vue学习笔记
1.vue对象和插值语法
1.想要vue工作必须new一个vue对象出来,容器依旧符合html模板规范,只是加入了一些vue的语法例如双括号{{}},
2.容器和一个vue示例对象是一一对应的,不能多个容器被一个vue对象服务
3.真实开发中一般只有一个vue示例,并且配合组件一起使用
4.{{xxxx}}xxx可以是js表达式,也可以读取vue示例中data所有的属性
5.{{}}是插值语法,使用在标签体内容读取插值,标签属性值得用指令语法v-bind:表示会把属性的值当做js语句来执行
6.v-bind:可以简写为:
7.指令语法包括v-bind:,v-if:等等,他可以用于解析标签体内容,标签属性,标签事件等
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body >
<div id="root1">
<h1 >vue绑定啊,{{value1}}h1>
<h1 >vue绑定啊,{{value2}}h1>
<h1 >表达式时间,{{Date.now()}}h1>
<h1>v-bind的例子
h1>
<a v-bind:href="urls.burl1">点击链接1a>
<hr>
<a :href="urls.burl2">点击链接2a>
div>
body>
html>
<script >
//1.想要vue工作必须new一个vue对象出来,容器依旧符合html模板规范,只是加入了一些vue的语法例如双括号{{}},
//2.容器和一个vue示例对象是一一对应的,不能多个容器被一个vue对象服务
//3.真实开发中一般只有一个vue示例,并且配合组件一起使用
//4.{{xxxx}}xxx可以是js表达式,也可以读取vue示例中data所有的属性
//5.{{}}是插值语法,使用在标签体内容读取插值,标签属性值得用指令语法v-bind:表示会把属性的值当做js语句来执行
//6.v-bind:可以简写为:
//7.指令语法包括v-bind:,v-if:等等,他可以用于解析标签体内容,标签属性,标签事件等
const x=new Vue(
{
el:'#root1',//指定为哪一个容器div服务,拿到div容器作为一个vue模板后扫描有没有vue的特殊语法,有的话就数据替换
data:{
value1:"刘钦华",
value2:"作业帮",
urls:{
burl1:"https://www.baidu.com/",
burl2:"https://www.baidu.com/"
}
}
}
)
script>
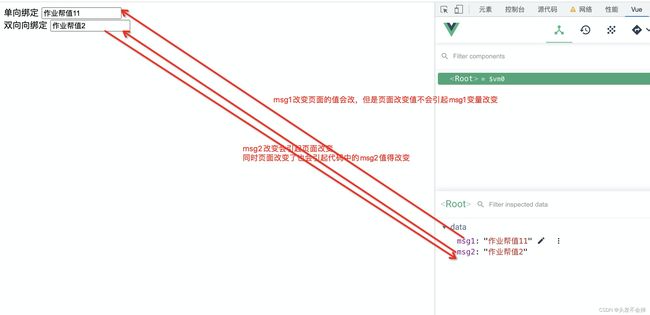
2.数据单向绑定和双向绑定
MVVM模型是什么??
M就是model:指的是data里面的数据,
V是view:是模板代码,容器,
vm是viewModel:指的就是vue实例对象,作为view和model的桥梁,data里面的数据都会作为vue实例的属性出现,data不是vue的一个属性,是他里面的k-v数据作为他的属性。最后vue原有的属性也可以像data里面的数据被view模板直接使用。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">
单向绑定 <input v-bind:value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定 <input v-model:value="msg2">
<br>
单向绑定简写 <input :value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定简写 <input v-model="msg2">
div>
body>
<script>
new Vue(
{
el:"#root",
data:{
msg1:"作业帮值111",
msg2:"作业帮值2"
}
}
)
script>
html>
3.挂载mount和data数据的写法
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">
单向绑定 <input v-bind:value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定 <input v-model:value="msg2">
<br>
单向绑定简写 <input :value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定简写 <input v-model="msg2">
div>
<hr>
<div id="root2">
单向绑定 <input v-bind:value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定 <input v-model:value="msg2">
<br>
单向绑定简写 <input :value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定简写 <input v-model="msg2">
div>
<hr>
<div id="root3">
<br>
单向绑定简写 <input :value="msg1"><br>
双向向绑定简写 <input v-model="msg2">
div>
body>
<script>
new Vue(
{
el:"#root",
data:{
msg1:"root1作业帮值111",
msg2:"root1作业帮值2"
}
}
)
//没有el使用mount挂载容器
const w= new Vue(
{
//el:"#root",
data:{
msg1:"root2作业帮值111",
msg2:"root2作业帮值2"
}
}
)
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(w)
w.$mount("#root2")//vue对象绑定某一个容器
},1000)//一秒钟之后再绑定
// data的第二种方法(组件的方式必须使用这种)
aa={
name:"张三",
myfunc1:function (){
return "aaa"
},
myfunc2(){//这里相当于函数名为myfunc2的函数缩写
return "bb"
}
}
console.log(aa.myfunc1())
console.log(aa.myfunc2())
//箭头函数没有自己的this
const m= new Vue(
{
el:"#root3",
data:function (){
console.log(this)//data里面的this指的是m整个对象,且不能写成箭头函数,
// 箭头函数里面的this是window对象不是vue对象
return {
msg1:"root3作业帮值111",
msg2:"root3作业帮值2"
}
}
}
)
console.log("======")
console.log(m.data)
console.log("=====")
script>
html>```
## 4.js基础Object.defineProperty,对象属性和某一个变量挂载(setter,getter)
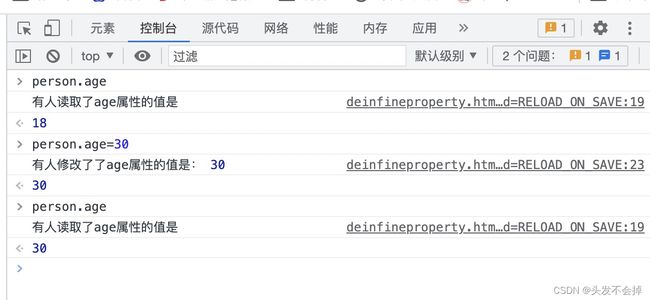
通过 Object.defineProperty就可以实现数据代理,数据代理就是通过一个对象可以对代理对另外一个对象的操作(读和写)
```javascript
<script type="text/javascript">
person={
"name":"作业帮",
"sex":"男",
}
number=18
Object.defineProperty(person,"age",{
// value:18,
// enumerable:true,//可枚举,默认值是false
// writable:true,//可修改,默认值是FALSE
get:function (){
console.log("有人读取了age属性的值是")
return number//这个return就是把number和person这个age属性绑定了,每次读取age就是返回number
},
set(value){//相当于set:function(value){
console.log("有人修改了了age属性的值是:",value)
number=value//这个赋值就是把改变了person.age改变之后自动改变了number,每次读取age就是返回number,也是改变自己
}
})
script>
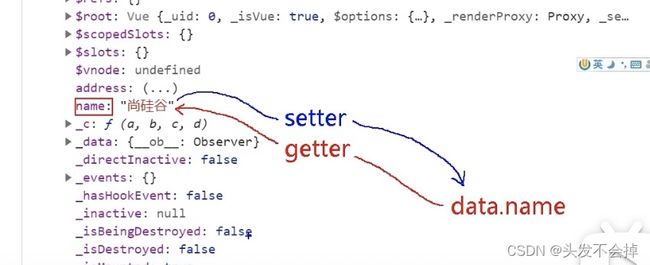
vue对象里面的属性msg1和msg2是由data对象里的数据代理,Vue对象会给他属性生成setter和getter完成对data数据的绑定。
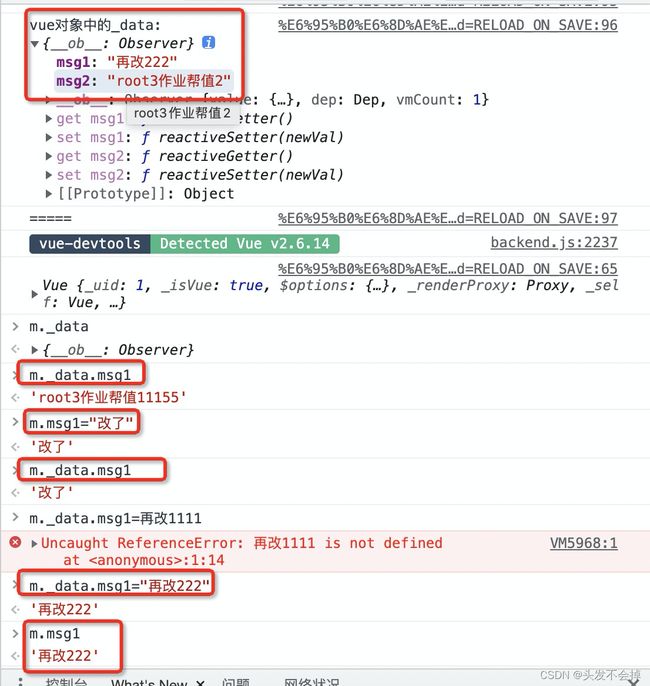
new实例化vue对象的时候实际上把data数据对象自己又存了了一份data。vue的直接属性msg1和msg2是给页面模板用,存的_data是作数据劫持的
5.vue的事件处理
1.使用v-on:xxx或者@xxx来绑定事件,作数据处理,xxx是事件名称,例如@click
2.所有事件回调函数要放在vue对象的methods里面,且回调函数不要写成箭头函数
3.事件的修饰符,vue的修饰符放在@XXX.修饰符名称=
常见事件修饰符参考:
3.1: .stop 等同于javaScript 中的event.stopPropagation(); 防止事件冒泡;
3.2: .prevent: 等同于javaScript 中event.preventDefault(); 防止执行预设的行为。
3.3: .capture: 与事件冒泡方向相反, 事件捕获由外到内。
3.4: .self: 只会触发自己范围内的事件, 不包含子元素。
3.5: .once() 事件 只会触发一次。
3.6: .passive()事件默认行为立刻执行,不会等回调函数执行完再执行默认行为
4.键盘事件参考:@keyup或则@keydown
具体要按下哪一个键才触发函数可以后面加key别名,例如@keyup.enter=“myfunc()”,按下回车键enter就会触发函数,单纯的@keyup或keydown后面没加别名,按下每一个键盘键都会触发函数。有些系统键盘别名配合事件使用是不行的
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件处理title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root1">
<h1>{{msg1}}h1>
<button @click="funct1(msg1)">点击展示信息1button><br>
<button v-on:click="funct2($event,num1)">点击展示信息2button><br>
<a @click.prevent="funct1(msg1)" href="https://www.baidu.com/">点击链接prevent不跳转a>
<br>
<div @click="funct1(msg1)" id="id1">
<div @click="funct1(msg1)" style="background-color: aqua">
<button @click.stop="funct1(msg1)">按钮stop阻断外面两个div的click事件button><br>
div>
div>
<div @click="funct1(msg1)" style="background-color: aqua">
<a @click.prevent.stop="funct1(msg1)" href="https://www.baidu.com/">@click.prevent.stop阻止外面冒泡也prevent不跳转a>
div>
<div>
<h1>键盘事件:h1>
<input @keyup="keyFunc">
<input @keyup.Control.y="keyFunc2">
div>
div>
body>
<style>
#id1{
padding: 10px 10px;
background-color: red;
}
style>
<script >
vm =new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
msg1:"作业帮11",
num1:111
}
},
methods:{
funct1:function (m){
console.log("func111")
alert("funct1事件弹窗你好"+m)
},
funct2:function (event ,a){
console.log("func111")
console.log(a)
console.log(event)
alert("funct2事件弹窗你好"+a)
},
keyFunc:function (e){
console.log(e.key)
if (e.keyCode!=13)//13是回车键key的编码
return
alert(e.target.value)//value是标签的值
},
keyFunc2:function (e){
console.log(e.key)
alert(e.target.value)//value是标签的值
},
}
})
vm.$mount("#root1")
script>
html>
6.vue的计算属性给vue对象传computed对象
1.计算属性:要用的属性不存在data里面,需要通过其他属性计算出来的,原理也是使用defineproperty,优势是使用了缓存
2.调用get函数时机,.在初次调用的时候调用然后存在缓存,下次用直接拿缓存的。.当get依赖的数据发生变化就会调用get函数
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>计算属性title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root1" style="margin: 50px 100px">
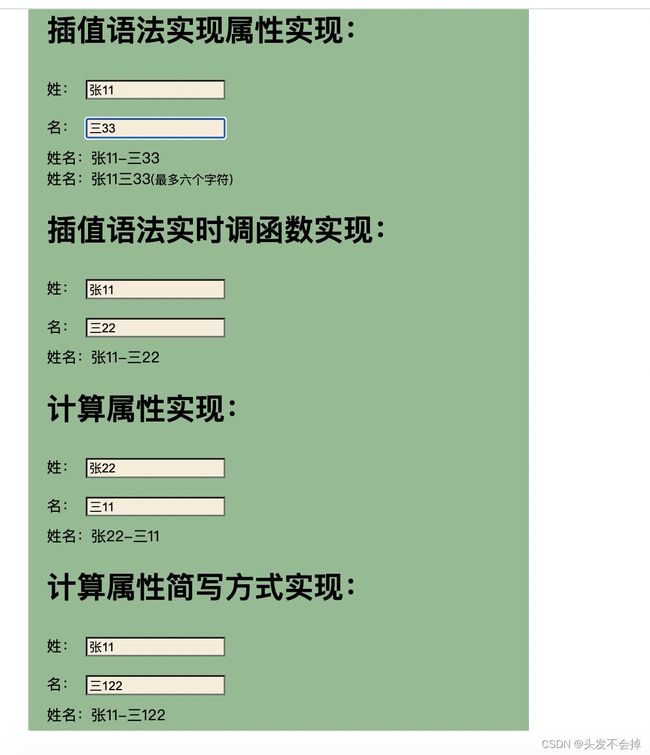
<h1>插值语法实现属性实现:h1>
姓:<input v-model:value="xing" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
名:<input v-model:value="ming" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
<span style="display: block">姓名:{{xing.slice(0,4)}}-{{ming}}span>
姓名:<span>{{(xing+ming).slice(0,6)}}<span style="font-size: smaller">(最多六个字符)span>span>
<h1>插值语法实时调函数实现:h1>
姓:<input v-model:value="xing2" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
名:<input v-model:value="ming2" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
<span style="display: block">姓名:{{nameFuct()}}span>
<h1>计算属性实现:h1>
姓:<input v-model:value="xing3" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
名:<input v-model:value="ming3" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
<span style="display: block">姓名:{{name}}span>
<h1>计算属性简写方式实现:h1>
姓:<input v-model:value="xing4" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
名:<input v-model:value="ming4" type="text" style="background-color: antiquewhite"><br>
<span style="display: block">姓名:{{name2}}span>
div>
body>
<style>
#root1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color:darkseagreen;
padding: 0px 20px;
overflow: auto;
}
input{
margin: 10px 0px 10px 10px;
}
style>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
xing:"张",
xing2:"张",
xing3:"张",
xing4:"张",
ming:"三",
ming2:"三",
ming3:"三",
ming4:"三",
}
},
methods:{
nameFuct:function (){
return this.xing2+'-'+this.ming2
}
},
//计算属性:要用的属性不存在data里面,需要通过其他属性计算出来的,原理也是使用defineproperty,优势是使用了缓存
computed:{//为属性调用各自的get函数然后放在vm身上
name:{//名字属性,不是一个函数
get:function (){//不是name这个属性被访问就会调用,但是加了缓存,1.在初次调用的时候调用然后存在缓存,下次用直接拿缓存的
//2.当get依赖的数据发生变化就会调用get函数
console.log(this)
return this.xing3+'-'+this.ming3
},
set:function (value){
arr= value.split('-')
this.xing3=arr[0]
this.ming3=arr[1]
}
},
name2:function (){//name2这个计算属性不会被修改,他的get函数可以这样子简写,name2作为一个属性放在vue对象下
return this.xing4+'-'+this.ming4
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root1")
script>
html>
7.监视属性(watch)
1.监视属性就是监视vue对象的data属性变化,也可以监听data属性的属性,对象嵌套,这叫深度监视
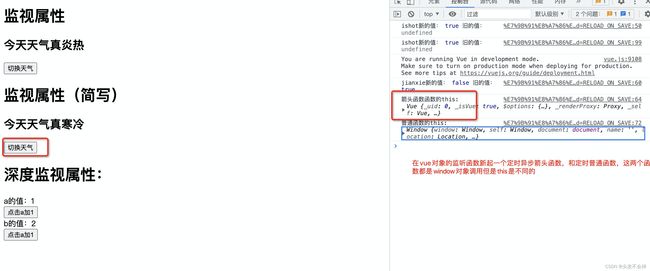
2.定义给vue对象的事件回调函数,计算属性函数,监听回调函数都是在vue外面定义的,这时候箭头函数的this还不属于Vue对象是window对象的,所以这些函数被vue对象直接管理的函数不能写成箭头函数,要写成普通函数。如果是在Vue的事件回调函数,计算属性函数,监听回调函数里面写箭头函数,那这时候的箭头函数的this就是vue对象,所以一般写vue代码时不是被vue管理的函数一般写成箭头函数,都是为了让this指向vue对象。看看this在箭头函数和普通函数原本的的区别:
1.1.普通函数的this:指向它的调用者,如果没有调用者则默认指向window
2.2:箭头函数的this: 指向箭头函数定义时所处的对象,而不是箭头函数使用时所在的对象,默认使用父级的this。
3.要异步实现功能时只能用监听属性不能用计算属性
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>监视属性title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root1">
<h1>监视属性h1>
<h2>今天天气真{{tianqi}}h2>
<button @click="qiehuan">切换天气button>
<h1>监视属性(简写)h1>
<h2>今天天气真{{jianxie}}h2>
<button @click="isHot2=!isHot2">切换天气button>
<h1>深度监视属性:h1>
<div>a的值:{{numbers.a}}<br>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点击a加1button>
div>
<div>b的值:{{numbers.b}}<br>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点击a加1button>
div>
div>
body>
<script>
const vm= new Vue({
data:function (){
return{
tianqi:"炎热",
jianxie:"炎热",
isHot:true,
isHot2:true,
numbers:{
a:1,
b:2
}
}
},
methods:{
qiehuan:function (){
this.isHot=!this.isHot
}
},
watch:{
isHot:{
immediate:true,//不用isHot这个属性发生改变也会调用,初始化立刻调用一次handle
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("ishot新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
if (newValue==true){
this.tianqi='炎热'
}else {
this.tianqi='寒冷'
}
return
}
},
isHot2(newValue,oldValue){//检测isHot2不需要检测加其他immediate,deep属性就可以直接用它的变量名直接作为函数名,相当于变化就调用的handler函数
console.log("jianxie新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
//1.普通函数的this:指向它的调用者,如果没有调用者则默认指向window,这个定时器是给浏览器的window对象调用的,所以不能写成普通函数
//2.箭头函数的this: 指向箭头函数定义时所处的对象,而不是箭头函数使用时所在的对象,默认使用父级的this.
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("箭头函数函数的this:",this)
if (newValue==true){
this.jianxie='炎热'
}else {
this.jianxie='寒冷'
}
},2000)
setTimeout(function (){
console.log("普通函数的this:",this)
},2000)
return
},
"numbers.a":{
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("numbers.a发生了改变,新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
}
},
"numbers.b":{
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("numbers.b发生了改变,新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
}
},
numbers:{
deep:true,//(深度监视)不加这个是检测不了整个numbers的变化的,只要有一个属性发生改变就会执行handler
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("numbers发生了改变,新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
}
}
}
})
vm.$mount('#root1')
vm.$watch(//监视isHot也可以这样子写
"isHot",{
immediate:true,//不用isHot这个属性发生改变也会调用,初始化立刻调用一次handle
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("ishot新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
if (newValue==true){
this.tianqi='炎热'
}else {
this.tianqi='寒冷'
}
return
}
},"isHot1",{//但是isHot1属性不存在,不报错
immediate:true,//不用isHot这个属性发生改变也会调用,初始化立刻调用一次handle
handler:function (newValue,oldValue){
console.log("ishot新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
if (newValue==true){
this.tianqi='炎热'
}else {
this.tianqi='寒冷'
}
return
}
},"isHot2",function (newValue,oldValue){//检测isHot2不需要检测加其他immediate,deep属性就可以直接用它的变量名直接作为函数名,相当于变化就调用的handler函数
console.log("jianxie新的值:",newValue,"旧的值:",oldValue)
if (newValue==true){
this.jianxie='炎热'
}else {
this.jianxie='寒冷'
}
return
}
)
script>
html>
8.样式绑定(:class和:style)
标签的class属性的值和style的值可以使用vue对象的data数据来指定,这就实现了样式的变化,:class和:style的值是一个表达式处理,值可以是一个z字段,对象名,数组。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>class绑定title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root1">
<h1>:class绑定h1>
<div class="basic" :class="stl" @click="qiehuan">
class样式随机
div>
<div class="basic" :class="styleObject" @click="qiehuan">
class 样式对象绑定
div>
<h1>:style绑定h1>
<div class="basic" :style="styleObj1" >
样式为data属性
div>
<div class="basic" :style="[styleObj1,styleObj2]" >
样式为多个data属性的数组
div>
div>
body>
<style>
.basic{
border-color: black;
border-width: 5px;
border-style: solid;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.style1{
background-color: darkseagreen;
}
.style2{
background-color:blueviolet;
font-style: inherit;
}
.style2{
background-color:yellow;
}
style>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
stl:"style1",
styleObject:{
"style1":true,
"style2":false,
},
styleObj1:{
fontSize:"40px",
fontStyle:"inherit",
backgroundColor:"yellow"
},
styleObj2:{
fontSize:"40px",
fontStyle:"inherit",
borderBottomColor:"red"
}
}
},
methods:{
qiehuan:function (){
arr=['style1','style2','style3']
index=Math.floor(Math.random()*3)//Math.random()返回0-1
this.stl=arr[index]
console.log("切换style:",arr[index])
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root1")
script>
html>
9.条件渲染(v-if和v-show)
v-if和v-show可以根据布尔值控制页面某一下标签直接展示或者不展示
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>条件渲染title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root" style="margin-left: 200px">
<h1>v-show测试:h1>
<div v-show="vshow">v-show根据布尔值是否展示 false相当于display:none,隐藏掉不占页面位置但是标签还在div>
<button @click="vshowValue">切换v-show布尔值button>
<h1>v-if测试:h1>
<div v-if="vif">v-if根据布尔值是否展示 false不是display:none,直接干掉这个标签div>
<button @click="vifValue">切换v-if布尔值button>
<h1>v-elif-else测试:h1>
<div>velif的值:{{velif}}div>
<button @click="velifValue">velif 加1button>
<div v-if="velif===0">v-if绑定渲染velif==0展示div>
<div v-else-if="velif===1">v-else-if绑定渲染velif==1展示div>
<div v-else>v-else绑定渲染velif==2展示div>
<h1>template标签只能和v-if配合使用h1>
<template v-if="vif">
<h3>原生html标签没有templateh3>
<h3>template在vue解析完之后是没有这个标签的h3>
<h3>template只是一个模板h3>
template>
div>
body>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
vshow:true,
vif:true,
velif:0,
}
},
methods:{
vshowValue:function (){
this.vshow=!this.vshow
},
vifValue:function (){
this.vif=!this.vif
},
velifValue:function (){
this.velif++
if (this.velif==3){
this.velif=0
}
return
},
}
})
vm.$mount("#root")
script>
html>
10.v-for列表渲染
v-for可以遍历生成html标签,每个标签最好根据数据的唯一值设置一个key值,详情看如下代码:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-for列表title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>遍历数组创建列表:h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(u,index) in users">
{{u.name}}--{{u.age}}--{{index}}
li>
ul>
<h1>遍历对象:h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(u,index) in car">
{{u}}--{{index}}
li>
ul>
<h1>遍历字符串:h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(u,index) in str">
{{u}}--{{index}}
li>
ul>
<h1>v-for不写key会出现风险:h1>
<button @click="unshiftPerson">列表新增老刘button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(u,index) in users" :key="u.id">
{{u.name}}--{{u.age}}--{{index}}<input >
li>
ul>
div>
body>
<script >
const vm=new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
users:[
{id:"001",name:"张三",age:18},
{id:"002",name:"李四",age:19},
{id:"003",name:"王五",age:20},
],
car:{
name:"宝马",
price:"30万",
weight:"100kg"
},
str:"刘小华"
}
},
methods:{
unshiftPerson:function (){//unshift是js给数组在前面新增一个元素的方法
this.users.unshift({id:"004",name:"老刘",age:40})
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root")
script>
html>
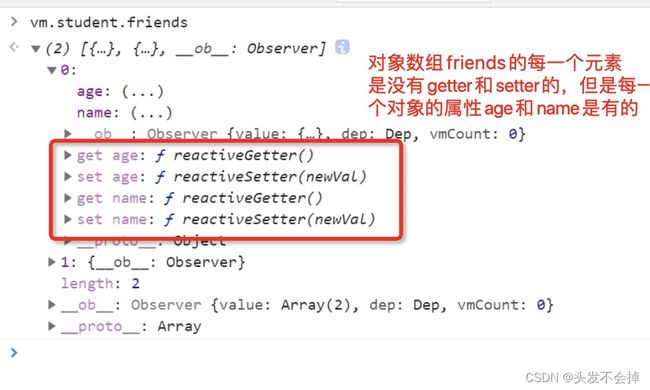
11.数组改变没渲染和setter之后会更新页面
1.setter一旦调用就回去重新渲染页面
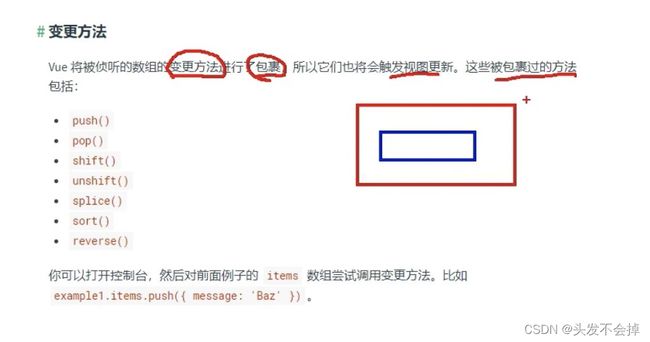
2.vue技术没有为data的数组每一个元素准备getter和setter的,所以直接根据下标index改变数组元素,是影响不到页面渲染的。。。但是给这个数组对象准备了getter和setter,可以通过下面这些数组方法进行改变数组元素会引起页面数据渲染,:
push
pop
shift
unshift 头部插入
splice 指定位置插入
sort
reverse
3.vue检测数据的原理
1.vue会监视data中所有层次的数据
2.如何监视对象中的数据
1.通过setter实现监视,且要在new Vue时传入要监视的数据
对对象追加睡醒Vue默认不做响应式处理
如需要后期添加属性做响应式,请使用(但是这两个set不能给vue对象直接加属性)
Vue.set(target,property/index,value)
this.$set(target,property/index,value)
3.如何监视数组中的数据
通过包装数组常用的更新元素的方法,本质做了两件事
1.调用原生api对数组进行更新
2.重新解析模板,进行页面更新
4.在Vue中修改数组的某个元素一定要使用如下方法
push
pop
shift
unshift 头部插入
splice 指定位置插入
sort
reverse
Vue.set() this.$set()
特别注意Vue.set() this.$set()不能给vm或者vm的根对象添加属性!!!
12.什么是数据劫持
_data是一个Observer监视器,_data中的数据是vm传入的要监控的数据
当有人要修改传入的数据时Observer的setter就会劫持数据的发改变,然后重新解析模板
重新渲染(劫持到后:重新改数据 > 解析模板 > 更新页面)
13.过滤器filters
过滤器能完成的计算属性都能实现,他是不会改变原的data的数据的
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>过滤器title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>过滤器演示h2>
原先字符串:{{msg}}<br>
fileterMethod1过滤之后:{{msg | fileterMethod1}}<br>
fileterMethod2过滤之后:{{msg | fileterMethod2}}<br>
fileterMethod1和fileterMethod2过滤之后:{{msg | fileterMethod1 | fileterMethod2 }}<br>
全局过滤器过滤quanju之后:{{msg | quanju }}<br>
div>
body>
<script>
Vue.filter("quanju" ,function (value){
console.log("全局的过滤器")
return value.slice(0,6)
})
const vm =new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
msg:"作业帮很牛的,是真的,我说的"
}
},
filters:{
fileterMethod1:function (value){
return value.slice(0,6)
},
fileterMethod2:function (value){
return value.slice(value.length-3,value.length)
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root")
script>
html>
14.v-text,v-html,v-cloak,v-once和v-pre
1.v-text能向绑定的标签渲染内容
2.v-html可以向绑定的标签渲染内容,且内容里面可以识别html标签,但是页面动态的插入v-html会存在xss攻击危险,会执行js代码拿走cookie,但是可以通过httpOnly这个限制js拿出cookie这样子就安全一点
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-html使用和xss攻击title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<div id="root">
<h1>v-text使用h1>
<h5 v-text="name">h5>
<h1>v-html使用h1>
<div v-html="neirong">div>
<h1>v-cloak使用h1>
<div v-cloak >v-cloak,Vue加载使用后机会把这个属性去掉div>
<h1>v-once使用h1>
<div v-once><h6>n的初始值:{{n}}h6>div>
<div>n当前值:{{n}}div>
<div><button @click="n++">n加1button>div>
<h1>v-pre使用h1>
<div v-pre>n当前值:{{n}}div>
div>
<body>
body>
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display: none;
}
style>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
neirong:"点击alert",
n:1,
name:"作业帮"
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root")
script>
html>
15.自定义指令directives
指令是可以自定义的,像v-bind和v-text是指令,vue对象要加一个directives属性,可以加自己自定义的指令,具体看代码注释
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>自定义指令title>
<script type="text/javascript"src="vue.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>{{name}},data其他数据变化也会引起所有指令的udapte函数被调用一次,包括自定义指令update函数div>
<button @click="name++">name++button>
<h1>指令写成函数式:h1>
<div>当前的n值:{{n}}div>
<div>放大10倍后的n值:<span v-big="n">span>div>
<button @click="n++">点击n+1button>
<hr>
<h1>指令写成对象式:h1>
<div>当前的m值:{{m}}div>
<div>放大10倍后的m值:<input v-fbig="m">div>
<button @click="m++">点击m+1button>
<hr>
<h1>全局vue自定义指令:h1>
<div>当前的w值:{{w}}div>
<div>放大10倍后的w值:<input v-wbig="w">div>
<button @click="w++">点击w+1button>
div>
body>
<script>
Vue.directive("wbig",{//bind,inserted,update这三个函数名字一定不能写错
//指令与元素成功绑定时调用bind
bind:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("wbig的bind函数")
element.focus()//获取鼠标焦点
},
//element被渲染inserted插入到到页面时调用,函数式的这个时机不会被调用
inserted:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("wbig的inserted函数")
element.focus()
},
//vue模板被重新解析时调用updated
update:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("wbig的update函数")
element.focus()
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("wbig指令update函数的箭头函数里面的this",this)//是window对象
},1)
console.log("wbig指令update函数里的this",this)//也是是window对象
}
})
const vm =new Vue({
data:function (){
return {
n:1,
m:2,
w:3,
name:100
}
},
directives:{
//自定义指令的函数默认传入有两个参数,一个指令是绑定的document对象,和绑定的内容bindging,包括绑定传入的值,指令名
//调用的时机:1.指令与元素成功绑定时;2.指令所在的模板发生改变重新解析模板时
big:function (element,binding){
console.log("指令定义函数传入的element:",element)
console.log("指令定义函数传入的binding:",binding)
console.log("指令定义函数传入的指令名称:",binding.name)
//原生的js
element.innerHTML=binding.value*10
return
},
fbig:{//bind,inserted,update这三个函数名字一定不能写错
//指令与元素成功绑定时调用bind
bind:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("fbig的bind函数")
element.focus()//获取鼠标焦点
},
//element被渲染inserted插入到到页面时调用,函数式的这个时机不会被调用
inserted:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("fbig的inserted函数")
element.focus()
},
//vue模板被重新解析时调用updated
update:function (element,binding){
element.value=binding.value*10
console.log("fbig的update函数")
element.focus()
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("fbig指令update函数的箭头函数里面的this",this)//是window对象
},1)
console.log("fbig指令update函数里的this",this)//也是是window对象
}
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root")
script>
html>