C语言中什么时候用“->”
使用说明
"->"是C语言中的一个运算符,它用于访问结构体或者联合体中的成员,其左边是一个指向结构体或者联合体的指针,右边是需要访问的成员名。
举例说明
定义结构体
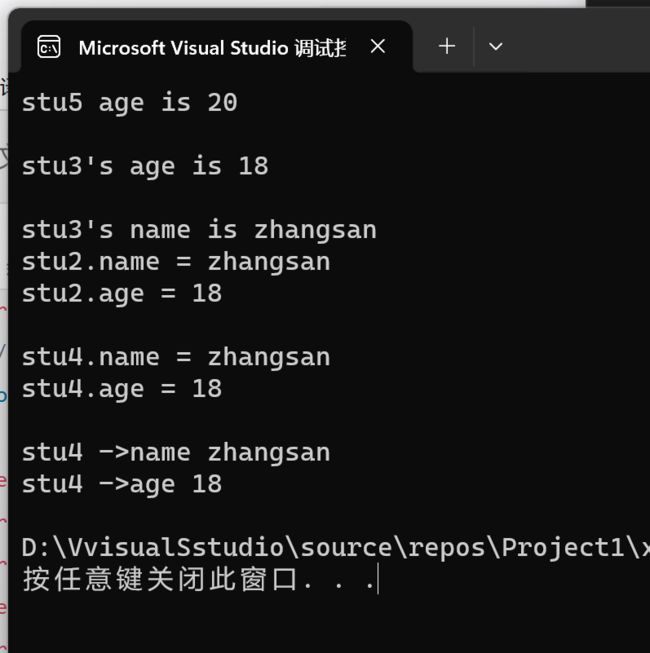
# include printf("stu4 ->name %s\n", stu4->name); // %s 输出字符串
printf("stu4 ->age %d\n", stu4->age); // %d 输出整数类型
以及
printf("stu3's age is %d\n\n", stu3->age); // pointer structure variable
// 结构变量
printf("stu3's name is %s\n", stu3->name);// 用箭头访问name的地址
用到取指针中的值