elasticsearch请求体查询
search API支持带请求体的GET请求,或者POST请求。
这里举例一kibana中的dev tools界面为例
本文参考了
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903890396135438#heading-18
一、通用请求
1.集群健康检测
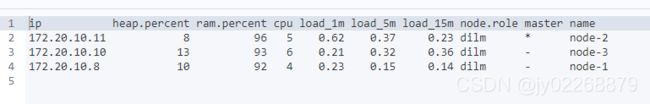
在linux上 curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/health?v'
在kibana dev tools上
GET /_cat/health?v绿色表示一切正常, 黄色表示所有的数据可用但是部分副本还没有分配,红色表示部分数据因为某些原因不可用
2.获取集群的节点列表
GET /_cat/nodes?v二、索引相关
索引的增删改查格式
curl -X: / / /
:REST风格的语法谓词
:节点ip
:节点端口号,默认9200
:索引名
:索引类型
:操作对象的ID号
3.列出所有索引
GET /_cat/indices?v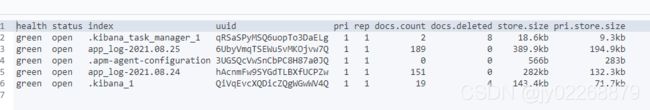 4.创建索引
4.创建索引
linux上
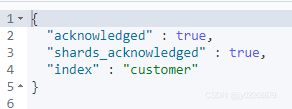
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/customer?pretty'或者kibana dev tools
PUT /customer?pretty表示创建一个名字叫customer的索引。pretty参数表示返回结果格式美观
执行后返回
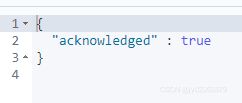
5.删除索引
DELETE /customer?pretty返回结果
6.对customer索引新增一条数据
现在我么插入一些数据到集群索引。我们必须指定类型、和ID。
如下语句:type类型是"external", id是1
主体为JSON格式的语句: { "name": "John Doe" }
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1?pretty' -d '
{
"name": "John Doe"
}'或者
PUT /customer/external/1?pretty
{
"name": "John Doe"
}那么此次type还可以是其他的比如:_doc
返回
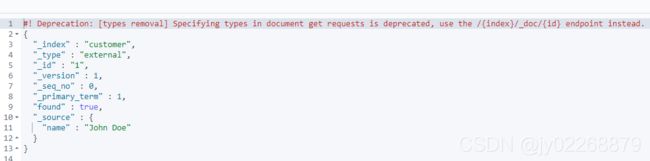
7.查询刚才新增的数据
GET /customer/external/1?pretty返回
 8.修改数据
8.修改数据
把id为1的数据name字段的值改为sid
PUT /customer/external/1?pretty
{"name": "sid"}返回结果
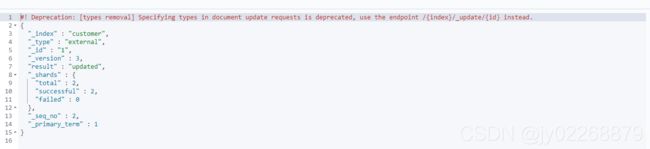
 将id为1数据的name字段更新为Jane Doe同时增加字段age为20
将id为1数据的name字段更新为Jane Doe同时增加字段age为20
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1/_update?pretty' -d '
{
"doc": { "name": "Jane Doe", "age": 20 }
}'或者
POST /customer/external/1/_update?pretty
{
"doc": { "name": "Jane Doe", "age": 20 }
}返回
 也可以通过一些简单的scripts来执行更新。一下语句通过使用script将年龄增加5:
也可以通过一些简单的scripts来执行更新。一下语句通过使用script将年龄增加5:
POST /customer/external/1/_update?pretty
{
"script" : "ctx._source.age += 5"
}9.删除数据
删除id为2的
curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/customer/external/2?pretty'或者
DELETE /customer/external/2?pretty10.bulk批处理
bulk批量操作可以在单次API调用中实现多个文档的create、index、update或delete。
这可以大大提高索引速度
bulk请求体如下
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
...
action必须是以下几种:
| 行为 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| create | 当文档不存在时创建 |
| index | 创建新文档或替换已有文档 |
| update | 局部更新文档 |
| delete | 删除一个文档 |
在索引、创建、更新或删除时必须指定文档的_index、_type、_id这些元数据(metadata)
bulk请求不是原子操作,它们不能实现事务。每个请求操作时分开的,所以每个请求的成功与否不干扰其它操作
示例
在一个批量操作中执行某索引下添加两条数据
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/doc/_bulk?pretty' -d '
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name": "John Doe" }
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name": "Jane Doe" }或者
POST /customer/doc/_bulk?pretty
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name": "John Doe" }
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name": "Jane Doe" }批处理执行更新id为1的数据然后执行删除id为2的数据
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/doc/_bulk?pretty' -d '
{"update":{"_id":"1"}}
{"doc": { "name": "John Doe becomes Jane Doe" } }
{"delete":{"_id":"2"}}或者
POST /customer/doc/_bulk?pretty
{"update":{"_id":"1"}}
{"doc": { "name": "John Doe becomes Jane Doe" } }
{"delete":{"_id":"2"}}示例
PUT _bulk
{ "create" : { "_index" : "ad", "_type" : "phone", "_id" : "6" }}
{ "doc" : {"name" : "bulk"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "ad", "_type" : "phone", "_id" : "6" }}
{ "doc" : {"name" : "bulk"}}
{ "delete":{ "_index" : "ad", "_type" : "phone", "_id" : "1"}}
{ "update":{ "_index" : "ad", "_type" : "phone", "_id" : "3"}}
{ "doc" : {"name" : "huawei p20"}}
11.导入数据
下载导入的json
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/{index}/account/_bulk?pretty' --data-binary "@XXX.json"12.准备数据供后续查询
为了方便后面演示查询,这里需要往es里面放一些数据
我们将使用书文档信息的集合(有以下字段:title(标题), authors(作者), summary(摘要), publish_date(发布日期)和 num_reviews(浏览数))。
创建索引
PUT /bookdb_index
{ "settings": { "number_of_shards": 1 }} 创建一个名字为bookdb_index的索引
批量上传文档
POST /bookdb_index/book/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide", "authors": ["clinton gormley", "zachary tong"], "summary" : "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine", "publish_date" : "2015-02-07", "num_reviews": 20, "publisher": "oreilly" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It", "authors": ["grant ingersoll", "thomas morton", "drew farris"], "summary" : "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization", "publish_date" : "2013-01-24", "num_reviews": 12, "publisher": "manning" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "title": "Elasticsearch in Action", "authors": ["radu gheorge", "matthew lee hinman", "roy russo"], "summary" : "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms", "publish_date" : "2015-12-03", "num_reviews": 18, "publisher": "manning" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "title": "Solr in Action", "authors": ["trey grainger", "timothy potter"], "summary" : "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr", "publish_date" : "2014-04-05", "num_reviews": 23, "publisher": "manning" }往bookdb_index索引book类型(其实这里的类型就有点像javabean的概念,我是这么理解的)中加入4条数据
三、url参数查询
格式
GET /users/_search?q=username:wupxURI Search 使用的是 GET 方式,其中 q 指定查询语句,语法为 Query String Syntax,是 KV 键值对的形式;上面的请求表示对 username 字段进行查询,查询包含 wupx 的所有文档。
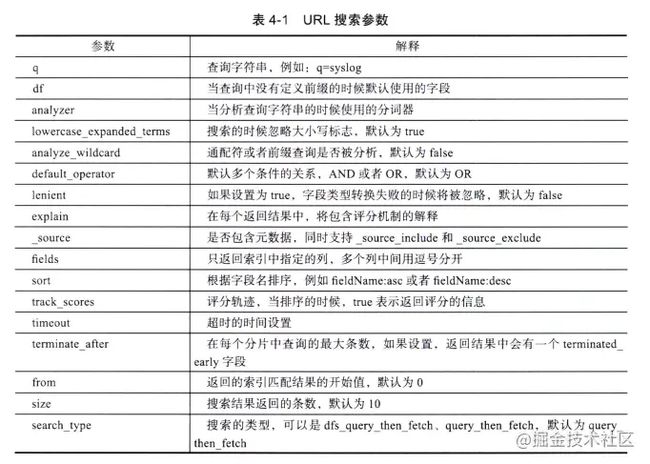
URI Search 有很多参数可以指定,除了 q 还有如下参数:
df:默认字段,不指定时会对所有字段进行查询
sort:根据字段名排序
from:返回的索引匹配结果的开始值,默认为 0
size:搜索结果返回的条数,默认为 10
timeout:超时的时间设置
fields:只返回索引中指定的列,多个列中间用逗号分开
analyzer:当分析查询字符串的时候使用的分词器
analyze_wildcard:通配符或者前缀查询是否被分析,默认为 false
explain:在每个返回结果中,将包含评分机制的解释
_source:是否包含元数据,同时支持 _source_includes 和 _source_excludes
lenient:若设置为 true,字段类型转换失败的时候将被忽略,默认为 false
default_operator:默认多个条件的关系,AND 或者 OR,默认为 OR
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful NOT Mind)search_type:搜索的类型,可以为 dfs_query_then_fetch 或 query_then_fetch,默认为 query_then_fetch
URI Search 还包括一些范围查询和数学运算符号,比如指定电影的年份大于 1994
GET /movies/_search?q=year:>=1994。URI Search 还支持通配符查询(查询效率低,占用内存大,不建议使用,特别是放在最前面),还支持正则表达式,以及模糊匹配和近似查询。
不指定字段,泛查询
GET /movies/_search?q=2012这里会对movies索引下所有type所有字段进行查询
查询某索引下某type下所有数据
GET /bookdb_index/book/_search这是查询bookdb_index索引book类型下所有数据
返回的是:
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in search requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 352, //查询耗时,毫秒
"timed_out" : false, //是否超时,timeout 不是停止执行查询,它仅仅是告知正在协调的节点返回到目前为止收集的结果并且关闭连接
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1, //请求的分片数量,索引拆成了5个分片,所以对于搜索请求,会打到所有的primary shard
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4, //符合条件的总条数,这里查的是所有
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0, //匹配分数
"hits" : [ //数据
{
"_index" : "bookdb_index",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors" : [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
],
"summary" : "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publish_date" : "2015-02-07",
"num_reviews" : 20,
"publisher" : "oreilly"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bookdb_index",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"authors" : [
"grant ingersoll",
"thomas morton",
"drew farris"
],
"summary" : "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization",
"publish_date" : "2013-01-24",
"num_reviews" : 12,
"publisher" : "manning"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bookdb_index",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Elasticsearch in Action",
"authors" : [
"radu gheorge",
"matthew lee hinman",
"roy russo"
],
"summary" : "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"publish_date" : "2015-12-03",
"num_reviews" : 18,
"publisher" : "manning"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bookdb_index",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Solr in Action",
"authors" : [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
],
"summary" : "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"publish_date" : "2014-04-05",
"num_reviews" : 23,
"publisher" : "manning"
}
}
]
}
}
多索引,多type搜索
在URL中指定特殊的索引和类型进行多索引,多type搜索
/_search:在所有的索引中搜索所有的类型
/school/_search:在 school 索引中搜索所有的类型
/school,ad/_search:在 school 和ad索引中搜索所有的类型
/s*,a*/_search:在所有以g和a开头的索引中所有所有的类型
/school/student/_search:在school索引中搜索student类型
/school,ad/student,phone/_search:在school和ad索引上搜索student和phone类型
/_all/student,phone/_search:在所有的索引中搜索student和phone类型按条件查询
GET /school/student/_search?q=name:sid查询school索引中student类型中,name字段是sid的记录
更多查询参数
这种方式就是类似于get请求,将请求参数拼接到链接上,例GET /school/student/_search?参数,多个参数用&分开
四、DSL查询
elasticsearch提供了基于JSON的完整查询DSL来定义查询,DSL拥有一套查询组件,这些组件可以以无限组合的方式进行搭配,构建各种复杂的查询
1.叶子语句
叶子语句:就像match语句,被用于将查询的字符串与一个字段或多个字段进行对比(单个条件) 比如:
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "phone"
}
}
}2.复合查询
用户合并其他查询语句,比如一个bool语句,允许你在需要的时候组合其他语句,包括must,must_not,should和filter语句(多条件组合查询) 比如:
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {
"name": "phone"
}}
]
, "must_not": [
{"match": {
"color": "red"
}}
]
, "should": [
{"match": {
"price": 5000
}}
]
, "filter": {
"term": {
"label": "phone"
}
}
}
}
}
must:表示文档一定要包含查询的内容
must_not:表示文档一定不要包含查询的内容
should:表示如果文档匹配上可以增加文档相关性得分
3.两种结构化语句
-
结构化查询
query DSL用于检查内容与条件是否匹配,内容查询中使用的bool和match字句,用于计算每个文档的匹配得分,元字段_score表示匹配度,查询的结构中以query参数开始来执行内容查询
-
结构化过滤
Filter DSL只是简单的决定文档是否匹配,内容过滤中使用的term和range字句,会过滤调不匹配的文档,并且不影响计算文档匹配得分
使用过滤查询会被es自动缓存用来提高效率
原则上来说,使用查询语句做全文本搜索或其他需要进行相关性评分的时候,剩下的全部用过滤语句
五、DSL查询的关键字
1.基础语法
GET /索引库名/_search
{
"query": {
"查询类型": {
"查询条件": "查询条件值"
}
}
}查询类型:match_all,match,term,range,fuzzy,bool 等等
查询条件:查询条件会根据类型的不同,写法也有差异
2.match_all
查询简单的匹配所有文档
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}3.size、from、sort (分页、排序、Limit)
查询所有数据但只返回1个
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 1
}返回从11到20的数据。(索引下标从0开始)
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 10,
"size": 10
}按照balance字段降序排序,并且返回前10条(如果不指定size,默认最多返回10条)
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": { "balance": { "order": "desc" } }
}注意:不要使用from,size进行深度分页,会有性能问题
这种分页方式如果进行深度分页,比如到100页,每页十条数据,它会从每个分片都查询出100*10条数据,假设有五个分片,就是5000条数据,然后在内存中进行排序,然后返回拍过序之后的集合中的第1000-1010条数据
4.只返回指定字段
这就是_source中只返回account_number和balance字段
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ["account_number", "balance"]
}显示要的字段、去除不需要的字段、可以使用通配符*
get lib3/user/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all": {}
},
"_source":{
"includes": "addr*",
"excludes": ["name","bir*"]
}
}5.match
支持全文搜索和精确查询,取决于字段是否支持全文检索
普通使用
查询某index中所有type中title字段包含单词white
GET /{index}/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "white"
}
}
}全文检索
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"ad": "a red"
}
}
}全文检索会将查询的字符串先进行分词,a red会分成为a和red,然后在倒排索引中进行匹配,所以这条语句会将包含 a、red、a red的文档都查出来
精确查询
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"price": "6000"
}
}
}
对于精确值的查询,可以使用 filter 语句来取代 query,因为 filter 将会被缓存
operator操作
match 查询还可以接受 operator 操作符作为输入参数,默认情况下该操作符是 or 。
我们可以将它修改成 and 让所有指定词项都必须匹配
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"ad": {
"query": "a red",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}这里只会查询出包含a red的文档,只包含a或者只包含red的都不会被查出来
精确度匹配
match 查询支持 minimum_should_match 最小匹配参数,可以指定必须匹配的词项数用来表示一个文档是否相关。我们可以将其设置为某个具体数字(指需要匹配倒排索引的词的数量),更常用的做法是将其设置为一个百分数,因为我们无法控制用户搜索时输入的单词数量
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"ad": {
"query": "a red",
"minimum_should_match": "2"
}
}
}
}
只会返回匹配上a和red两个词的文档返回,如果minimum_should_match是1,则只要匹配上其中一个词,文档就会返回
6.multi_match 多字段匹配查询
查询color和ad字段包含单词red的文档
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "red",
"fields": ["color","ad"]
}
}
}7.range 范围查询
范围查询,查询价格大于4000小于6000的文档
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gt": 4000,
"lt": 6000
}
}
}
}范围查询操作符:gt (大于),gte(大于等于),lt(小于),lte(小于等于)
参数:from,to,include_lower,include_upper,boost
include_lower:是否包含范围的左边界,默认是true
include_upper:是否包含范围的右边界,默认是true
GET /lib3/user/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"birthday": {
"from": "1990-10-10",
"to": "2000-05-01",
"include_lower": true,
"include_upper": false
}
}
}
}
8.term词条查询
(不分词,查询结果跟分词器有关,如果保存的内容分词了则不会被查询到)
精确值查询
查询price字段等于6000的文档
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"price": {
"value": "6000"
}
}
}
}查询name字段等于phone 8的文档
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "phone 8"
}
}
}
}
返回值如下,没有查询到名称为phone 8的文档
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 0,
"max_score": null,
"hits": []
}
}
为什么没有查到phone 8的这个文档那,这里需要介绍一下term的查询原理
term查询会去倒排索引中寻找确切的term,它并不会走分词器,只会去配倒排索引 ,而name字段的type类型是text,会进行分词,将phone 8 分为phone和8,我们使用term查询phone 8时倒排索引中没有phone 8,所以没有查询到匹配的文档
term查询与match查询的区别
term查询时,不会分词,直接匹配倒排索引match查询时会进行分词,查询phone 8时,会先分词成phone和8,然后去匹配倒排索引,所以结果会将phone 8和xiaomi 8两个文档都查出来
还有一点需要注意,因为term查询不会走分词器,但是会去匹配倒排索引,所以查询的结构就跟分词器如何分词有关系,比如新增一个/ad/phone类型下的文档,name字段赋值为Oppo,这时使用term查询Oppo不会查询出文档,这时因为es默认是用的standard分词器,它在分词后会将单词转成小写输出,所以使用oppo查不出文档,使用小写oppo可以查出来
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "Oppo" //改成oppo可以查出新添加的文档
}
}
}
}
复制代码这里说的并不是想让你了解standard分词器,而是要get到所有像term这类的查询结果跟选择的分词器有关系,了解选择的分词器分词方式有助于我们编写查询语句
9.terms 多词条查询
terms查询与term查询一样,但它允许你指定多值进行匹配,如果这个字段包含了指定值中的任何一个值,那么这个文档满足条件
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"ad": ["red","blue"]
}
}
}
10. exists 查询和 missing 查询
用于查找那些指定字段中有值 (exists) 或无值 (missing) 的文档
指定name字段有值:
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"exists": {
"field": "name"
}
}
}
}
}指定name字段无值:
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"missing": {
"field": "name"
}
}
}
}
}11. match_phrase查询
短语查询,精确匹配,查询a red会匹配ad字段包含a red短语的,而不会进行分词查询,也不会查询出包含a 其他词 red这样的文档
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"ad": "a red"
}
}
}
12. scroll查询
类似于分页查询,不支持跳页查询,只能一页一页往下查询。
scroll查询不是针对实时用户请求,而是针对处理大量数据。
例如为了将一个索引的内容重新索引到具有不同配置的新索引中
POST /ad/phone/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 1,
"from": 0
}
返回值包含一个 "_scroll_id"
下次查询的时候使用_scroll_id就可以查询下一页的文档
POST /_search/scroll
{
"scroll" : "1m",
"scroll_id" : "XXXXXXXX"
}
13. multi get查询
允许基于索引,类型(可选)和id(以及可能的路由)获取多个文档,如果某个文档获取失败则将错误信息包含在响应中
```json
GET /ad/phone/_mget
{
"ids": ["1","8"]
}
```14. fuzzy模糊查询
模糊查询,fuzzy 查询会计算与关键词的拼写相似程度
fuzzy 查询是 term 查询的模糊等价。
a、是 包含(contains) 操作,而非 等值(equals) (判断)。
b、不知道分词器的存在,所以不会去分词,
c、所谓的包含是文档分词结果某个分词是否包含,不是整个文档是否包含
d、因为是在分词结果中匹配,所以大写要转换为小写,大写字母是匹配不到
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"color":{
"value": "res",
"fuzziness": 2,
"prefix_length": 1
}
}
}
}参数设置:
fuzziness:最大编辑距离,默认为AUTO
prefix_length:不会“模糊化”的初始字符数。这有助于减少必须检查的术语数量,默认为0
max_expansions:fuzzy查询将扩展到 的最大术语数。默认为50,设置小,有助于优化查询
transpositions:是否支持模糊转置(ab→ ba),默认是false
value:查询的关键字
boost:查询的权值,默认值是1.0
min_similarity:设置匹配的最小相似度,默认值为0.5,对于字符串,取值为0-1(包括0和1);对于数值,取值可能大于1;对于日期型取值为1d,1m等,1d就代表1天
prefix_length:指明区分词项的共同前缀长度,默认是0
max_expansions:查询中的词项可以扩展的数目,默认可以无限大
15. wildcard查询
支持通配符的模糊查询。
*代表0个或多个字符
?代表任意一个字符
为了防止极其缓慢通配符查询,*或?通配符项不应该放在通配符的开始
GET /ad/phone/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"color": "r?d"
}
}
}16.Bool查询
为了提供更相关或者特定的结果,AND/OR/NOT 操作符可以用来调整我们的查询。它是以 布尔查询 的方式来实现的。布尔查询 接受如下参数:
must等同于ANDmust_not等同于NOTshould等同于OR
打比方,如果我想要查询这样类型的书:
书名包含 ElasticSearch 或者(OR) Solr,
并且(AND)它的作者是 Clinton Gormley 不是(NOT)Radu Gheorge
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"bool" : { "should": [
{ "match": { "title": "Elasticsearch" }},
{ "match": { "title": "Solr" }} ] }
},
"must": { "match": { "authors": "clinton gormely" }},
"must_not": { "match": {"authors": "radu gheorge" }}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.3672021,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors": [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
],
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07",
"num_reviews": 20,
"publisher": "oreilly"
}
}
]
注:正如你所看到的,布尔查询 可以包装任何其他查询类型,包括其他布尔查询,以创建任意复杂或深度嵌套的查询。
17.Regexp正则查询
正则查询 让你可以使用比 通配符查询 更复杂的模式进行查询:
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp" : {
"authors" : "t[a-z]*y"
}
},
"_source": ["title", "authors"],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"authors" : {}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
]
},
"highlight": {
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
]
}
}
]18.Multiple Filters 多重过滤
多重过滤 可以结合 布尔查询 使用,下一个例子中,过滤查询决定只返回那些包含至少20条评论,且必须在 2015 年前出版,且由 O’Reilly 出版的结果。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"filtered": {
"query" : {
"multi_match": {
"query": "elasticsearch",
"fields": ["title","summary"]
}
},
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"range" : { "num_reviews": { "gte": 20 } }
},
"must_not": {
"range" : { "publish_date": { "lte": "2014-12-31" } }
},
"should": {
"term": { "publisher": "oreilly" }
}
}
}
}
},
"_source" : ["title","summary","publisher", "num_reviews", "publish_date"]
}