Leetcode 算法题合集
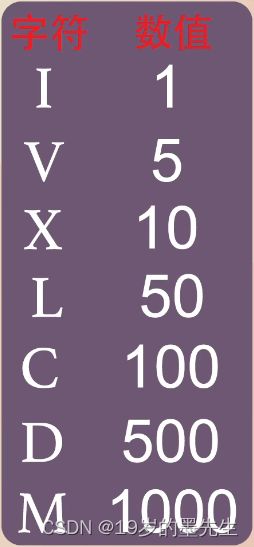
1. 罗马数字转整数
如图:输入 I,返回 1;输入 IV,返回 4…
const obj = {
'I': 1,
'V': 5,
'X': 10,
'L': 50,
'C': 100,
'D': 500,
'M': 1000
}
function romanToInt(s) {
const length = s.length
let result = 0
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const front = s[i]
const back = s[i + 1]
if (obj[back] > obj[front]) {
result -= obj[front]
} else {
result += obj[front]
}
}
return result
}
const a = romanToInt('MMDC')
const b = romanToInt('DXI')
const c = romanToInt('V')
console.log(a, b, c) // 2600 511 5
2. 整数反转
function reverseInt(x) {
const min = Math.pow(-2, 31)
const max = Math.pow(2, 31)
const sign = Math.sign(x)
x = Math.abs(x)
let result = 0
let remainder = 0
while (x > 0) {
remainder = x % 10
x = (x - remainder) / 10
result = result * 10 + remainder
}
result *= sign
if (result < min || result > max) return 0
return result
}
const a = reverseInt(123)
const b = reverseInt(-45678)
console.log(a, b) // 321 -87654
3. 两数之和
const nums = [2, 7, 11, 15]
const target = 26
function twoSum(nums, target) {
const box = new Map()
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (box[target - nums[i]] >= 0) {
return [box[target - nums[i]], i]
}
// 以数组的值为键,索引为值存储到新对象
box[nums[i]] = i
}
}
console.log(twoSum(nums, target)) // [2, 3]
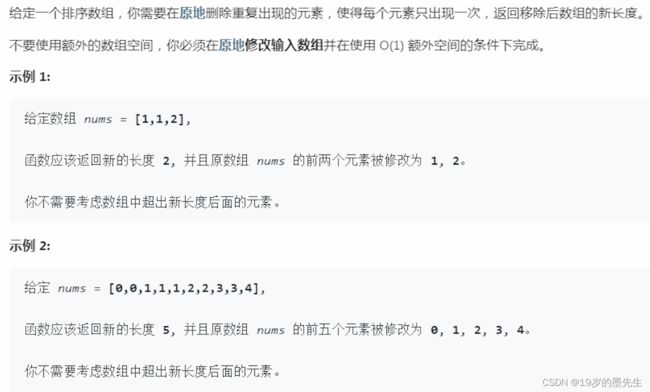
4. 删除排序数组的重复项
// 遍历移除法
const nums = [1, 1, 2]
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) {
nums.splice(i, 1)
i--
}
}
console.log(nums) // [1, 2]
console.log(nums.length) // 2
// 双指针法
const nums = [2, 2, 4, 4, 4, 6]
let length = 0
for (let father = 0, child = 0; father < nums.length; father++) {
if (nums[child] !== nums[father]) {
child++
nums[child] = nums[father]
}
length = child
}
console.log(nums) // [2, 4, 6, 4, 4, 6]
console.log(length + 1) // 3
5. 统计素数
// 暴力算法
function statisticalPrime(n) {
let count = 0
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
count += isPrime(i) ? 1 : 0
}
return count
}
function isPrime(x) {
// 一个数若可以进行因素分解,那么分解时得到的两个数一定是一个小于等于 sqrt(x),一个大于等于 sqrt(x)
// 例如 16 拆成 2 * 8 或 4 * 4 都满足上述条件,所以在遍历的时候只需到 x 的平方根
for (let i = 2; i * i <= x; i++) {
if (x % i === 0) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
console.log(statisticalPrime(10)) // 4
console.log(statisticalPrime(100)) // 25
// 埃筛法 筛选合数,减少遍历次数
function statisticalPrime(n) {
const primes = Array.from({ length: n }, () => true) // 将素数标记为 true
let count = 0
for (let i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (primes[i]) {
count++
for (let j = i * i; j < n; j += i) {
primes[j] = false // 将合数标记为 false
}
}
}
return count
}
console.log(statisticalPrime(10)) // 4
console.log(statisticalPrime(100)) // 25
6. 无重复字符的最长字串
输入 ‘abcabcbb’, 最长 ‘abc’, 输出 3
输入 ‘pwwkew’, 最长 ‘kew’, 输出 3
function lengthOfLongestSubstring(s) {
const set = new Set()
let maxLength = 0
for (let i = 0, j = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
const curr = s[i]
if (!set.has(curr)) {
set.add(curr)
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, set.size)
} else {
while (set.has(curr)) {
set.delete(s[j])
j++
}
set.add(curr)
}
}
return maxLength
}
console.log(lengthOfLongestSubstring('abcabcbb')) // 3
console.log(lengthOfLongestSubstring('pwwkew')) // 3
7. 最长回文字符串
输入 ‘babad’, 输出 ‘bab’
输入 ‘cbbd’, 输出 ‘bb’
/* 解题步骤
* 1. 如果字符串长度小于 2, 直接返回字符串
* 2. 定义两个变量, 一个 start 存储当前找到的最大回文字符串的起始位置, 另一个 maxLength 记录字符串的长度
* 3. 创建一个 helper function, 判断左边和右边是否越界, 同时最左边的字符是否等于最右边的字符
* 如果三个条件都满足, 则判断是否需要更新回文字符串最大长度及最大字符串的起始位置
* 然后将 left--, right++, 继续判断, 直到不满足三个条件之一
* 4. 遍历字符串, 每个位置调用 helper function 两遍。第一遍检查 i-1, i+1; 第二遍检查 i, i+1
*/
function longestPalindrome(s) {
if (s.length < 2) return s
let start = 0
let maxLength = 1
function exoandAroundCenter(left, right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length && s[left] === s[right]) {
if (right - left + 1 > maxLength) {
maxLength = right - left + 1
start = left
}
left--
right++
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
exoandAroundCenter(i - 1, i + 1)
exoandAroundCenter(i, i + 1)
}
return s.substr(start, maxLength)
}
console.log(longestPalindrome('babad')) // bab
console.log(longestPalindrome('cbbd')) // bb
8. 三数之和
输入一个有序数组 [-4, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2], 计算三数之和等于0, 输出 [[-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2]]
注意不能出现相同的数组
function threeSum(nums) {
const result = []
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (i !== 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue
let start = i + 1, end = nums.length - 1
while(start < end) {
let sum = nums[i] + nums[start] + nums[end]
if (sum === 0) {
result.push([nums[i], nums[start], nums[end]])
start++
end--
while(start < end && nums[start] === nums[start - 1]) {
start++
}
while(start < end && nums[end] === nums[end + 1]) {
end--
}
} else if (sum > 0) {
end--
} else {
start++
}
}
}
return result
}
console.log(threeSum([-4, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2])) // [[-1, -1, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]
9. 有效的括号
输入 ‘({}[]){}’, 输出 true
输入 ‘{}()[’, 输出 false
解题步骤
- 创建一个 HashMap,把括号配对放进去
- 创建一个 stack(array),for 循环遍历字符串,对于每一个字符
- 如果 map 里有这个 key,那说明它是个左括号,从 map 里取得相对应的右括号,把它 push 进 stack 里
- 否则的话,它就是右括号,需要 pop 出 stack 里的第一个字符,然后看它是否等于当前的字符。如果不相符,则返回 false
- 循环结束后,如果 stack 不为空,说明还剩下左括号没有被闭合,返回 false。否则返回 true
function isValid(s) {
const map = new Map()
map.set('(', ')')
map.set('{', '}')
map.set('[', ']')
const stack = []
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (map.has(s[i])) {
stack.push(map.get(s[i]))
} else {
if (stack.pop() !== s[i]) {
return false
}
}
}
if (stack.length) return false
return true
}
console.log(isValid('({}[]){}')) // true
console.log(isValid('{}()[') // false
10. 反转链表
function ListNode(val) {
this.val = val
this.next = null
}
function reverseList(head) {
// 1.创建两个变量,一个是未反转的链表指针,另一个是反转后的链表
let cur = head
let prev = null
// 2.递归遍历未反转的链表
while (cur) {
// 3.修改 next 指针,并且当前链表指针向前继续遍历,直到 next 等于 null
const tmp = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = tmp
}
return prev
}
11. Group Anagrams
/*
* 1.检查数组是否为空数组
* 2.遍历字符串数组
* 3.建立一个长度为26的数组,起始值为0;建立一个 hashMap
* 字母每出现一次,对应索引就加一;a -> 0、b -> 1、c -> 2 ......
* 4.遍历数组的字符串,将字母的出现频率放到数组的对应位置里
* 利用 ascii 码, a -> 97、b -> 98、c -> 99 ......
* 5.将长度为26的数组转成字符串当 map 的 key
* 6.判断 key 是否存在
* 存在:合并
* 不存在:直接添加
* 7.遍历map,将结果返回
*/
function groupAnagrams(strs) {
if (!strs.length) return []
const map = new Map()
for (const str of strs) {
const characters = Array(26).fill(0)
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const ascii = str.charCodeAt(i) - 97
characters[ascii]++
}
const key = characters.join('')
if (map.has(key)) {
map.set(key, [...map.get(key), str])
} else {
map.set(key, [str])
}
}
const result = []
for (const value of map.values()) {
result.push(value)
}
return result
}
12. 最大子序和
function maxSubArray(nums) {
const memo = []
memo[0] = nums[0]
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
memo[i] = Math.max(nums[i] + memo[i - 1], nums[i])
}
const max = Math.max.apply(null, memo)
return max
}
console.log(maxSubArray([1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4])) // 6
13. 不同路径
function uniquePaths(m, n) {
const memo = []
// 1. push 二维数组, m 为横轴
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
memo.push([])
}
// 2. 横向填充 1
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
memo[row][0] = 1
}
// 3. 纵向填充 1
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
memo[0][col] = 1
}
// 4. 填充每个格子数
for (let row = 1; row < m; row++) {
for (let col = 1; col < n; col++) {
memo[row][col] = memo[row - 1][col] + memo[row][col - 1]
}
}
// 5. 求最大值
return memo[m - 1][n - 1]
}
console.log(uniquePaths(3, 2)) // 3
console.log(uniquePaths(7, 3)) // 28
14. 爬楼梯
function climbStairs(n) {
// 1. 初始化
const memo = [0, 1, 2]
// 2. 根据规律,后面的每一项都等于前两项之和
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
memo[i] = memo[i - 2] + memo[i - 1]
}
return memo[n]
}
console.log(climbStairs(2)) // 2
console.log(climbStairs(3)) // 3
15. 求子集
function subSets(nums) {
const result = []
function backtrack(start, curr) {
// 1. 把 curr 添加到 result
result.push([...curr])
// 2. 循环
for (let i = start, len = nums.length; i < len; i++) {
// 2.1 把numsi]加入curr数组
curr.push(nums[i])
// 2.2 backtrack(i+1,curr)
backtrack(i + 1, curr)
// 2.3 把curr数组的最后一个元素移除
curr.pop()
}
}
backtrack(0, [])
return result
}
console.log(JSON.stringify(subSets([1, 2, 3]))) // [[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3],[2],[2,3],[3]]