拓扑排序详解及C++实现
拓扑排序详解及C++实现
定义
百度百科定义如下:
拓扑排序,是对一个有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph简称DAG)G进行拓扑排序,是将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v,若边(u,v)∈E(G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前。
很显然这一段话不是人话十分晦涩难懂,令人深思。
有向无环图
图论基础知识可以参考图论(一)基本概念_图论是什么_翟羽嚄的博客-CSDN博客。
需要注意:有向无环图不一定是树,例如:
拓扑序列
对于一个有向无环图将图中的顶点排成一个序列,其中每个边的起点在序列中一定在终点之前;
(↑↑ 不是人话
通俗一点解释为:将一张图“压扁”,使顶点从左到右排成序列,且压扁后每条边的方向只能朝右,那么这个序列是这张图的拓扑序列。
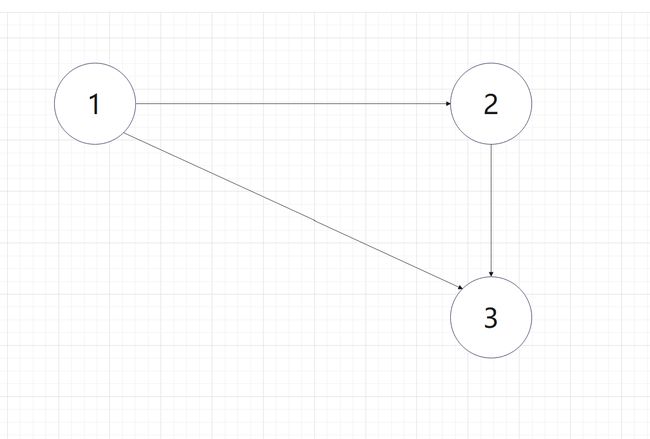
例如这张图:
其拓扑序列为1-2-4-3:
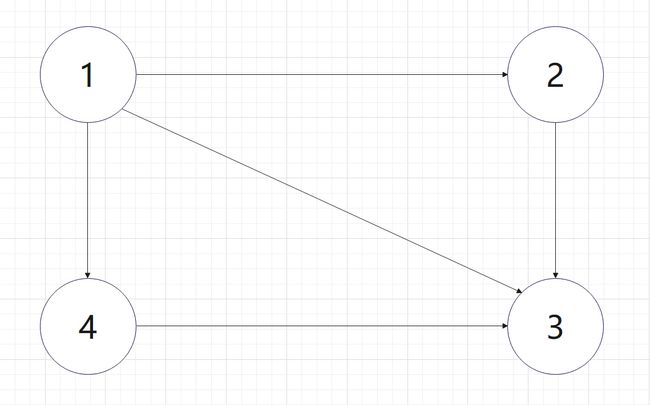
对于同一张图,可能存在不止一个拓扑序列。例如上图的另一个拓扑序列为1-4-2-3:
拓扑排序
那么拓扑排序可表示为:计算一个有向无环图的拓扑序列。
逻辑
拓扑排序的逻辑如下:
- 集合 S S S表示所有入度为0的点;队列 L L L表示拓扑序列。初始时为空。
- 找到所有入度为0的点,放入 S S S中。
- 从 S S S中取出一个点 u u u,放入 L L L中。
- 在图中删除 s s s,并删除所有以 s s s为起点的边。
- 重复2~4,直到 S S S为空。
手动模拟拓扑排序的步骤如下:
手动模拟内容较长,如已经理解可以跳过
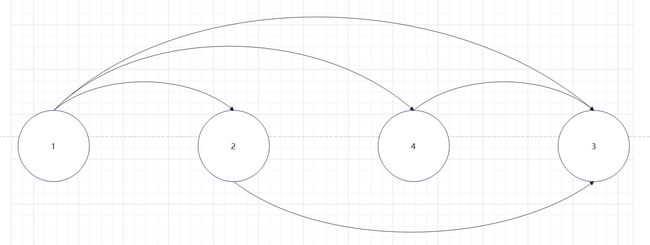
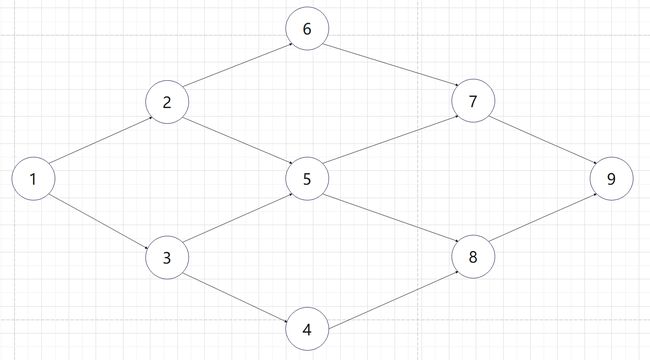
对于这张图:
其中入度为0的点为1,因此 S S S和 L L L初始化如下:
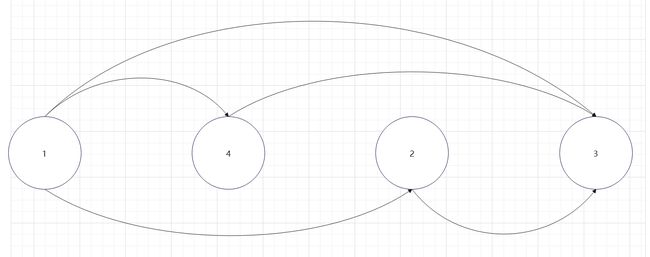
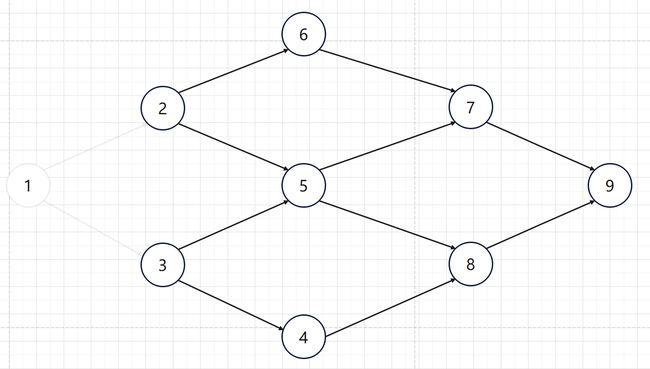
将1从 S S S中取出并放入 L L L:
删除点1和所有以1为起点的边:
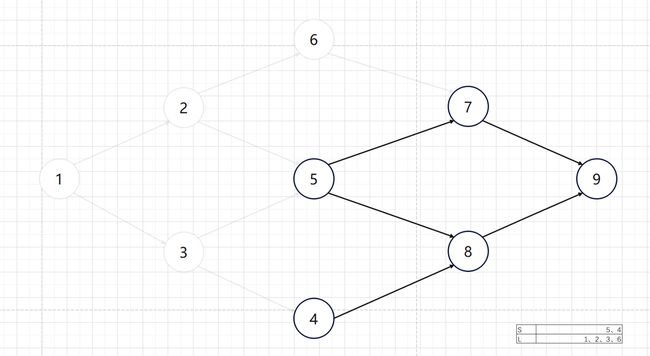
此时2和3的入度更新为0,所以将2和3放入 S S S:
重复上述步骤。将2从 S S S中取出、放入 L L L;删除2和以2为起点的边;将6推入队列:
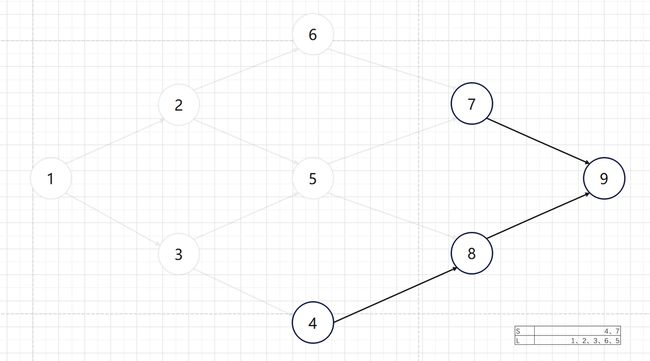
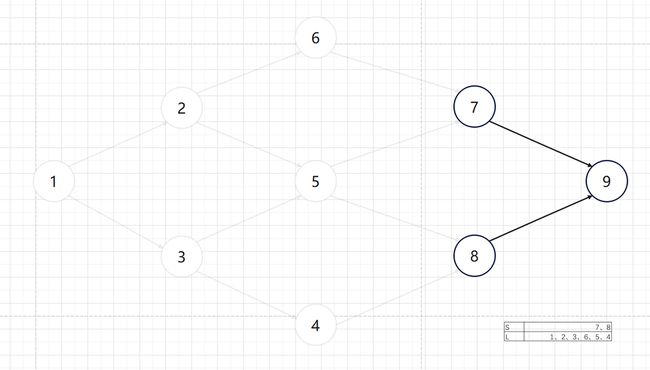
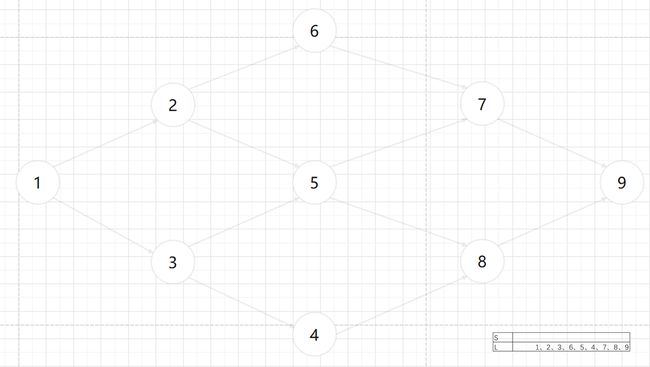
继续重复此步骤,分别从 S S S中取3、6、5、4、7、8、9
此时 S S S为空,所以结束计算。
拓扑序列为1 2 3 6 5 4 7 8 9:
代码实现
读入部分
使用链式向前星储存图:
struct edge
{
int to;
int next;
};
int head[100005];
edge graph[100005];
int n, m;
读入图:
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int s, e;
cin >> s >> e;
graph[i].next = head[s];
graph[i].to = e;
head[s] = i;
}
由于需要计算点的入度,因此使用d数组储存节点的入度:
int d[100005];
在读入图时计算:
d[e]++;
读图部分完整代码为
#include 拓扑排序部分
使用队列que储存集合 S S S:
queue<int> que;
遍历 1 ∼ N 1\sim N 1∼N,将入度为0(d[i] == 0)的点插入队列:
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (d[i] == 0)
{
que.push(i);
}
}
当que不为空时,从que中取出一个点 u u u,并输出(加入拓扑序列 L L L)
while (!que.empty())
{
int now = que.front();
que.pop();
cout << now << " ";
}
删除所有以 u u u为起点的边;实现时不需要真正从图中删除,直接将终点的入度减1即可:
for (int i = head[now]; i != 0; i = graph[i].next)
{
d[graph[i].to]--;
}
如果某个点的入度更新后变为0,那么将这个点推入que:
for (int i = head[now]; i != 0; i = graph[i].next)
{
d[graph[i].to]--;
if (d[graph[i].to] == 0)
{
que.push(graph[i].to);
}
}
拓扑排序部分完整代码为:
...
queue<int> que;
...
int main()
{
...
while (!que.empty())
{
int now = que.front();
que.pop();
cnt--;
cout << now << " ";
for (int i = head[now]; i != 0; i = graph[i].next)
{
d[graph[i].to]--;
if (d[graph[i].to] == 0)
{
que.push(graph[i].to);
}
}
}
}
拓扑排序判环
上文中提到拓扑排序的只能对有向无环图进行排序。
如果图中出现环,则 S S S为空时图不为空。
利用这个特点,可以判断有向图中是否存在环。
使用cnt变量计算que中的元素数量(出队元素数量):
...
int main()
{
...
int cnt = n;
while (!que.empty())
...
}
每出队一个元素,cnt--:
while (!que.empty())
{
int now = que.front();
que.pop();
cnt--;
...
}
如果计算结束后图不为空,即cnt > 0,则图中有环:
if (cnt) // cnt > 0
{
cout << "Circle!" << endl;
}
完整代码
#include