二叉树——刷题笔记
索引目录
- 翻转二叉树
- 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 二叉树展开为链表
- 最大二叉树
- 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 寻找重复的子树
- 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
- 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
- 验证二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
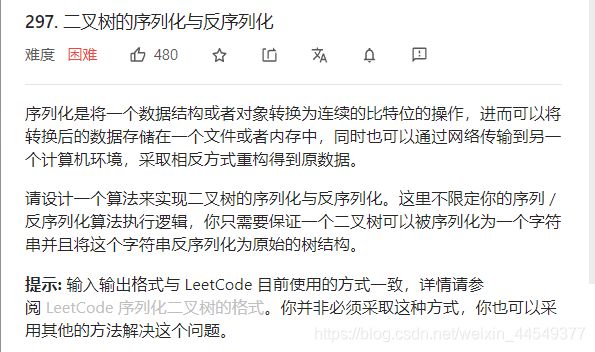
- 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
1、写递归算法的关键是要明确函数的 「定义」 是什么,然后相信这个定义,利用这个定义推导最终结果,绝不要跳入递归的细节。
2、写树相关的算法,先搞清楚 当前 root 节点 该做什么,然后根据函数定义递归调用子节点,递归调用会让孩子节点做相同的事情。
3、二叉树题目的一个难点就是,如何把题目的要求细化成每个节点需要做的事情。
4、核心框架:前序、中序、后序遍历
5、对于构造二叉树的问题,根节点要做的就是把想办法把自己构造出来。
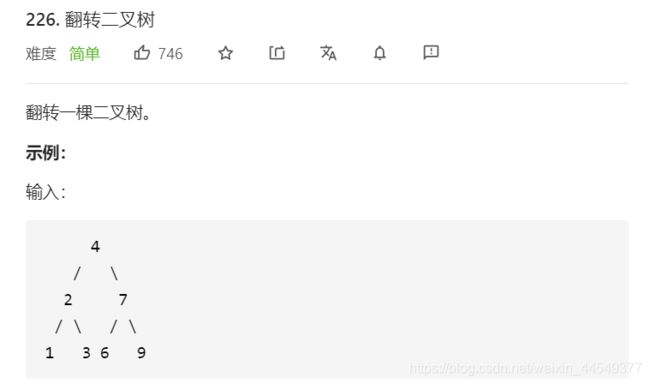
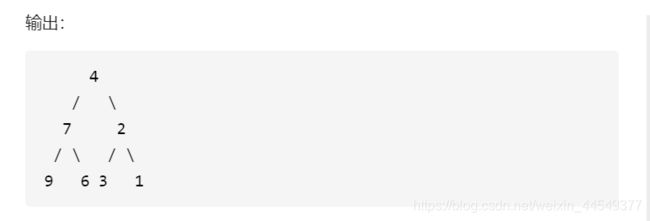
翻转二叉树
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return root;
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = tmp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
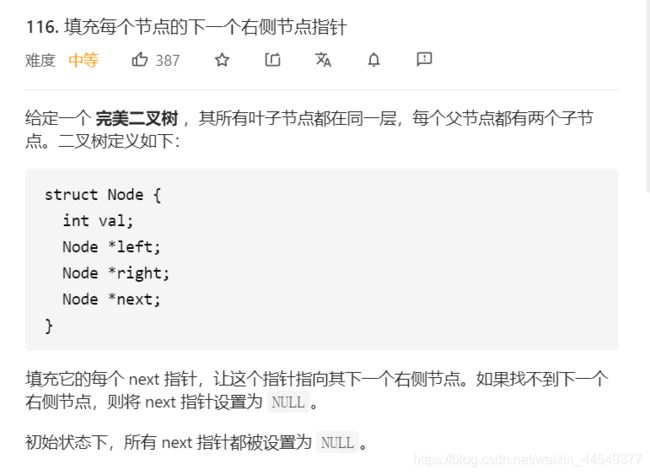
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root == null || root.left == null) return root;
connectTwoNode(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
//辅助函数
public void connectTwoNode(Node left, Node right){
if(left == null || right == null) return;
left.next = right;
connectTwoNode(left.left, left.right);
connectTwoNode(left.right, right.left);
connectTwoNode(right.left, right.right);
}
}
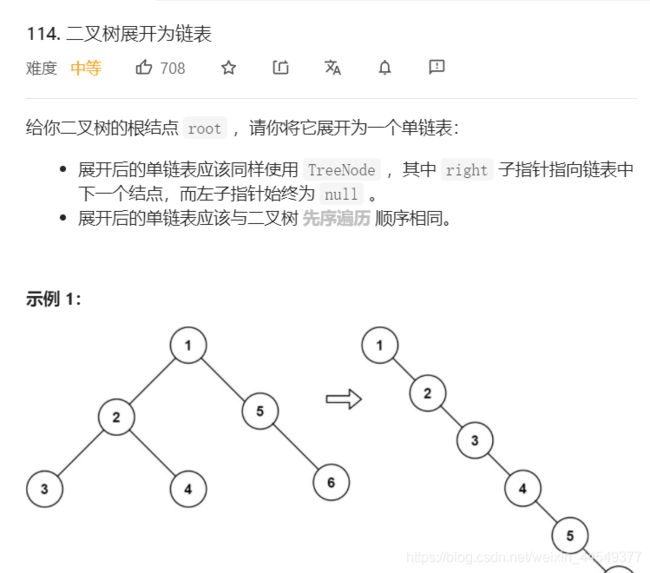
二叉树展开为链表
//自底向上,先把root的左子树left放到右边,再把原来的右子树接到left(新的右子树,也就是原来的左子树)后面
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
TreeNode cur_left = root.left;
TreeNode cur_right = root.right;
root.left = null;
root.right = cur_left;//把左子树放到右边
//这里是为了找到新的右子树的最后一个节点,也就是接入点
TreeNode tmp = root;
while(tmp.right != null){
tmp = tmp.right;
}
tmp.right = cur_right;//接上原来的右子树
}
}
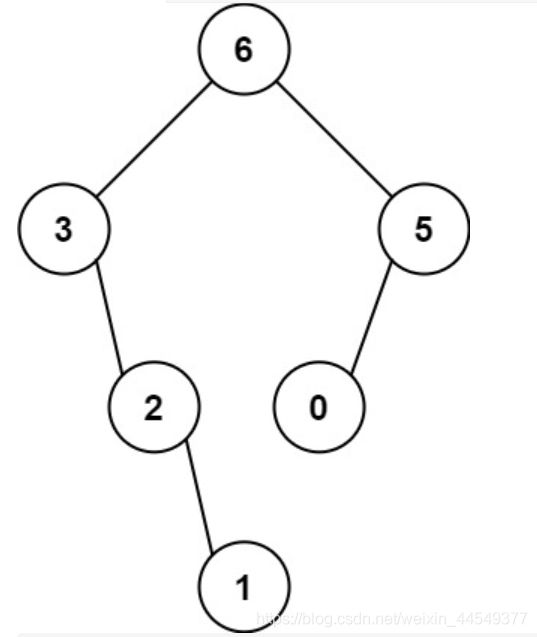
最大二叉树
//对于每个根节点,只需要找到当前nums中的最大值和对应的索引,然后递归调用左右数组构造左右子树即可。
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return null;
return build(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] nums, int left, int right){
if(left > right) return null;
int maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE, idx = -1;
for(int i=left; i<=right; i++){
if(nums[i] > maxVal){
maxVal = nums[i];
idx = i;
}
}
//递归二叉树关键:明确每个节点要做的事情
//这个题每个节点要做的事情,就是在当前数组中找到最大的,并将其作为根
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
//然后递归调用,完成左右子树
root.left = build(nums, left, idx-1);
root.right = build(nums, idx+1, right);
return root;
}
}
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
//要想办法确定根节点的值,把根节点做出来,然后递归构造左右子树即可。
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0) return null;
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length-1, inorder, 0, inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd){
if(preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) return null;
int rootVal = preorder[preStart], idxAtInorder = -1;
for(int i=inStart; i<=inEnd; i++){
if(inorder[i] == rootVal){
idxAtInorder = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
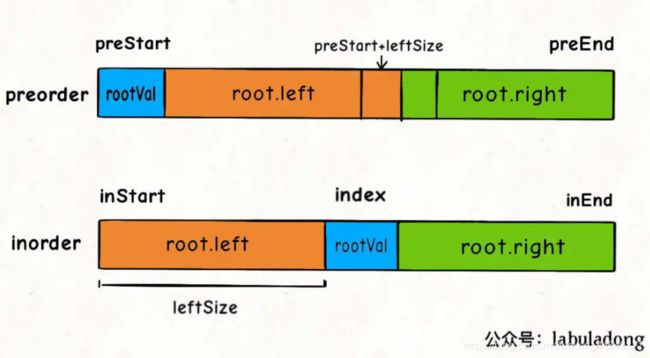
//确定了递归之后,另一个关键点在此处,怎么确定两个数组的新参数?
//尤其是索引位置,很简单,画图
int leftSize = idxAtInorder - inStart;
root.left = build(preorder, preStart+1, preStart+leftSize, inorder, inStart, idxAtInorder-1);
root.right = build(preorder, preStart+leftSize+1, preEnd, inorder, idxAtInorder+1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
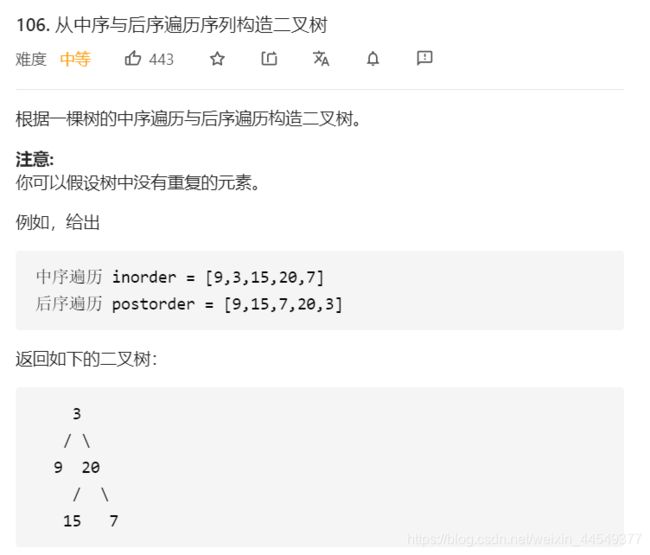
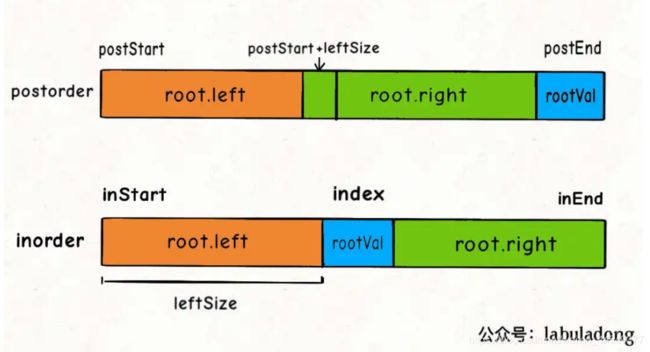
思路和上一题一样,唯独就是后序遍历和前序遍历传入索引参数的时候有点区别
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(inorder.length == 0 || postorder.length == 0) return null;
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length-1, postorder, 0, postorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd){
if(inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) return null;
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd], idxAtInorder = -1;
for(int i=inStart; i<=inEnd; i++){
if(inorder[i] == rootVal){
idxAtInorder = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
int leftSize = idxAtInorder - inStart;
root.left = build(inorder, inStart, idxAtInorder-1, postorder, postStart, postStart+leftSize-1);
root.right = build(inorder, idxAtInorder+1, inEnd, postorder, postStart+leftSize, postEnd-1);
return root;
}
}
寻找重复的子树
1、以我为根的这棵二叉树(子树)长啥样?
通过拼接字符串的方式把二叉树序列化,使用后序遍历
2、以其他节点为根的子树都长啥样?
使用hashmap存储出现过的子树和次数
class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<>();
public HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
reverse(root);
return list;
}
public String reverse(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return "#";
String leftTree = reverse(root.left);
String rightTree = reverse(root.right);
String res = leftTree + "," + rightTree + "," + root.val;
if(map.get(res) == null){
map.put(res, 1);
}else{
if(map.get(res) == 1){
list.add(root);
}
map.put(res, map.get(res)+1);
}
return res;
}
}
二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
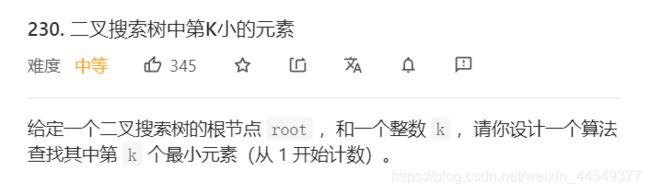
中序遍历,就是从小到大的顺序,记录排名,到第K个返回,停止递归。
但注意这不是最优解法。只是用于理解和训练递归思维。
class Solution {
public int res = 0, count = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
reverse(root, k);
return res;
}
public void reverse(TreeNode root, int k){
if(root == null) return;
reverse(root.left, k);
count++;
if(count == k){
res = root.val;
return;
}
reverse(root.right, k);
}
}
把二叉搜索树转换为累加树

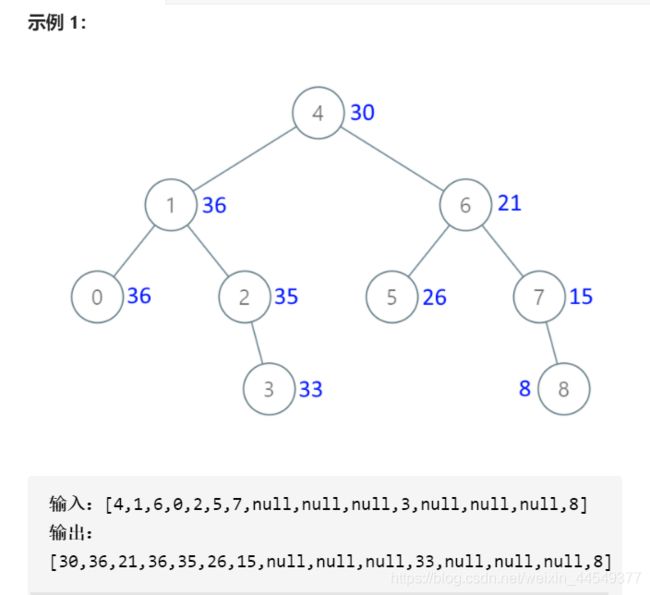
利用中序遍历特性,从右向左遍历,这样每遍历一次,进行一次求和计算,将sum值赋给当前节点,就完成了累加树的计算。
class Solution {
public int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
recur(root);
return root;
}
public void recur(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
recur(root.right);
sum += root.val;
root.val = sum;
recur(root.left);
}
}
验证二叉搜索树
二叉树算法小技巧:
通过使用辅助函数,增加函数参数列表,在参数中携带额外信息,将这种约束传递给子树的所有节点。
/* 限定以 root 为根的子树节点必须满足 max.val > root.val > min.val */
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return recur(root, null, null);
}
public boolean recur(TreeNode root, TreeNode min, TreeNode max){
if(root == null) return true;
if(min != null && min.val >= root.val) return false;
if(max != null && max.val <= root.val) return false;
return recur(root.left, min, root) && recur(root.right, root, max);
}
}
二叉搜索树中的搜索
//利用二叉搜索树的性质,代码有套路,找到怎么样,大于怎么样,小于怎么样
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root.val == val) return root;
TreeNode res = null;
if(root.val > val){
res = searchBST(root.left, val);
}
if(root.val < val){
res = searchBST(root.right, val);
}
return res;
}
}
二叉搜索树中的插入操作
//沿用BST的套路模板
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
if(root.val < val){
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
}
if(root.val > val){
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
}
return root;
}
}
删除二叉搜索树中的节点


关键在于,如果删除的节点的左右子树都不为空,怎么处理。
删除自己后,找谁替代自己?——右子树的最小值,也就是右子树的左子树,单独写一个getMin函数进行寻找。
找到之后呢?把右子树最小值的val赋给自己。
那么右子树怎么办呢?右子树要把这个最小值所在的节点删掉。
怎么删呢?递归调用自己删除,传入的参数变为(root.right, minInRight.val)
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root.val == key){
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
root = null;
return root;
}else if(root.left != null && root.right == null){
root = root.left;
return root;
}else if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
root = root.right;
return root;
}else if(root.left != null && root.right != null){
TreeNode minInRight = getMin(root.right);
root.val = minInRight.val;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minInRight.val);
}
}
if(root.val < key){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
if(root.val > key){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}
return root;
}
public TreeNode getMin(TreeNode root){
while(root.left != null) {
root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
}
二叉树的序列化与反序列化
//方法一,层次遍历
public class Codec {
public String SEP = ",";
public String NULL = "#";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return "";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
if(cur == null){
sb.append(NULL).append(SEP);
continue;
}
sb.append(cur.val).append(SEP);
q.offer(cur.left);
q.offer(cur.right);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data.isEmpty()) return null;
String[] nodes = data.split(SEP);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(nodes[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
for(int i=1; i<nodes.length;){
TreeNode parent = q.poll();
String leftVal = nodes[i++];
if(leftVal.equals(NULL)){
parent.left = null;
}else{
parent.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(leftVal));
q.offer(parent.left);
}
String rightVal = nodes[i++];
if(rightVal.equals(NULL)){
parent.right = null;
}else{
parent.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(rightVal));
q.offer(parent.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
//方法二,递归方法
public class Codec {
public String SEP = ",";
public String NULL = "#";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
tranverse(root, sb);
return sb.toString();
}
public void tranverse(TreeNode root, StringBuilder sb){
if(root == null) {
sb.append(NULL).append(SEP);
return;
}
sb.append(root.val).append(SEP);
tranverse(root.left, sb);
tranverse(root.right, sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] nodes = data.split(",");
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
for(String node: nodes){
list.addLast(node);
}
return deserialize(list);
}
public TreeNode deserialize(LinkedList<String> list){
if(list.isEmpty()) return null;
String node = list.removeFirst();
if(node.equals(NULL)) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(node));
root.left = deserialize(list);
root.right = deserialize(list);
return root;
}
}