linux下使用backtrace记录程序崩溃时的堆栈信息,并进行分析
写在前面:
linux下跟踪并打印某程序的堆栈信息指令为:
strace -tT -f [size] [appName]如在terminal中执行:strace -tT -f -s 1024 ./app
正文:
在项目软件代码开发中,当软件代码量多了后,由于各种疏忽和编码审查不严格,导致代码中存在缺陷,程序运行后总是有各种异常出现,严重的导致程序崩溃,这个时候就期望能够在程序崩溃时,记录异常点相关的堆栈信息,用于对异常的分析,常见的方法有在系统中配置程序崩溃生成coredump文件,后续用gdb分析,这种方法需要了解gdb常用指令,并且涉及到修改了系统的一些配置,同时release版本下,有时候用gdb分析不一定有效,因此本文通过软件代码实现,简单记录程序崩溃的信息,主要使用到的是backtrace、abi::__cxa_demangle、nm、addr2line等函数和指令。
0. 程序中需要用到的头文件信息如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#if defined (__linux__)
#include 1. 注册异常处理函数:
// 信号处理的map集合
static const std::map gsc_mp4Signals =
{
{SIGSEGV, "SIGSEGV"},
{SIGABRT, "SIGABRT"},
{SIGINT, "SIGINT"},
{SIGFPE, "SIGFPE"},
{SIGILL, "SIGILL"},
{SIGSYS, "SIGSYS"},
{SIGBUS, "SIGBUS"}
// 可以添加其他信号
};
/*************************************************************
* 功能:注册异常处理,linux系统
* ***********************************************************/
static void registerExceptionHandler()
{
// 需要配合nm,addr2line等指令使用
struct sigaction action;
sigemptyset(&action.sa_mask);
action.sa_sigaction = &pfnExceptionHandler_linux;
action.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
for (const auto& signals: gsc_mp4Signals)
{
if (0 > sigaction(signals.first, &action, NULL))
{
printf("Error: sigaction failed!\n");
}
}
return;
} 1.5. 实现异常处理函数之前,还需要实现几个辅助接口,获取进程名称,运行路径,格式化的时间,实现如下:
涉及到的宏定义如下:
#define FORMAT_TIME_MAX_LEN 64 // 格式化时间最长长度
#define APP_NAME_MAX_LEN 128 // APP名称最大长度
#define APP_MAX_LEN 1024 // 定义APP处理最长长度
#define RATIO_1000 1000 // 1000的进率
#define FOLDER_MAX_LEN 512 // 文件夹长度最大值/*************************************************************
* 功能:获取应用运行目录,不包含应用名称
* 输入参数:
* pPath:存放应用运行目录的内存空间
* uiLen:存放应用运行目录的内存空间长度,字节
* 输出参数:
* pPath:存放应用运行目录的内存空间
* ***********************************************************/
void getAppRunPath(char* pPath, unsigned int uiLen)
{
if (!pPath)
{
return;
}
memset(pPath, 0, uiLen);
std::string strPath = "";
char szAbsPath[APP_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
ssize_t iPathLen = readlink("/proc/self/exe", szAbsPath, APP_MAX_LEN); // 获取可执行程序的绝对路径
if (0 < iPathLen && iPathLen < APP_MAX_LEN)
{
std::string strFullPath(szAbsPath);
size_t iPos = strFullPath.find_last_of('/');
if (iPos != std::string::npos)
{
strPath = strFullPath.substr(0, iPos); // return the directory without the file name
}
}
memcpy(pPath, strPath.data(), (uiLen < strPath.length() ? uiLen : strPath.length()));
return;
}/*************************************************************
* 功能:创建文件目录
* 输入参数:
* pFolderPath:文件目录
* 返回值:
* bool:创建结果,true -- 成功,false -- 失败
* ***********************************************************/
bool createDirectory(const char* pFolderPath)
{
if (!pFolderPath)
{
return false;
}
bool bRet = true;
// 创建目录,函数方式
if (0 != access(pFolderPath, 0))
{
// 返回0表示创建成功,-1表示失败
if (0 > mkdir(pFolderPath, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IXUSR | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO))
{
bRet = false;
}
}
return bRet;
}或者使用:
// 创建文件夹
bool createDirectory(const char *pFolderPath)
{
if (!pFolderPath)
{
return false;
}
bool bRet = true;
#if defined(__linux__)
struct stat info;
if (0 != stat(pFolderPath, &info))
{
// 文件/目录不存在,info.st_mode & S_IFDIR为目录
std::string command = std::string("mkdir -p ") + std::string(pFolderPath); // -p表示可以创建多级目录
system(command.data());
}
#endif
return bRet;
}/*************************************************************
* 功能:获取应用名称
* 输入参数:
* pName:存放应用名称的内存空间
* uiLen:存放应用名称的内存空间长度,字节
* 输出参数:
* pName:存放应用名称的内存空间
* ***********************************************************/
void getAppName(char* pName, unsigned int uiLen)
{
if (!pName)
{
return;
}
memset(pName, 0, uiLen);
std::string strAppName = "unknown";
char szAbsPath[APP_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
ssize_t iPathLen = readlink("/proc/self/exe", szAbsPath, APP_MAX_LEN); // 获取可执行程序的绝对路径
if (0 < iPathLen && iPathLen < APP_MAX_LEN)
{
std::string strFullPath(szAbsPath);
size_t iPos = strFullPath.find_last_of('/');
if (iPos != std::string::npos)
{
strAppName = strFullPath.substr(iPos + 1);
}
}
memcpy(pName, strAppName.data(), (uiLen < strAppName.length() ? uiLen : strAppName.length()));
return;
}/*************************************************************
* 功能:获取格式化时间,格式为yyyyMMdd_HHmmss.zzz
* 返回值:
* std::string:格式化时间
* ***********************************************************/
static std::string getFormatTime()
{
time_t stTimeNow;
time(&stTimeNow);
char szTmp[FORMAT_TIME_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
strftime(szTmp, sizeof(szTmp), "%Y%m%d_%H%M%S", localtime(&stTimeNow));
int iMillsec = 0;
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
iMillsec = tv.tv_usec / RATIO_1000;
char szTime[FORMAT_TIME_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
sprintf(szTime, "%s_%03d", szTmp, iMillsec);
std::string strTime(szTime);
return strTime;
}2. 实现异常处理接口:
/*************************************************************
* 功能:注册异常处理,linux系统
* 输入参数:
* signum:信号值
* info:信息
* ctx:上下文
* ***********************************************************/
static void pfnExceptionHandler_linux(int signum, siginfo_t* info, void* ctx)
{
signal(signum, SIG_DFL); // 还原默认的信号处理
// 创建dump日志文件夹
char szAppFolder[FOLDER_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
getAppRunPath(szAppFolder, sizeof(szAppFolder));
std::string strFolder = std::string(szAppFolder) + "/dump/";
if (!createDirectory(strFolder.data()))
{
return;
}
// 写入异常自定义头部信息
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "Stack Trace: " << std::endl;
oss << "Signal (" << signum << "), " << strsignal(signum) << std::endl;
// 读取堆栈信息
const size_t sFrameSize = 32; // 堆栈大小
void* pStackBuffer[sFrameSize] = { 0 };
int iSize = backtrace(pStackBuffer, sFrameSize);
//backtrace_symbols_fd(pStackBuffer, iSize, STDOUT_FILENO);
char** symbols = backtrace_symbols(pStackBuffer, iSize);
if (!symbols)
{
return;
}
// 解析函数符号信息
for (int i = 0; i < iSize; ++i)
{
char* mangleName = 0;
char* offsetBegin = 0;
char* offsetEnd = 0;
for (char* p = symbols[i]; *p; ++p)
{
if ('(' == *p)
{
mangleName = p;
}
else if ('+' == *p)
{
offsetBegin = p;
}
else if (')' == *p)
{
offsetEnd = p;
break;
}
}
if (mangleName && offsetBegin && offsetEnd && (mangleName < offsetBegin))
{
*mangleName++ = '\0';
*offsetBegin++ = '\0';
*offsetEnd++ = '\0';
int status = -4;
// 获取混淆解析后可读的函数符号信息
char* retRealName = abi::__cxa_demangle(mangleName, nullptr, nullptr, &status); // 解析符号,得到真正的函数名
if (0 == status && retRealName)
{
oss << "[Bt" << i << "] status(" << status << "), " << symbols[i] << ": " << retRealName << " + ";
}
else
{
oss << "[Bt" << i << "] status(" << status << "), " << symbols[i] << ": " << mangleName << " + ";
}
oss << offsetBegin << offsetEnd << std::endl;
if (retRealName)
{
free(retRealName);
retRealName = nullptr;
}
}
else
{
oss << "[Bt" << i << "] status(-4), " << symbols[i] << std::endl;
}
}
free(symbols);
oss << std::endl;
// 异常写入文件
char szAppName[APP_NAME_MAX_LEN] = { 0 };
getAppName(szAppName, sizeof(szAppName));
std::string strAppName(szAppName);
std::string strFilePath = strFolder + "core-" + strAppName + "-" + getFormatTime();
std::ofstream fout(strFilePath.data());
do
{
if (!(fout.is_open()))
{
break;
}
fout << oss.str().data();
fout.close();
} while (0);
exit(1);
return;
}3. 在main函数中靠前的位置注册函数即可:
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
registerExceptionHandler();
// TODO 添加业务代码
}4. 编译业务程序,注:编译过程中,编译选项需要添加:-g和-rdynamic,否则异常日志是不可识别的。
例如:直接使用g++编译:
g++ -g -rdynamic local.h local.cpp exceptionhelper.h exceptionhelper.cpp main.cpp -o App使用cmakelists中时,需添加:
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "-std=gnu99 -g -rdynamic")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -g -rdynamic")使用qtcreator编译时,在pro中配置:
QMAKE_CFLAGS += -std=gnu++11 -g -rdynamic
QMAKE_CXXFLAGS += -std=c++11 -g -rdynamic
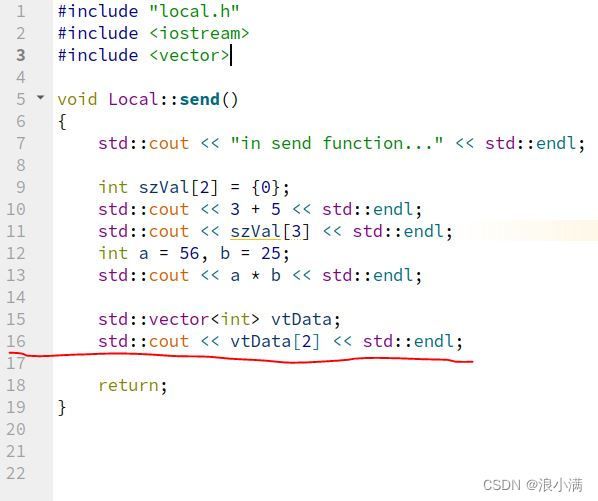
QMAKE_LFLAGS += -g -rdynamic5. 结果测试,使用了异常程序和main函数同一个工程,以及使用导出动态库的方式分别进行测试,编译的应用名称为App,导出库名为libApple.so。分别设置的异常代码如下图所示:
生成的三个异常日志信息如下:
日志中可以看到记录了异常的函数入口,以及偏移地址。
6. 借助nm、addr2line分析,查看函数地址的指令(在应用和库同级目录下,启动终端(Terminal))如下:
nm -C [appName] | grep [functionName]
nm -C [libName] | grep [functionName]
查看行数的指令如下:
addr2line -e [appName] [address]
addr2line -e [libName] [address]
查询到Local::send()地址为0x71a0,加上偏移地址0x159,即0x71a0 + 0x159 = 0x72f9。
即看到和第5步中展示的程序代码行数一致的,其他两个如下:
表明了该方式的可行性。