SpringBoot--Web开发篇:含enjoy模板引擎整合,SpringBoot整合springMVC;及上传文件至七牛云;restFul
SpringBoot的Web开发
官网学习:
进入spring官网 --> projects --> SpringBoot --> LEARN --> Reference Doc. --> Web --> 就能看到上述页面
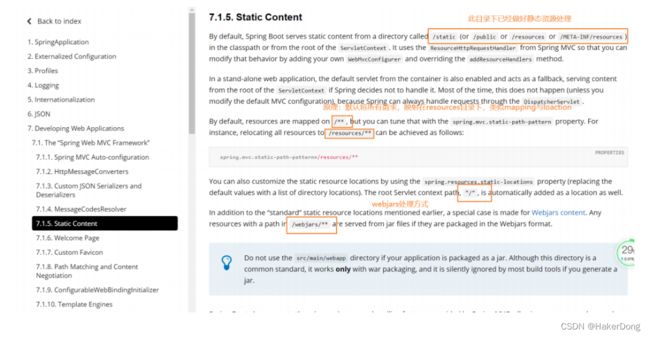
静态资源映射规则
官方文档
-
总结:
只要是静态资源,放在类路径下:called
/static(or
/publicor/resourcesor/META-INF/resources) -
访问:当前项目根路径/+静态资源名称
-
静态资源访问前缀修改
spring: mvc: static-path-pattern: /dong/** #添加此配置,所有静态资源的访问路径就需要添加一级路径/dong
一般来说,创建好SpringBoot项目之后,resources路径下会有一个static目录,css,js,图片,视频,音频都需要存放在此目录下
enjoy模板引擎
SpringBoot整合enjoy模板引擎步骤:
-
将页面保存在templates目录下
-
添加enjoy的坐标
<dependency> <groupId>com.jfinalgroupId> <artifactId>enjoyartifactId> <version>5.0.3version> dependency> -
开启配置(配置类)
在启动类同级新建config包,包下新建EnjoyConfig类(不需要自己写,JFinal官网有)
import com.jfinal.template.Engine; import com.jfinal.template.ext.spring.JFinalViewResolver; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class SpringBootConfig { @Bean(name = "jfinalViewResolver") public JFinalViewResolver getJFinalViewResolver() { // 创建用于整合 spring boot 的 ViewResolver 扩展对象 JFinalViewResolver jfr = new JFinalViewResolver(); // 对 spring boot 进行配置 jfr.setSuffix(".html"); jfr.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); jfr.setOrder(0); // 设置在模板中可通过 #(session.value) 访问 session 中的数据 jfr.setSessionInView(true); // 获取 engine 对象,对 enjoy 模板引擎进行配置,配置方式与前面章节完全一样 Engine engine = JFinalViewResolver.engine; // 热加载配置能对后续配置产生影响,需要放在最前面 engine.setDevMode(true); // 使用 ClassPathSourceFactory 从 class path 与 jar 包中加载模板文件 engine.setToClassPathSourceFactory(); // 在使用 ClassPathSourceFactory 时要使用 setBaseTemplatePath // 代替 jfr.setPrefix("/view/") engine.setBaseTemplatePath("/templates/"); // 更多配置与前面章节完全一样 // engine.addDirective(...) // engine.addSharedMethod(...); return jfr; } }唯一需要改动的地方:engine.setBaseTemplatePath(“/templates/”);
填写页面目录:/templates/
-
编写代码
Spring MVC请求处理
常用五种请求处理方式注解:
@RequestMapping
可以点击查看源码
-
意义:处理用户的请求,相似于doget与dopost
-
位置:
类上:一级目录
方法:二级目录
例如:user/save
user/delete
student/save
student/delete
-
属性:
-
value = " " ,path= " " :表示请求路径
eg:@RequestMapping(value=“/show”)或@RequestMapping(path=“/show”)
也可以省略:@RequestMapping(“/show”)
-
method=常量:此请求的类型(get,post),若不设置则此请求适配所有的请求方式
eg:@RequestMapping(value=“/show”,method={RequestMethod.POST})
必须用post请求才能请求到此路径
-
params = " ":限制请求参数,例如:params={“msg1”,“msg2”}表示请求路径中必须携带参数名为msg1与msg2的参数
注意:1.超链接默认发送的是get请求
2.所有请求所携带的参数格式均为:key = value
eg:@RequestMapping(value=“/show”,params = {“msg1=aa”,“msg2=bb”})
请求必须携带参数msg1和msg2,且msg1的值必须是aa,msg2的值必须是bb才能访问
-
@DeleteMapping 删除
@PutMapping 修改
@GetMapping 查询
@PostMapping 新增
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
METHOD==代表修饰方法,TYPE==代表修饰类
Postman测试工具
在没有页面表单的情况下,Postman可以模拟浏览器请求方式进行测试
Postman官网,下载注册登录即可使用
Spring MVC参数绑定
Spring MVC请求参数绑定机制:
SpringMVC 绑定请求参数的过程是通过把表单提交请求参数,作为控制器中方法参数进行绑定的
-
支持的数据类型:
-
基本类型参数:基本数据类型和String类型
-
POJO类型参数:实体类,以及关联的实体类
-
数组和集合类型参数:包括 List 结构和 Map 结构的集合(包括数组)
-
使用:ServletAPI 对象作为方法参数
HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、HttpSession、java.security.Principal、Locale、InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer
-
-
使用要求:
- 发送请求中携带数据的key与方法参数的name必须一致
- 数据类型合法
总结:
- 参数从页面传递过来时,名字必须和接收的参数相同
- 参数的数据类型必须合法
- 不同类型的数据演示如下
演示,步骤:
-
创建SpringBoot项目,并导入enjoy坐标
-
添加配置类
-
templates目录下的页面
one.html
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="cn" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>springMVC控制器方法参数作用:接受用户请求中的数据h1> <hr/> <h3>基本类型和 String 类型作为参数h3> <a href="/one/show1?msg1=9527">发送请求1a> <a href="/one/show2?msg1=jdk&msg2=9527">发送请求2a> <h3>POJO 类型作为参数h3> <a href="/one/show3?eid=1&ename=郭凡&esex=小奶狗">发送请求3a> <form action="/one/show4" method="post"> 员工编号:<input type="text" name="eid" ><br/> 员工姓名:<input type="text" name="ename" ><br/> 员工性别:<input type="text" name="esex" ><br/> 部门编号:<input type="text" name="dept.did" ><br/> 部门名称:<input type="text" name="dept.dname" ><br/> <input type="submit" value="发送请求4"/> form> <form action="/one/map" method="post"> 员工编号:<input type="text" name="eids"><br/> 员工姓名:<input type="text" name="enames"><br/> 员工性别:<input type="text" name="esexs"><br/> <input type="submit" value="发送请求4(map)"/> form> <h3>POJO 类中包含集合类型参数h3> <form action="/one/show5" method="post"> 部门编号:<input type="text" name="did" ><br/> 部门名称:<input type="text" name="dname" ><br/> 员工编号1:<input type="text" name="mylist[0].eid" ><br/> 员工姓名1:<input type="text" name="mylist[0].ename" ><br/> 员工性别1:<input type="text" name="mylist[0].esex" ><br/> 员工编号2:<input type="text" name="mylist[1].eid" ><br/> 员工姓名2:<input type="text" name="mylist[1].ename" ><br/> 员工性别2:<input type="text" name="mylist[1].esex" ><br/> 员工编号3:<input type="text" name="myMap['one'].eid" ><br/> 员工姓名3:<input type="text" name="myMap['one'].ename" ><br/> 员工性别3:<input type="text" name="myMap['one'].esex" ><br/> 员工编号4:<input type="text" name="myMap['two'].eid" ><br/> 员工姓名4:<input type="text" name="myMap['two'].ename" ><br/> 员工性别4:<input type="text" name="myMap['two'].esex" ><br/> <input type="submit" value="发送请求5"/> form> <a href="/one/show6?nums=123&nums=456&nums=789">发送请求6a> <h3>使用 ServletAPI 对象作为方法参数h3> <a href="/one/show7">发送请求7a> body> html>success.html 访问成功页面
DOCTYPE html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>spring成功页面h1> body> html> -
创建POJO类:
Emp
public class Emp implements Serializable { private int eid; private String ename; private String esex; /*依赖对象Dep*/ private Dep dept; //get、set、toString()方法 }Dep
public class Dep { private int did; private String dname; //集合类型的参数 private List<Emp> mylist; private Map<String,Emp> myMap; //get、set、toString()方法 } -
控制器
@Controller @RequestMapping("one") public class UserController { @RequestMapping(path = "/show") public String show(){ return "one"; } // 一个参数,页面传过来参也得是msg1,且数据合法 @RequestMapping(path = "/show1") public String show1(int msg1){ System.out.println("show1-->msg1的参为:"+msg1); return "success"; } // 两个参,页面要传递msg1,msg2 @RequestMapping(path = "/show2") public String show2(String msg1,int msg2){ System.out.println("show2-->msg1==="+msg1+"msg2==="+msg2); return "success"; } // 页面传递时参数必须按照Emp实体类中属性的顺序进行传递 @RequestMapping(path = "/show3") public String show3(Emp emp){ System.out.println("show3-->对象参数emp:"+emp.toString()); return "success"; } // 对象中嵌套了一个对象,被嵌套的对象也需要按实体类中顺序传递 @PostMapping(path = "/show4") public String show4(Emp emp){ System.out.println("show4-->对象参数嵌套emp"+emp.toString()); return "success"; } // map接收数据必须要加@RequestParam注解 @PostMapping(path = "/map") public String map(@RequestParam Map map){ System.out.println(map); return "success"; } // Dep实体类中有List和Map类型的数据类型,用Dep类型接收 @RequestMapping("/show5") public String show5(Dep dept){ System.out.println("show5-->dept==="+dept); return "success"; } // 接收数组类型,页面传参:nums=1&nums=2$nums=3,多用于复选框 @RequestMapping("/show6") public String show6(int[] nums){ System.out.println("show6-->int[] 数组:"+ Arrays.toString(nums)); return "success"; } // 请求和响应的接收 @RequestMapping("/show7") public String show7(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){ System.out.println(request); System.out.println(response); request.getParameter("msg1"); HttpSession session = request.getSession(); System.out.println(session); session.setAttribute("",""); try { response.sendRedirect("重定向"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); return "success"; } } -
启动项目,浏览器访问localhost:8080/one/show,点击按钮超链接控制台即可打印传参
Spring MVC常用注释
@RequestParam
-
作用:
把请求中指定名称的参数给控制器中的形参赋值。
如果页面标签名称和方法参数名称不一致,可以使用此注解实现
-
属性:
name属性:设置参数名称
defaultValue属性:设置默认值
required属性:设置是否为必传
-
@RequestParam(“名称必须与页面标签或者url地址key名称一致”)
@RequestMapping("/show1")
public String show1(@RequestParam(name="msg1") String msg){
System.out.println("=====接受到用户发送数据为:"+msg+"=======");
return "success";
}
获取请求中的参数msg1赋值给msg
@RequestMapping("/show2")
public String show2(@RequestParam("msg1") String msg, @RequestParam("msg2") int num){
System.out.println("=====接受到用户发送数据为:"+msg+"=======");
System.out.println("=====接受到用户发送数据为:"+num+"=======");
return "success";
}
获取请求中的参数msg1赋值给msg,参数msg2赋值给num
@RequestMapping("/show3")
public String show4(@RequestParam(name = "uname",defaultValue = "暂无用户") String name){
System.out.println("账号:"+name);
return "success";
}
获取请求中的参数uname赋值给name,若uname为null,name则为:暂无用户
@RequestMapping("/show3")
public String show4(@RequestParam(name = "uname",required = false) String name){
System.out.println("账号:"+name);
return "success";
}
获取请求中的参数uname赋值给name,required=fales,uname是非必传参数
@RequestBody
-
作用:
用于获取"请求体"内容。直接使用得到是 key=value&key=value…
结构的数据,并可以转换为对象
-
属性:
required:是否必须有请求体。默认值是:true。
-
@RequestBody一般用于前后端分离,@RequestBody可以将json ----> javaBean
注意:前端不能使用GET方式提交数据,GET方式无请求体
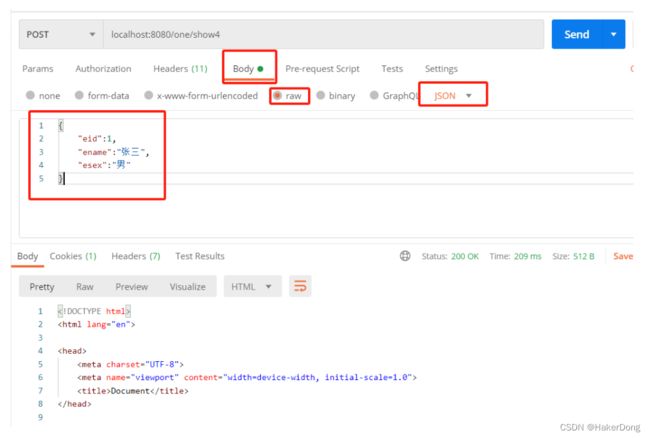
/*从请求获取到JSON格式*/
@RequestMapping("/show4")
public String show4(@RequestBody Emp emp){
System.out.println("=========="+emp+"==========");
return "success";
}
Postman模拟请求:
控制器获取请求中的Json格式将Json转换为Emp实体类
@PathVaribale
-
作用:
用于绑定 url 中的占位符。例如:请求 url 中 /delete/{id},这个{id}就是 url 占位符。url 支持占位符是 spring3.0 之后加入的。是 springmvc 支持 rest 风格 URL 的一个重要标志
-
属性:
value:用于指定url中占位符的名称
required:是否必须提供占位符。
-
Restful:
是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件
主要用于客户端和服务器交互类的软件,基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存机制等。
eg:localhost:8080/one/show/{uname}/{pwd}
Restful风格的请求是使用“url+请求方式”表示一次请求目的的,HTTP 协议里面四个表示操作方式的动词如下:
- GET:用于获取资源
- POST:用于新建资源
- PUT:用于更新资源
- DELETE:用于删除资源
例如:
/users/1 GET : 得到 id = 1 的 user
/users/1 DELETE: 删除 id = 1 的 user
/users/1/新名/新性 PUT: 更新 id = 1 的 user
/users/新名/新性 POST: 新增 user
@PostMapping("/show5/{uname}/{pwd}")
public String show5(@PathVariable("uname") String msg1, @PathVariable("pwd") String msg2){
System.out.println(msg1);
System.out.println(msg2);
return "success";
}
url:localhost/one/show5/tom/123456,请求url中携带数据占位符{uname}位置的值为tom,占位符{pwd}位置的值为123456,将uname值赋给msg1,pwd值赋给msg2
@PostMapping("/show6/{uname}/{pwd}")
public String show6(@PathVariable String uname, @PathVariable String pwd){
System.out.println(uname);
System.out.println(pwd);
return "success";
}
url:localhost/one/show5/tom/123456,当方法中的参数和占位符的名称相同时,只需要写注解@PathVariable,不需要再写value
@RequestHeader
-
作用:
用于获取请求消息头。
-
属性:
value:提供消息头名称
required:是否必须有此消息头
-
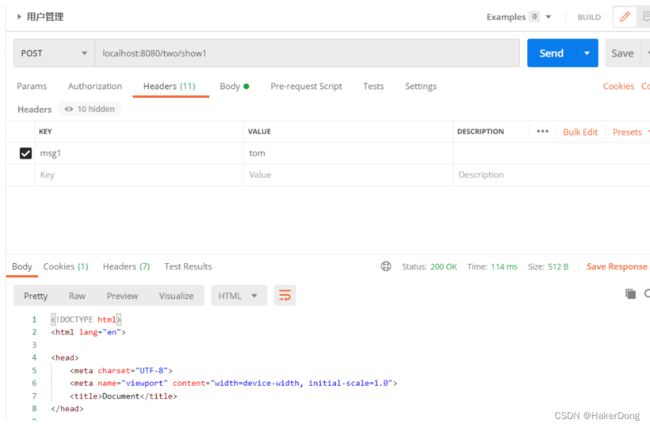
只获取头信息中的Accept-Language对应的数据
@RequestMapping("/show1")
public String show1(@RequestHeader(value = "msg1")String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
return "test";
}
获取Headers中的信息:msg1赋值给msg
@CookieValue
-
作用:
用于把指定 cookie 名称的值传入控制器方法参数
-
属性:
value:指定 cookie 的名称
required:是否必须有此 cookie
@RequestMapping("/show2")
public String show2(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID",required = false)String jsessionid){
System.out.println(jsessionid);
return "test";
}
浏览器中请求url:localhost:8080/show2,获取Cookie中的JSESSIONID赋值给jseesionid
第一次访问时,jsessionid为null
第二次访问起,jsessionid有值
Spring MVC数据传递
String
返回值为页面名称
@RequestMapping("/show1")
public String show1(){
System.out.println("=========show1=========");
return "success_String";
}
充当视图的逻辑名称,默认页面跳转为请求转发方式
redirect:show1
@RequestMapping("/show2")
public String show2(){
System.out.println("=========show2=========");
return "redirect:show1";
}
redirect:重定向到show1
forward:show1
@RequestMapping("/show3")
public String show3(){
System.out.println("=========show3=========");
return "forward:show1";
}
forward:转发到show1
session存储参数
@RequestMapping("/show4")
public String show4(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("=========show4=========");
//1.查询数据库(模拟)
Emp emp = new Emp(1,"张毅老师","男");
//2.获取session
request.getSession().setAttribute("emp",emp);
return "success_String";
}
Json
返回值为Json字符串,主要用于前后端分离
@ResponseBody
-
作用:
对象====>json
-
位置:
- 类
- 方法
@RequestMapping("/show1")
@ResponseBody
public List<Emp> show1(){
//1模拟数据库
Emp emp1 = new Emp(1,"张三","男");
Emp emp2 = new Emp(2,"李四","男");
Emp emp3 = new Emp(3,"王五","男");
List<Emp> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(emp1);
list.add(emp2);
list.add(emp3);
return list;
}
页面显示一个json格式的字符串
@RequestBody
-
作用:
json====>对象
-
位置:
方法参数
@RequestMapping("/show2")
@ResponseBody
public String show2(){
return "helloWorld";
}
页面显示字符串“helloworld”
@RestController=@Controller + @ResponseBody
若添加了@RestController注解的类,类不需要写@Controller、返回Json的方法也不需要写@ResponseBody
Spring MVC上传文件
上传文件可以存储在本地物理磁盘,但存储磁盘占用内存,成本高,开销大,不建议
还可以上传到云服务器进行存储,采用技术为:七牛云
七牛云
七牛云官网
存储空间名称:按要求起名字
存储区域:选择地理位置近的
访问控制:选择公开
上传文件至七牛云
-
创建SpringBoot Web项目
-
pom文件导坐标
除web启动器和test启动器外,还需要导入enjoy、七牛云、上传文件的坐标
<dependency> <groupId>com.jfinalgroupId> <artifactId>enjoyartifactId> <version>5.0.3version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.qiniugroupId> <artifactId>qiniu-java-sdkartifactId> <version>7.2.25version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3groupId> <artifactId>okhttpartifactId> <version>3.14.2version> <scope>compilescope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gsongroupId> <artifactId>gsonartifactId> <version>2.8.5version> <scope>compilescope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.qiniugroupId> <artifactId>happy-dns-javaartifactId> <version>0.1.6version> <scope>testscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-iogroupId> <artifactId>commons-ioartifactId> <version>2.6version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId> <artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId> <version>1.3.3version> dependency> -
添加enjoy模板配置类,此处省略
-
页面,存放在resources下的templates目录
index.html
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文件上传title> head> <body> 文件上传: <ol> <li>坐标li> <li>制作页面-form表单编码li> <li>通过*****接受文件li> ol> <hr/> <form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 用户名:<input name="uname"/><br/> 图片:<input name="upic" type="file"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> form> body> html>success.html
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文件上传title> head> <body> <h1>成功页面h1> <div> <img src="http://s3e0wu5bp.hb-bkt.clouddn.com/#(session.picname)"> div> body> html>img标签的src拼接路径是七牛云空间的外链域名+文件名
-
控制器
@Controller public class OneController { //进入测试页面 @RequestMapping("/show") public String show(){ return "index"; } //文件上传 @RequestMapping("/fileupload") public String fileupload(String uname, MultipartFile upic, HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("用户名:"+uname); System.out.println(upic); System.out.println(upic.getOriginalFilename()); System.out.println(upic.getName()); //方式1.将文件upic以流的方式写入当前服务器磁盘(应用服务器) //方式2.文件服务器(七牛云) //构造一个带指定 Region 对象的配置类 Configuration cfg = new Configuration(Region.autoRegion()); //...其他参数参考类注释 UploadManager uploadManager = new UploadManager(cfg); //...生成上传凭证,然后准备上传 String accessKey = "iUMJ8ouFFclMTRnz6Us-aZzbP1qoYa4W2-LQL4pk"; String secretKey = "YeSnxdjbjs2DSGuKNIXqH2uva-HGwWcqGdVpWAJi"; String bucket = "programmerdong"; //默认不指定key的情况下,以文件内容的hash值作为文件名 String key = null; String name = null; try { byte[] uploadBytes = upic.getBytes(); Auth auth = Auth.create(accessKey, secretKey); String upToken = auth.uploadToken(bucket); try { Response response = uploadManager.put(uploadBytes, key, upToken); //解析上传成功的结果 DefaultPutRet putRet = new Gson().fromJson(response.bodyString(), DefaultPutRet.class); System.out.println(putRet.key);//获取文件名 System.out.println(putRet.hash);//获取文件hash值 name = putRet.key; } catch (QiniuException ex) { Response r = ex.response; System.err.println(r.toString()); try { System.err.println(r.bodyString()); } catch (QiniuException ex2) { //ignore } } } catch (Exception ex) { //ignore } request.getSession().setAttribute("picname",name); return "success"; } }
注册Servlet三大组件
三大组件:Servlet、Filter、Listener
方式一注解
pom.xml坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
-
@WebServlet:注入Servlet
@WebServlet("/myservlet") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("进入servlet"); resp.getWriter().println("Hello Servlet
"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doGet(req, resp); } } -
@WebFilter:注入Filter
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/*"}) public class MyFilter implements Filter { public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("============请求过滤"); request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //分水岭 chain.doFilter(request, response); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); System.out.println("============响应过滤"); } } -
@WebListener:注入Listener
@WebListener public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("ServletContext创建"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("ServletContext销毁"); } } -
程序主启动器还需要添加注解@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class SpringbootWeb06Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootWeb06Application.class, args); } }
测试:浏览器访问结果
方式二配置类
pom.xml文件与方式一相同,存在springboot web环境就可以
配置类的方式不需要再写各自的注解:
-
ServletRegistrationBean:注册自定义Servlet
-
FilterRegistrationBean:注册自定义Filter
-
ServletListenerRegistrationBean:注册自定义Listener
-
配置类:
@Configuration public class MyConfig { //注册Servlet //替换:@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/myServlet") @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean doServlet() { ServletRegistrationBeanbean = new ServletRegistrationBean (); bean.setServlet(new MyServlet()); bean.setUrlMappings(Arrays.asList("/servlet")); bean.setLoadOnStartup(1); return bean; } //注册Filter @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean doFilter(){ FilterRegistrationBean filter = new FilterRegistrationBean(); filter.setFilter(new MyFilter()); filter.addUrlPatterns("/*"); return filter; } //注册Listener @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean doListener(){ //关闭监听器切记不要直接点击红色按钮,太暴力,点击控制台左侧exist ServletListenerRegistrationBean listener = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(); listener.setListener(new MyListener()); return listener; } } -
Servlet、Filter、Listener和方式一中相同,注解去掉
-
程序的主启动器不需要再添加格外注解
-
测试结果与方式一相同
切换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器
SpringBoot 默认针对Servlet容器提供以下支持:
- Tomcat(默认使用)
- Jetty :支持长连接项目(如:聊天页面)[ˈdʒeti]
- Undertow : 不支持 JSP , 但是并发性能高,是高性能非阻塞的容器[ˈʌndətəʊ]
-
默认Tomcat容器
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcatartifactId> <version>2.1.0.RELEASEversion> <scope>compilescope> dependency> -
切换Jetty容器
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcatartifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> exclusion> exclusions> dependency> <dependency> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jettyartifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> dependency>切换Jetty容器首先需要将tomcat移除,在引入其他容器
-
使用外置Servlet容器omcat9.x
嵌入式Servlet容器:运行启动类就可启动,或将项目打成可执行的 jar 包
优点:简单、快捷;
缺点:默认不支持JSP、优化定制比较复杂使用定制器,
还需要知道每个功能的底层原理
外置Servlet容器:配置 Tomcat, 将项目部署到Tomcat中运行
restFul
REST 指的是一组架构约束条件和原则,rest原则有部分组成: URL定位资源,HTTP动词操作(GET,POST, PUT,DELETE) 描述操作。
满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是 RESTful。
设计RESTful风格的API:
-
在RESTful风格的架构中, 每个网址代表一种资源,所以网址中不能有动词,只能有名词。而且所用的名词往往与数据库的表名对应
-
HTTP动词设计: GET (获取资源) POST (新建资源) PUT (更新资源,客户端提供改变后的完整资源)DELETE (删除资源)
请求方式 含义
GET /zoos 列出所有动物园
POST /zoos 新建一个动物园
GET /zoos/ID 获取某个指定动物园的信息
在spring-boot-starter-web 启动器中默认引入了tomcat容器
PUT /zoos/ID 更新某个指定动物园的信息(提供该动物园的全部信息)
DELETE /zoos/ID 删除某个动物园
GET /zoos/lD/animals 列出某个指定动物园的所有动物
DELETE /zoos/lD/animals/ID 删除某个指定动物园的指定动物