「代码随想录」Python刷题笔记Day6-哈希表
哈希表第一天
-
- 哈希表理论基础
- 242.有效的字母异位词
- 349.两个数组的交集
- 202.快乐数
- 1.两数之和
哈希表理论基础
链接
242.有效的字母异位词
链接
leetcode-242
题目
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
示例 1: 输入: s = “anagram”, t = “nagaram” 输出: true
示例 2: 输入: s = “rat”, t = “car” 输出: false
说明: 你可以假设字符串只包含小写字母。
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
dic1 = {}
for i in s:
if i in dic1.keys():
dic1[i]+=1
else:
dic1[i]=1
for j in t:
if j not in dic1.keys():
return False
else:
dic1[j] -= 1
return False if any(dic1.values())!=0 else True
没有采用数组的方式,而是得益于方便的字典,结合加1和减1用来对照s和t中的每个字母出现的次数(无序)。
也被安利到了一个函数
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
from collections import Counter
a_count = Counter(s)
b_count = Counter(t)
return a_count == b_count
时间复杂度为O(n),空间上因为定义是的一个常量大小的辅助数组,所以空间复杂度为O(1)
349.两个数组的交集
链接
leetcode-349
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
dic = dict()
for i in nums1:
dic[i] = dic.get(i, 0) + 1
res = set()
for i in nums2:
if i in dic.keys():
res.add(i)
del dic[i]
return list(res)
时间复杂度O(mn),空间复杂度O(n)
直接使用set 不仅占用空间比数组大,而且速度要比数组慢,set把数值映射到key上都要做hash计算的。二刷考虑改进。
202.快乐数
链接
leetcode-202
题目
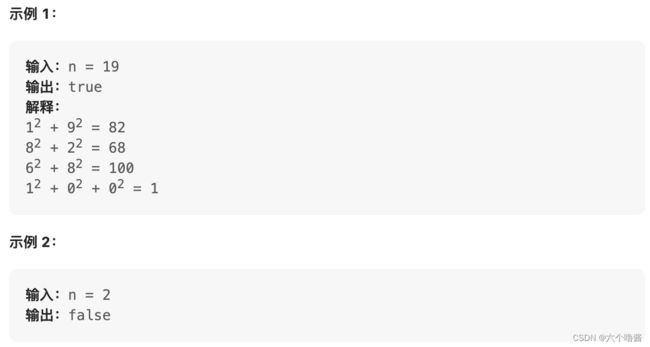
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
「快乐数」 定义为:
对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。如果这个过程 结果为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
record = set()
while True:
n = self.Sum(n)
if n == 1:
return True
if n in record:
return False
else:
record.add(n)
def Sum(self, n):
sums = 0
while n:
sums += (n%10)*(n%10)
n = n/10
return sums
直接这么写的话在leetcode中超时。
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
record = set()
while n not in record:
record.add(n)
n = sum(int(i) ** 2 for i in str(n))
if n == 1:
return True
return False
当我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法了。题目中说了会 无限循环,那么也就是说求和的过程中,sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!如果重复出现某个sum值,说明不是快乐数了。
卡哥给出了6种解法:采用数组或者set进行重复的判断都可,初次之外的区别在于求和的方式。使用n = sum(int(i) ** 2 for i in str(n))精简版的,还是新建一个函数循环divmod(n, 10)求解。后者肯定相对更慢,容易超时。
1.两数之和
链接
leetcode-1
题目
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
# 暴力解法
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1,len(nums)):
if nums[i]+nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
# Hashmap
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
hashtable = dict()
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if target - num in hashtable:
return [hashtable[target - num], i]
hashtable[nums[i]] = i
return []
感悟:
小白第一遍刷,真的好困难,慢慢跟着走。争取一遍先熟悉题目和方法,以及基本的数据结构。
