}
进入到TomcatServletWebServerFactory,可以看到如下启动内置Tomcat的过程
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory
extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory
implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware {
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
// 启动Tomcat
return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0);
}
}
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer {
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
initialize();
}
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
...
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start(); // 启动Tomcat
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
....
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
// 阻塞当前Tomcat线程,否则Tomcat就直接退出了
startDaemonAwaitThread();
} catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
}
至此,Tomcat继承Spring的AbstractApplicationContext类,覆盖它的模板方法onRefresh,SpringBoot在自身启动的过程中,启动了内置的Tomcat服务器