小黑子—spring:第四章 事务控制与整合web环境
spring入门4.0
- 四 小黑子基于AOP的声明式事务控制
-
- 1. Spring事务编程概述
- 2. 搭建测试环境
- 3. 基于XML声明式事务控制
-
- 3.1 入门操作
- 3.2 声明式事务控制详解
- 4. 基于注解的声明式事务控制
- 五 小黑子用spring进行web环境整合
-
- 5. JavaWeb三大组件作用及其特点
- 6. Spring整合web环境的思路及实现
-
- 6.1 模拟ContextLoaderListener
- 7. Spring的Web开发组件spring-web
- web层MVC框架思想与设计思路
四 小黑子基于AOP的声明式事务控制
1. Spring事务编程概述
事务是开发中必不可少的东西,使用JDBC开发时,我们使用connnection对事务进行控制,使用MyBatis时,我们使用SqlSession对事务进行控制,缺点显而易见,当我们切换数据库访问技术时,事务控制的方式总会变化,Spring 就将这些技术基础上,提供了统一的控制事务的接口。Spring的事务分为:编程式事务控制和声明式事务控制
| 事务控制方式 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 编程式事务控制 | Spring提供了事务控制的类和方法,使用编码的方式对业务代码进行事务控制,事务控制代码和业务操作代码耦合到了一起,开发中不使用 |
| 声明式事务控制 | Spring将事务控制的代码封装,对外提供了Xml和注解配置方式,通过配置的方式完成事务的控制,可以 |
Spring事务编程相关的类主要有如下三个:
| 事务控制相关类 | 解释 |
|---|---|
平台事务管理器 PlatformTransactionManager |
是一个接口标准,实现类都具备事务提交、回滚和获得事务对象的功能,不同持久层框架可能会有不同实现方案 |
事务定义 TransactionDefinition |
封装事务的隔离级别、传播行为、过期时间等属性信息 |
事务状态 TransactionStatus |
存储当前事务的状态信息,如果事务是否提交、是否回滚、是否有回滚点等 |
虽然编程式事务控制我们不学习,但是编程式事务控制对应的这些类我们需要了解一下,因为我们在通过配置的方式进行声明式事务控制时也会看到这些类的影子
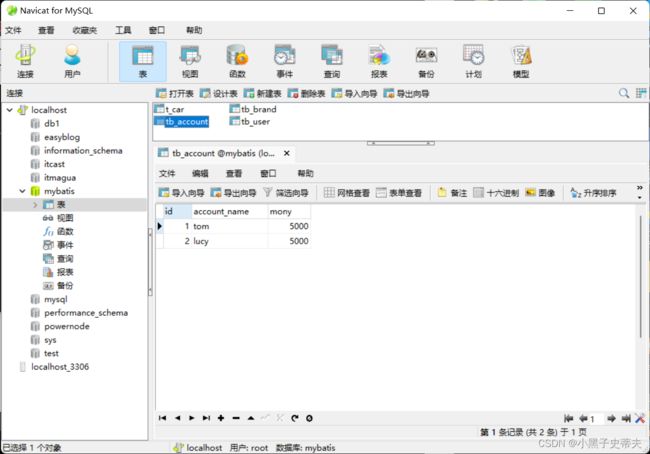
2. 搭建测试环境
搭建一个转账的环境,dao层一个转出钱的方法,一个转入钱的方法service层一个转账业务方法,内部分别调
用dao层转出钱和转入钱的方法,准备工作如下:
public interface AccountMapper {
/*
* 加钱
* */
@Update("update tb_account set money = money+#{money} where account_name = #{accountName}")
public void incrMoney(@Param("accountName") String accountName,@Param("money") Integer money);
/*
* 减钱
* */
@Update("update tb_account set money = money-#{money} where account_name = #{accountName}")
public void decrMoney(@Param("accountName") String accountName,@Param("money") Integer money);
}
- service层准备一个transferMoney方法,分别调用incrMoney和decrMoney方法;
package com.itheima.service;
public interface AccountService {
void transferMoney(String outAccount,String inAccount,Integer money);
}
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public void transferMoney(String outAccount, String inAccount, Integer money) {
accountMapper.decrMoney(outAccount,money);
accountMapper.incrMoney(inAccount,money);
}
}
- 在applicationContext文件中进行Bean的管理配置;
jdbc.driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username = root
jdbc.password = root
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.mapper">property>
bean>
beans>
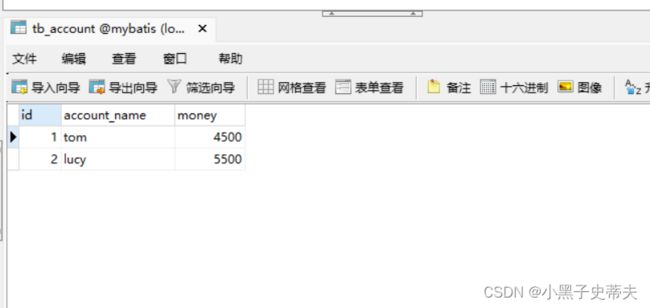
- 测试正常转账与异常转账
public class AccountTest {
@Test
public void accountTest1(){
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountService accountService = app.getBean(AccountService.class);
accountService.transferMoney("tom","lucy",500);
}
}
3. 基于XML声明式事务控制
3.1 入门操作
结合上面我们学习的AOP的技术,很容易就可以想到,可以使用AOP对Service的方法进行事务的增强。
- 目标类:自定义的AccountServicelmpl,内部的方法是切点
- 通知类: Spring提供的,通知方法已经定义好,只需要配置即可
我们分析:
- 通知类是Spring提供的,需要导入Spring事务的相关的坐标;
- 配置目标类AccountServicelmpl;
- 使用advisor标签配置切面。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.mapper">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPonitcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPonitcut">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
beans>
3.2 声明式事务控制详解
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" propagation="" timeout="3" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="registAccount"/>
<tx:method name="add*"/>
<tx:method name="update*"/>
<tx:method name="delete*"/>
<tx:method name="select*"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
- isolation属性:指定事务的隔离级别,事务并发存在三大问题:脏读、不可重复读、幻读/虚读。可以通过设置事务的隔离级别来保证并发问题的出现,常用的是
READ_COMMITTED和REPEATABLE_READ
| isolation属性 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| DEFAULT | 默认隔离级别,取决于当前数据库隔离级别,例如MySQL默认隔离级别是REPEATABLE_READ |
| READ_UNCOMMITTED | A事务可以读取到B事务尚未提交的事务记录,不能解决任何并发问题,安全性最低,性能最高 |
| READ_COMMITTED | A事务只能读取到其他事务已经提交的记录,不能读取到未提交的记录。可以解决脏读问题,但是不能解决不可重复读和幻读 |
| REPEATABLE_READ | A事务多次从数据库读取某条记录结果一致,可以解决不可重复读,不可以解决幻读 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 串行化,可以解决任何并发问题,安全性最高,但是性能最低 |
-
read-only属性:设置当前的只读状态,如果是查询则设置为true,可以提高查询性能,如果是更新(增删改)操作则设置为false
<tx:method name="select*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="false"/> -
timeout属性:设置事务执行的超时时间,单位是秒,如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务,不在继续执行。默认值是-1,即没有超时时间限制
<tx:method name="select*" read-only="true" timeout="3" /> -
propagation属性:设置事务的传播行为,主要解决是A方法调用B方法时,事务的传播方式问题的,例如:使用单方的事务,还是A和B都使用自己的事务等。事务的传播行为有如下七种属性值可配置:
| 事务传播行为 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED (默认值) | A调用B,B需要事务,如果A有事务B就加入A的事务中,如果A没有事务,B就自己创建一个事务 |
| REQUIRED_NEW | A调用B,B需要新事务,如果A有事务就挂起,B自己创建一个新的事务 |
| SUPPORTS | A调用B,B有无事务无所谓,A有事务就加入到A事务中,A无事务B就以非事务方式执行 |
| NOT_SUPPORTS | A调用B,B以无事务方式执行,A如有事务则挂起 |
| NEVER | A调用B,B以无事务方式执行,A如有事务则抛出异常 |
| MANDATORY | A调用B,B要加入A的事务中,如果A无事务就抛出异常 |
| NESTED | A调用B, B创建一个新事务,A有事务就作为嵌套事务存在,A没事务就以创建的新事务执行 |
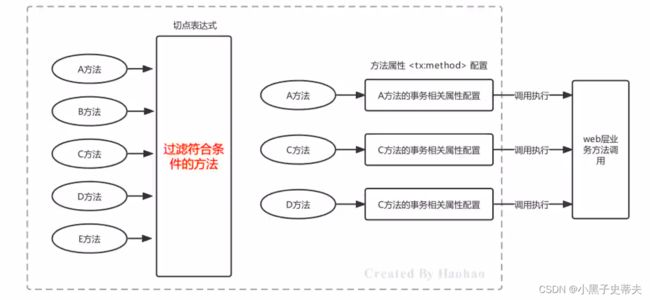
声明式事务控制原理刨析
4. 基于注解的声明式事务控制
其中,name属性名称指定哪个方法要进行哪些事务的属性配置,此处
有尽要分的是切点表达式指定的方法与此处指定的方法的区别?切点表达式,是过滤哪些方法可以进行事务增强;事务属性信息的name,是指定哪个方法要进行哪些事务属性的配置
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
//那个方法需要加事务,就用注解@Transactional
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transferMoney(String outAccount, String inAccount, Integer money) {
accountMapper.decrMoney(outAccount,money);
int i= 1/0;
accountMapper.incrMoney(inAccount,money);
}
public void registAccount(){}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.mapper">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager1" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager1"/>
beans>
- 对以上采用全注解的方式进行修改:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@MapperScan("com.itheima.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement//相当于五 小黑子用spring进行web环境整合
5. JavaWeb三大组件作用及其特点
在Java语言范畴内,web层框架都是基于Javaweb基础组件完成的,所以有必要复习一下Javaweb组件的特点
| 组件 | 作用 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| Servlet | 服务端小程序,负责接收客户端请求并作出响应的 | 单例对象,默认第一次访问创建,可以通过配置指定服务器启动就创建,Servlet创建完毕会执行初始化init方法。每个Servlet有一个service方法,每次访问都会执行service方法,但是缺点是一个业务功能就需要配置一个Servlet |
| Filter | 过滤器,负责对客户端请求进行过滤操作的 | 单例对象,服务器启动时就创建,对象创建完毕执行init方法,对客户端的请求进行过滤,符合要求的放行,不符合要求的直接响应客户端,执行过滤的核心方法doFilter |
| Listener | 监听器,负责对域对象的创建和属性变化进行监听的 | 根据类型和作用不同,又可分为监听域对象创建销毁和域对象属性内容变化的,根据监听的域不同,又可以分为监听Request域的,监听Session域的,监听ServletContext域的 |
6. Spring整合web环境的思路及实现
在进行Java开发时要遵循三层架构+MVC,Spring操作最核心的就是Spring容器,web层需要注入Service,service层需要注入Dao (Mapper) , web层使用Servlet技术充当的话,需要在Servlet中获得Spring容器
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/accountServlet")
public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//web层调用service层,获得AccountService,accountService存在applicationContext中
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountService accountService = app.getBean(AccountService.class);
accountService.transferMoney("tom","lucy",500);
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.mapper">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPonitcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPonitcut">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
beans>
编译的时候把config.SpringConfig里面的spring注解给去掉,然后用的是IDEA的Maven插件运行tomcat7

web层代码如果都去编写创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的代码,那么配置类重复被加载了,Spring容器也重复被创建了,不能每次想从容器中获得一个Bean都得先创建一次容器,这样肯定是不允许。所以,我们现在的诉求很简单,如下:
- ApplicationContext创建一次,配置类加载一次;
- 最好web服务器启动时,就执行第1步操作,后续直接从容器中获取Bean使用即可;
- ApplicationContext的引用需要在web层任何位置都可以获取到。
针对以上诉求我们给出解决思路,如下:
- 在ServletContextListener的contextInitialized方法中执行ApplicationContext的创建。或在Servlet的init方法中执行ApplicationContext的创建,并给Servlet的load-on-startup属性一个数字值,确保服务器启动Servlet就创建;
- 将创建好的ApplicationContext存储到ServletContext域中,这样整个web层任何位置就都可以获取到了
6.1 模拟ContextLoaderListener
Listener的代码
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
private String CONTEXT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "contextConfigLocation";
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println();
ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext();
//0. 获取ContextLoaderListener域中
String contextConfigLocation = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CONFIG_LOCATION);
//1.创建spring容器
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.将容器储存到servletContext域中
servletContext.setAttribute("applicationContext",app);
}
}
WebApplicationContextUtils
package com.itheima.web;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
public class WebApplicationContextUtils {
public static ApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext){
ApplicationContext applicationContext =(ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("applicationContext");
return applicationContext;
}
}
Servlet/web层的代码
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/accountServlet")
public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//web层调用service层,获得AccountService,accountService存在applicationContext中
//从servletContext域中去applicationContext
// ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
// ApplicationContext app = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("applicationContext");
ApplicationContext app = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
AccountService accountService = app.getBean(AccountService.class);
accountService.transferMoney("tom","lucy",500);
}
}
webapp.WEB-INF下的web.xml:
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>com.itheima.listener.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
web-app>
7. Spring的Web开发组件spring-web
到此,就将一开始的诉求都解决了,当然我们能想到的Spring框架自然也会想到,Spring其实已经为我们定义好了一个ContextLoaderListener,使用方式跟我们上面自己定义的大体一样,但是功能要比我们强百倍,所以,遵循Spring "拿来主义"的精神,我们直接使用Spring提供的就可以了,开发如下:
先导入Spring-web的坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>5.3.7version>
dependency>
web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
web-app>
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/accountServlet")
public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//web层调用service层,获得AccountService,accountService存在applicationContext中
//从servletContext域中去applicationContext
// ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
// ApplicationContext app = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("applicationContext");
ApplicationContext app = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
AccountService accountService = app.getBean(AccountService.class);
accountService.transferMoney("tom","lucy",500);
}
}
扩展-核心配置类方式如何配置
web层MVC框架思想与设计思路
Java程序员在开发一般都是MVC+三层架构,MVC是web开发模式,传统的Javaweb技术栈实现的MVC如下

原始Javaweb开发中,Servlet充当Controller的角色,Jsp充当View角色,JavaBean充当模型角色,后期Ajax异步流行后,在加上现在前后端分离开发模式成熟后,View就被原始Html+Vue替代。原始Javaweb开发中,Service充当Controller有很多弊端,显而易见的有如下几个:
| Servlet作为Controller的问题 | 解决思路和方案 |
|---|---|
| 每个业务功能请求都对应一个Servlet | 根据业务模块去划分Controller |
| 每个Servlet的业务操作太繁琐 | 将通用的行为,功能进行抽取封装 |
| Servlet获得Spring容器的组件只能通过客户端代码去获取,不能优雅的整合 | 通过spring的扩展点,去封装一个框架,从原有的Servlet完全接手过来web层的业务 |
负责共有行为的Servlet称之为前端控制器,负责业务行为的JavaBean称之为控制器Controller
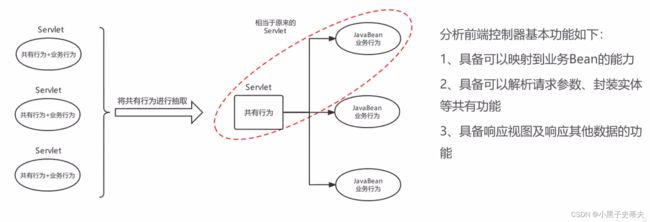
分析前端控制器基本功能如下:
- 具备可以映射到业务Bean的能力
- 具备可以解析请求参数、封装实体等共有功能
- 具备响应视图及响应其他数据的功能