Codeforces Round #726 (Div. 2)题解A-E1
A. Arithmetic Array
分析:
当sum大于n时,那么添加(sum-n)个0,当sum小于n时,只需要添加一个数即可。
#include B. Bad Boy
分析:
走离起始点较远的两角即可。
#include C. Challenging Cliffs
分析:
排序后,不难发现此时的排列是权重最大的。
但是因为还需要满足约束,开头和末尾的差的绝对值应该最小。
那么我们找到那对数,从中间断开,即可。
#include D. Deleting Divisors
一道博弈论。
分析:
首先考虑1和全体素数是奇异局势, 某一方得到奇异局势时便必败.
然后考虑操作的性质:
不妨设 x = a ∗ b ( a , b > 1 ) x = a*b\space\space\space (a ,b>1) x=a∗b (a,b>1)
考虑 x − a = a ∗ ( b − 1 ) x - a = a*(b-1) x−a=a∗(b−1)
也就是说一个数x减去自己的约数a, 结果y还是a的倍数; 同时设b为x的约数, 且 b = x / a b=x/a b=x/a, 那么b-1将是结果y的约数.
由此我们可得, 一个奇合数经过一次操作后, 必然会得到一个偶数; 一个(含奇素因子的)偶合数经过一次操作, 可以得到一个奇合数。
这是因为一个偶合数为了操作后得到一个奇数结果, 那么势必把减去所有偶素因子的乘积。 但是因为没有奇素因子所以所有偶素因子的乘积为该数本身,不符合题意约束。
于是我们有了一个初步的模型:
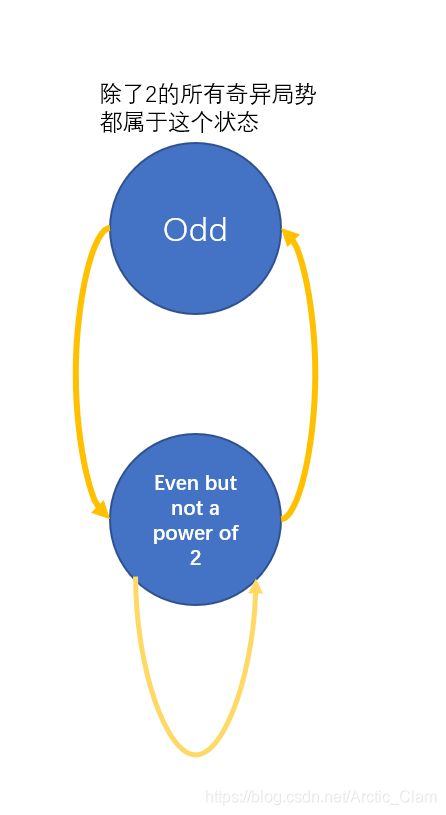
那么再来考虑2的幂次
不妨设 t = 2 k ( k = 1 , 2 , 3 , . . . ) t = 2^k \space (k=1,2,3,...) t=2k (k=1,2,3,...)
- 当k=1时:
先手必败 - 当k=2时:
先手必胜 - 当k>2时,有两种操作:
1). t = t − 2 i ( i = 1 , 2 , . . . , k − 2 ) t = t - 2^{i} \space (i=1,2,...,k-2) t=t−2i (i=1,2,...,k−2). 此时t为变为一个不是2的幂次的偶数, 因此这种操作对方必胜.
2). t = t − 2 k − 1 t=t-2^{k-1} t=t−2k−1. 此时t变为2的幂, 且幂次-1.
不难看出当k为奇数的时候, 先手必败, k为偶数的时候后手必败.
于是给出修正后的模型

代码:
#include E1. Erase and Extend (Easy Version)
分析:
暴力枚举所有前缀形成的串, 取字典序最小的即可.
时间复杂度 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
#include