Spring及SpringBoot中AOP的使用
Spring中AOP示例
org.springframework spring-core 5.3.6 org.springframework spring-beans 5.3.6 org.springframework spring-context 5.3.6 org.springframework spring-expression 5.3.6 commons-logging commons-logging 1.2 junit junit 4.12 org.springframework spring-aop 5.3.6 org.springframework spring-aspects 5.3.6 org.aspectj aspectjrt 1.9.6
配置类
/**
* @author TB
* @date 2020/2/12 0:14
*/
@Configuration//标识是个配置类
@ComponentScan("com")//包扫描路径
//SpringBoot的AOP是默认开启的,不需要加注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy” 这里用的Spring所以要加
//让Spring认识加了@Aspect类的注解 不然Spring不认识切面@Aspect
//其实是启动AOP注解创建代理
//默认启用JDK动态代理,当目标对象没有实现接口时则采用CGlib代理
//该注解有个proxyTargetClass属性,默认是false 如果改成@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=true)则使用CGlib代理
//JDK代理创建速度快,运行时稍慢,CBlib代理创建时速度慢,运行速度快
//可以通过属性的true或false来指定JDK代理和CGlib代理 默认CBG代理 找不到实现类的话会自动用CGlib代理
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
//@EnableAsync//告诉spring框架启动时创建线程池 然后在需要异步请求时在池里拿线程直接用 然后需要用异步请求的方法上加@Async
public class SpringConfig {
}标注的AOP类
/**
* AOP(面向切面编程) 主要利用**动态代理**的模式 **降低程序的耦合度,扩展业务功能方法.**
* 1.AOP需要被Spring容器管理 @Component
* 2.标识该类是AOP切面 @Aspect
* 关于AOP名词介绍
* 1).连接点: 用户可以被扩展的方法 其实我们将自定义注解放到目标方法上做标识,那么该注解其实就是个连接点
* 2).切入点: 用户实际扩展的方法 确定了连接点,那么该方法也就是个切入点
* 3).通知: 扩展方法的具体实现 5个通知
* 4).切面: 将通知应用到切入点的过程
*
* 通知类型(必会)
* 1. before: 在目标方法执行之前执行
* 2. afterReturning: 在目标方法执行之后返回时执行
* 3. afterThrowing: 在目标方法执行之后,抛出异常时执行
* 4. after: 无论程序是否执行成功,都要最后执行的通知
* 5. around: 在目标方法执行前后 都要执行的通知(完美体现了动态代理模式)
* 功能最为强大 只有环绕通知可以控制目标方法的执行
*
* 关于通知方法总结:
* 1.环绕通知是处理业务的首选. 可以修改程序的执行轨迹
* 2.另外的四大通知一般用来做程序的监控.(监控系统) 只做记录
* @author TB
* @date 2020/2/12 0:24
*/
@Component
//虽然标识了该类为AOP切面 但是Spring容器默认不能识别切面注解,需要手动配置
//需要在配置类SpringConfig里加上注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Aspect
public class SpringAOP {
/**
* 切入点表达式
* 概念:当程序满足切入点表达式,才能进入切面,执行通知方法.
*
* 1.bean("bean的ID") 根据beanId进行拦截 只能匹配一个
* 2.within("包名.类名") 可以使用通配符*? 能匹配多个.
* 粒度: 上述的切入点表达式 粒度是类级别的. 粗粒度.
* 3.execution(返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表...))
* 粒度: 控制的是方法参数级别. 所以粒度较细. 最常用的.
* 4.@annotation(包名.注解名) 只拦截注解.
* 粒度: 注解是一种标记 根据规则标识某个方法/属性/类 细粒度
*/
/**
* 切入点表达式练习
* within:
* 1.within(com.jt.*.DeptServiceImpl) 一级包下的类
* 2.within(com.jt..*.DeptServiceImpl) ..代表多级包下的类
* 3.within(com.jt..*) 包下的所有的类
*
* execution(返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表))
* 1.execution(* com.jt..*.DeptServiceImpl.add*())
* 注释: 返回值类型任意的, com.jt下的所有包中的DeptServiceImpl的类
* 的add开头的方法 ,并且没有参数.
*
* 2.execution(* com.jt..*.*(..))
* 注释: 返回值类型任意,com.jt包下的所有包的所有类的所有方法 任意参数.
*
* 3.execution(int com.jt..*.*(int))
* 4.execution(Integer com.jt..*.*(Integer))
* 强调: 在Spring表达式中没有自动拆装箱功能! 注意参数类型
*
* @annotation(包名.注解名)
* @Before("@annotation(com.jt.anno.Cache)")
* 只拦截特定注解的内容.
*/
//1.定义before通知
//@Before("bean(deptServiceImpl)")//扫描的是一个类 因此该类里所有方法都被扩展到了
//@Before("within(com.jt.service.DeptServiceImpl)")//和上面效果一样
//@Before("execution(* com.jt.service.DeptServiceImpl.add*())")//*表示返回值类型任意 add*表示以add开头的方法名 最后()表示参数是空的
//@Before("@annotation(com.jt.anno.Cache)")//意思有该注解 就作为切入点 因此用注解标识最常用(自定义个注解)
/**
* spring为了AOP动态获取目标对象及方法中的数据,则通过Joinpoint
* JoinPoint是所有通知的公共参数,无论哪种通知里都可以使用
* 在Before里可以获取
* 对象做数据传递获取如:
* 1.获取目标对象的类型
* 2.获取目标方法的名称
* 3.获取目标方法的参数
* @param joinPoint
*/
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){//前置方法一般作用获取参数,方法名,等等
System.out.println("目标对象的Class类对象: "+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("获取目标方法的方法签名: "+joinPoint.getSignature());
System.out.println("获取目标对象的类名: "+ joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("获取目标对象方法名: "+ joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("获取目标方法参数: "+ Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
System.out.println("我是before通知");
}
//1.定义一个切入点
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.jt.anno.Cache)")
public void pointcut(){
}
//如果每个通知前都加个切入点表达式 那么也太冗余了 因此我们可以定义个切入点 其他通知都围绕切入点
//@BafterReturning("@annotation(com.jt.anno.Cache)")
/**
* JoinPoint参数是所有通知方法公有的
*AfterReturning是目标方法返回执行之后返回时执行
* 可以记录方法的返回值
* AfterReturning注解里 value和pointcut是相同的效果:也就是说
* @AfterReturning(value="pointcut()",returning="result")和@AfterReturning(pointcut="pointcut()",returning="result")
* 效果一样
* returning:将方法的返回值,通过形参result(这个随便取名)来进行传递(Spring会将返回值赋值给你定义的这个变量)
*/
@AfterReturning(value="pointcut()",returning="result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){//这里注意 如果有需要用到JointPoint参数 那么必须放在第一个位置 不用可以去掉
System.out.println("目标返回值结果是: "+result);
System.out.println("我是AfterReturning的通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pointcut()",throwing="e")//当目标方法执行时,抛出异常时,可以用AfterThrowing记录
public void afterThrowing(Exception e){
System.out.println("获取目标异常信息: "+e.getMessage());
System.out.println("获取目标异常类型: "+e.getClass());
System.out.println("我是AfterThrowing的通知,出现异常了");
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("我是After的通知");
}
/**
* 关于环绕通知的说明
* 作用: 可以控制目标方法是否执行.
* 参数: ProceedingJoinPoint 通过proceed方法控制目标方法执行.
* 注意事项:
* ProceedingJoinPoint 只能适用环绕通知
* @return
*/
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){//注意多参情况ProceedingJoinPoint要放第一位
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
//1.执行下一个通知 2.执行目标方法 3.接收返回值
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
result = joinPoint.proceed();
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start));
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
return result;
}
}切入点注解类
//控制注解的生命周期,什么时候起作用
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//注解的作用对象: 类上 方法上 变量上
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.FIELD})
public @interface Cache {
}测试
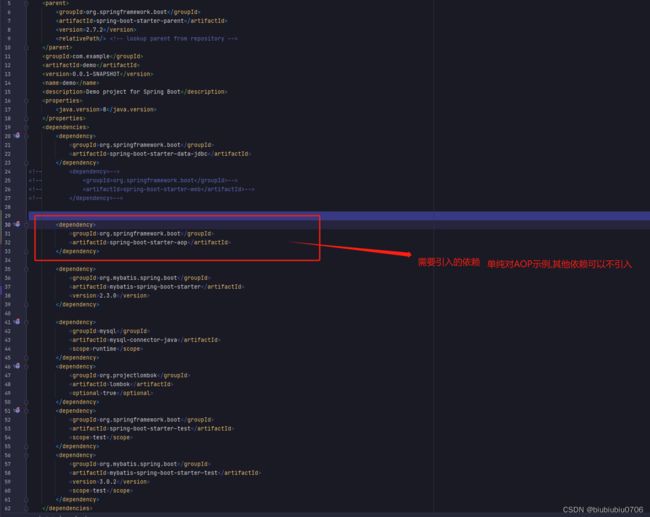
SpringBoot中使用AOP
/**
* @author hrui
* @date 2023/10/30 21:58
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class SpringAOP {
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){//前置方法一般作用获取参数,方法名,等等
// System.out.println("目标对象的Class类对象: "+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
// System.out.println("获取目标方法的方法签名: "+joinPoint.getSignature());
// System.out.println("获取目标对象的类名: "+ joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
// System.out.println("获取目标对象方法名: "+ joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
// System.out.println("获取目标方法参数: "+ Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
System.out.println("我是before通知");
}
//1.定义一个切入点
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.demo.aop.AnyAnno)")
public void pointcut(){
}
@AfterReturning(value="pointcut()",returning="result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){//这里注意 如果有需要用到JointPoint参数 那么必须放在第一个位置 不用可以去掉
// System.out.println("目标返回值结果是: "+result);
System.out.println("我是AfterReturning的通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pointcut()",throwing="e")//当目标方法执行时,抛出异常时,可以用AfterThrowing记录
public void afterThrowing(Exception e){
// System.out.println("获取目标异常信息: "+e.getMessage());
// System.out.println("获取目标异常类型: "+e.getClass());
System.out.println("我是AfterThrowing的通知,出现异常了");
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("我是After的通知");
}
/**
* 关于环绕通知的说明
* 作用: 可以控制目标方法是否执行.
* 参数: ProceedingJoinPoint 通过proceed方法控制目标方法执行.
* 注意事项:
* ProceedingJoinPoint 只能适用环绕通知
* @return
*/
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){//注意多参情况ProceedingJoinPoint要放第一位
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
//1.执行下一个通知 2.执行目标方法 3.接收返回值
result = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知里方法执行完了");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
return result;
}
}切入点注解类
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD})
public @interface AnyAnno {
}自己随便测试下