A summary on the FRI low degree test前2页导读
1. 引言
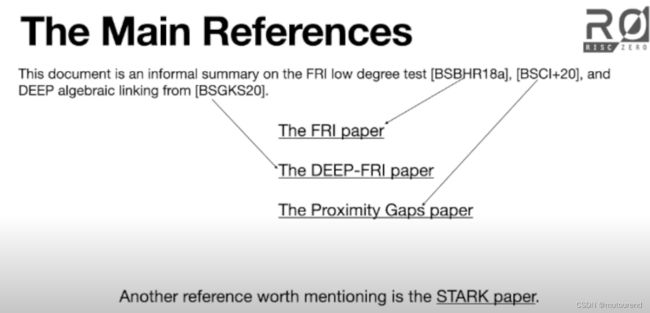
Polygon Labs Ulrich Hab¨ock 2022年论文《A summary on the FRI low degree test》,其所参考的关键论文有:
- STARK论文:Eli Ben-Sasson等人2018年论文 Scalable, transparent, and post-quantum secure computational integrity
- FRI论文:Eli Ben-Sasson等人2017年论文Fast Reed-Solomon Interactive Oracle Proofs of Proximity,即[BSBHR18a]。
- DEEP-FRI论文:Eli Ben-Sasson等人2019年论文DEEP-FRI: Sampling outside the box improves soundness,即[BSGKS20]。
- Proximity Gaps论文:Eli Ben-Sasson等人2020年论文Proximity Gaps for Reed–Solomon Codes,即[BSCI+20]。
2. A summary on the FRI low degree test论文摘要第一句
《A summary on the FRI low degree test》论文摘要中的第一句话为:
This document is an informal summary on the FRI low degree test [BSBHR18a], [BSCI+20], and DEEP algebraic linking from [BSGKS20].
即本文为对FRI、Proximity Gaps的FRI low degree test非正式总结,也为对DEEP-FRI的DEEP algebraic linking非正式总结。
相关论文有:
- 1)STARK论文提出了证明计算完整性的新方法。
A STARK中包含了2部分:【每个都有2个版本:常规版本和DEEP版本。其中DEEP是Domain Extending for Eliminating Pretenders的简称。】- 1.1)an algebraic linking protocol(ALI或DEEP-ALI):
- 用于将计算完整性assertion,reduce为,Reed-Solomon proximity assertion。
- 更技术的角度来说,首先将计算完整性assertion,reduce为,an “Algebraic Intermediate Representation(AIR)”,即,在algebraic linking protocol之前,需将logic checks,转换为,arithmetic checks。
- 1.2)a Reed-Solomon proximity testing protocol(FRI或DEEP-FRI):
- 用于证明Reed-Solomon proximity。
- 1.1)an algebraic linking protocol(ALI或DEEP-ALI):
- 2)FRI论文出了对“Reed-Solomon Proximity Testing problem”的新解决方案。
- 3)DEEP-FRI论文同时对ALI和FRI进行了改进。
- 4)Proximity Gaps论文展示了FRI实际优于DEEP-FRI。
- DEEP-ALI + FRI
3. A summary on the FRI low degree test论文摘要第二句
《A summary on the FRI low degree test》论文摘要中的第二句话为:
Based on its most recent soundness analysis [BSCI+20], we discuss parameter settings for practical security levels, how FRI is turned into a polynomial commitment scheme, and the soundness of DEEP sampling in the list decoding regime.
即,基于最近的Proximity Gaps论文的soundness分析,本文讨论了:
1)实用安全级别的参数设置;
2)如何将FRI转换为多项式承诺方案;
3)在list decoding体制下,DEEP sampling的soundness。
其中包含的关键词有:
- 1)soundness分析?:
- 即,How small is ϵ \epsilon ϵ?( ϵ \epsilon ϵ有多小?)
- 2)实用安全级别的参数设置?:
- 即,如何让 ϵ \epsilon ϵ small?
- 3)多项式承诺方案?:
- 即,如何在RISC Zero的interactive proof protocol中进行数据“commit”和“reveal”?
- 4)list decoding体制下的DEEP sampling soundness?:
- 即,How secure is DEEP-ALI?
3.1 何为soundness分析?
假设你收到一个源自untrusted第三方(运行RISC Zero zkVM)的receipt,你运行该verifier并验证通过。
从中可学到什么呢?
无法保证生成receipt的不可信第三方是百分百诚实的。在ZKP以及密码学argument中,无法做到100%保证,而是获得某种概率上限 ϵ \epsilon ϵ。
- except with probability ϵ \epsilon ϵ,该prover知道某明确满足如下约束的execution trace:
- RISC-V ISA
- 以及 由method_id标记的二进制文件
所谓soundness分析,其分析的就是“except with probability ϵ \epsilon ϵ,该prover知道某明确满足如下约束的execution trace”中所关联的概率 ϵ \epsilon ϵ:
- 将 ϵ \epsilon ϵ称为soundness error。
- 通过让 ϵ \epsilon ϵ small,可实现高级别的安全等级。
3.2 实用安全级别的参数设置?
实用安全级别的参数设置,关注的是如何让 ϵ \epsilon ϵ small。
3.3 多项式承诺方案?
所谓承诺方案,是指:
- 一种不允许某人应答之后修改答案的方式。
- 所有的承诺方案都应具有binding属性,
- 有的承诺方案还具有hiding属性。
承诺方案中包括:
- 1)commit方法:对something进行承诺。
- 2)reveal方法:对承诺值(commitment)中的片段进行reveal。
- 3)check方法:检查所revealed片段,是否与原始承诺值匹配。
本文关注的承诺方案是基于Merkle trees的:
- 1)commit方法:通过构建Merkle tree来进行承诺,并将该Merkle tree root作为承诺值。
- 2)reveal方法:展示该Merkle tree中某叶子节点。
- 3)check方法:检查所展示Merkle叶子节点的Merkle branch。
若所承诺的数据源自evaluating a polynomial,则将相应的承诺方案称为“多项式承诺方案”。
在基于Merkle的多项式承诺方案中,该Merkle tree的每个叶子节点,对应某“evaluation domain”内的一个point。
3.4 list decoding体制下的DEEP sampling soundness?
首先,要理解“何为list decoding体制”?
Reed-Solomon Proximity Testing关注的是:
- How close is the closest Reed-Solomon codeword?
- 有时,存在单个closest RS codeword:则在unique decoding体制。unique decoding体制下,事情都很简单。
- 有时,存在多于一个可称为“closest”的RS codeword:则在list decoding体制。list decoding体制下,事情就更复杂刺激了。【本文关注的是list decoding体制】
4. A summary on the FRI low degree test论文摘要第三句
《A summary on the FRI low degree test》论文摘要中的第三句话为:
In particular, we illustrate the DEEP method applied to proving satisfiability of algebraic intermediate representations and prove a soundness error bound which slightly improves the one in [Sta21].
即,特别地,本文展示了用于证明algebraic intermediate representations(AIR)的DEEP方法,并证明了某soundness error bound,该soundness error bound是对StarkWare的ethSTARK论文中的小幅改进。
即,展示了使用由DEEP-ALI和FRI组成的STARK来证明某计算完整性assertion,同时,其Orbis security 要略微超过 ethSTARK security。
何为algebraic intermediate representations(AIR)?
对计算完整性的某check进行算术化,即可生成an algebraic intermediate representations(AIR)。
5. A summary on the FRI low degree test论文引言
《A summary on the FRI low degree test》论文引言中有内容:
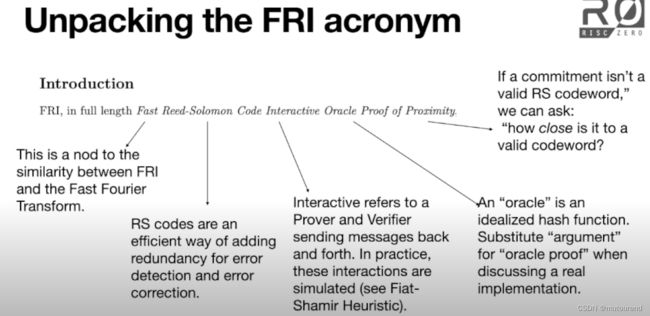
FRI,全称为Fast Reed-Solomon Code Interactive Oracle Proof of Proximity,为对函数在某FFT domain的low-degree test。所谓FFT domain,是指有限域 F F F的某smooth乘法子群 D D D。已知某函数 f : D → F f:D\rightarrow F f:D→F,FRI证明 f f f对应某low degree多项式,其degree与 D D D size相关。
- Fast:类似于普遍存在的快速傅立叶变换FFT。
- Reed-Solomon Code:为错误探测和纠错添加冗余的一种高效方式。【可查看博客 Reed-Solomon Codes——RS纠错码】
- Interactive:是指Prover和Verifier相互发送消息。实际上,这些交互可模拟(具体见Fiat-Shamir Heuristic)。
- Oracle Proof:"oracle"是一种理想的哈希函数。当讨论实际实现时,会将“argument”替换为“oracle proof”。
- Proximity:当某承诺值不是一个有效的RS codeword,则可问“how close is it to a valid codeword?”。
何为Code?这是Coding Theory的基础问题。
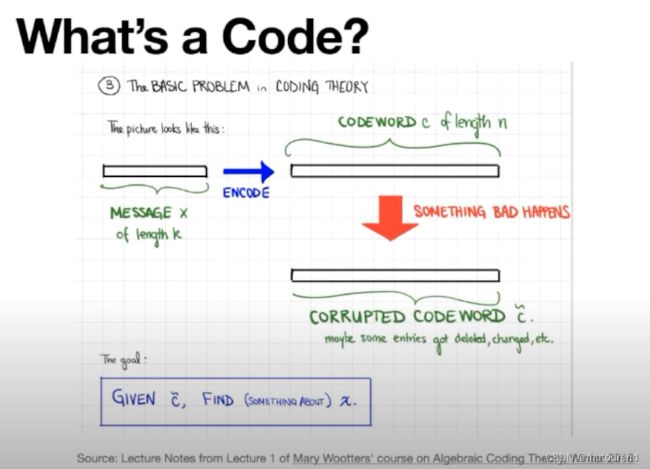
Code的正式定义为:

code理论中的distance和decoding是指:
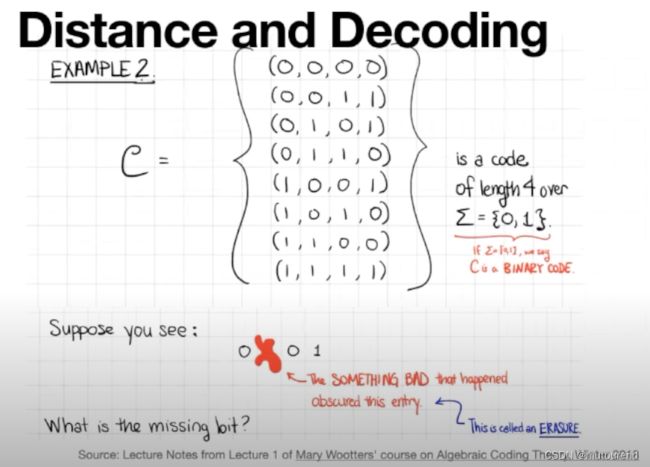
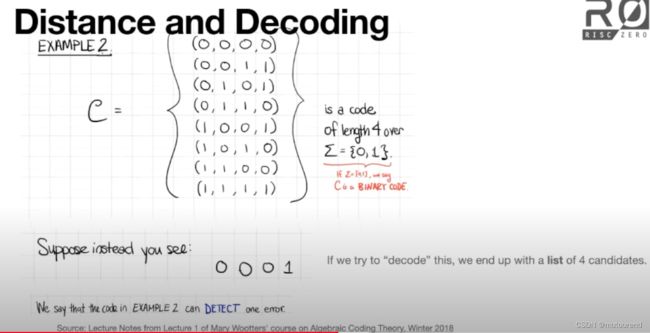
所谓distance,是指:
- 2个block之间Hamming distance,是指二者不同的元素数。

函数 f : D → F f:D\rightarrow F f:D→F是指:
- 对于每个point x ∈ D x\in D x∈D,可evaluate f ( x ) f(x) f(x)。所获得的结果 f ( x ) ∈ F f(x)\in F f(x)∈F。
- D D D:为“initial FRI commitment domain”,可基于 D D D中的每个元素来构建一个Merkle tree叶子节点。
- F F F:为所做算术化的域。
- 在老电路中,其为Baby Bear域。
- 在新电路中,其为Goldilocks域。
所谓"FFT domain, i.e. a smooth multiplicative subgroup D D D of a finite field F F F",是指:
- FFT domain:为有利于有限域傅里叶变换的domain。
- smooth:是指可递归切分为越来越小的片段。
- a smooth multiplicative subgroup of a finite field:本文不展开讲。
《A summary on the FRI low degree test》论文引言中还提到:
由FRI Porver提供的oracles,也是基于 D D D(或 D D D的subdomain)的函数,FRI会仅从这些domain来选points进行query相应的values。由于 D D D的size是small的(相对于polynomial IOPs的密码学large sampling space来说),区分2个多项式 f , g f,g f,g的关键在于statistical sampling(统计学采样)。但是,statistical test(统计学测试)仅能保证proximity,所谓proximity,可通过做如下fractional Hamming distance来衡量:
δ ( f , g ) = 1 ∣ D ∣ ⋅ ∣ x ∈ D : f ( x ) ≠ g ( x ) ∣ \delta (f,g)=\frac{1}{|D|}\cdot |x\in D: f(x)\neq g(x)| δ(f,g)=∣D∣1⋅∣x∈D:f(x)=g(x)∣。
所谓Testing Proximity:
- 简短来说,FRI支持test:
参考资料
[1] 2022年10月RISC Zero培训视频 Intro to FRI: RISC Zero Study Club(Slide见Study Club-FRI Summary)
RISC Zero系列博客
- RISC0:Towards a Unified Compilation Framework for Zero Knowledge
- Risc Zero ZKVM:zk-STARKs + RISC-V
- 2023年 ZK Hack以及ZK Summit 亮点记
- RISC Zero zkVM 白皮书
- Risc0:使用Continunations来证明任意EVM交易
- Zeth:首个Type 0 zkEVM
- RISC Zero项目简介
- RISC Zero zkVM性能指标
- Continuations:扩展RISC Zero zkVM支持(无限)大计算