基于Feign的微服务文件与复杂参数传输
1、问题背景
随着微服务普及程度的提升,IT人员面对的问题也随之复杂。原先微服务之间只进行简单参数的传输,而随着文件服务的微量化,微服务之间也需要进行文件传输,因此本文旨在解决以下两个问题:
(1) 实现服务之间的文件传输;
(2) 实现服务之间复杂参数的传输(例如:实体中含有文件类型参数);
2、结构介绍
本文主要使用上图红色框中的四个组件:
eureka-server:服务注册中心
eureka-common:公共类与工具存放
eureka-client:服务提供者
eureka-feign-client:服务消费者
3、系统搭建
3.1 eureka-server
该组件主要作用是服务注册与发现
依赖部分:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
配置信息:
---
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
client:
# 防止eureka-server自己注册自己
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/启动项:
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}本组件比较简单,各位看官按图操作即可。
3.2 eureka-common
个人习惯与将多个组件之间可能会共用的类、工具抽离为一个公共组件,便于管理与维护。
依赖部分:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
1.5.3.RELEASE
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.70
复杂参数实体:
@FileFeignAnnotation
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String sex;
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private MultipartFile file;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public MultipartFile getFile() {
return file;
}
public void setFile(MultipartFile file) {
this.file = file;
}
}自定义注解:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FileFeignAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}此处自定义一个注解是为了后面区分普通参数与复杂参数。通过注解去控制,避免太多冗余代码。
3.3 eureka-client
此组件为服务提供者
依赖部分:
com.forezp
eureka-common
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-eureka
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
配置信息:
spring:
application:
name: eureka-client
eureka:
client:
service-url:
# 服务注册地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
server:
port: 8763接口信息:
// 用于测试复杂参数
@PostMapping("/test")
public String test(UserInfo info) {
LOGGER.info(JSON.toJSON(info).toString());
return "Hello World!";
}
// 用于测试文件传输
@PostMapping("/file")
public String file(@RequestPart(value = "file") MultipartFile file) {
return file.getOriginalFilename();
}接口测试结果:
文件传输:
复杂参数:
由以上测试结果可知:服务提供者接口测试正常。
3.4 eureka-feign-client
依赖部分:
com.forezp
eureka-common
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-eureka
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-feign
1.3.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-hystrix
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-hystrix-dashboard
io.github.openfeign.form
feign-form
3.0.3
io.github.openfeign.form
feign-form-spring
3.0.3
配置信息:
spring:
application:
name: eureka-feign-client
server:
port: 8766
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true3.4.1 问题一:文件传输
feign不支持文件传输的原因是在对Form参数进行编码时,没有默认的HttpMessageConverters对Form格式的参数进行编码转换,需要自己注入配置。
接口定义:
@FeignClient(value = "eureka-client")
public interface UploadFeign {
@RequestMapping(value = "/load/file", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE
, produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE})
String upload(@RequestPart("file") MultipartFile file);
}在接口定义中声明了以下信息:
@FeignClient: 声明了服务提供者的服务名
@RequestMapping:声明了接口信息与请求headers
@RequestPart:声明了文件参数的接收体
引入配置,声明编码转换:
@Configuration
public class MultipartSupportConfig {
@Autowired
private ObjectFactory messageConverters;
/**
* override a new FormEncoder to match complex param
* param include properties and MultipartFile
* @return
*/
@Bean
Encoder feignFormEncoder() {
return new SpringFormEncoder(new SpringEncoder(messageConverters))
}
} 测试结果:
3.4.2 源码分析
编码过程中,底层源码主要涉及下图代码:
SpringFormEncoder:
public void encode (Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException {
if (!bodyType.equals(MultipartFile.class)) {
super.encode(object, bodyType, template);
return;
}
val file = (MultipartFile) object;
val data = singletonMap(file.getName(), object);
super.encode(data, MAP_STRING_WILDCARD, template);
}在SpringFormEncoder中根据请求参数的type,选择不同的处理方式:
(1) 参数类型不为MultipartFile(文件格式),调用父类FormEncoder.encode()方法,参数不处理
(2) 参数类型为MultipartFile时,参数转换为Map,type设置为MAP_STRING_WILDCARD
FormEncoder:
public void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException {
String contentTypeValue = this.getContentTypeValue(template.headers());
ContentType contentType = ContentType.of(contentTypeValue);
if (MAP_STRING_WILDCARD.equals(bodyType) && this.processors.containsKey(contentType)) {
Charset charset = this.getCharset(contentTypeValue);
Map data = (Map)object;
try {
((ContentProcessor)this.processors.get(contentType)).process(template, charset, data);
} catch (Exception var9) {
throw new EncodeException(var9.getMessage());
}
} else {
this.delegate.encode(object, bodyType, template);
}
}根据SpringFormEncoder中传值bodyType的区别,决定不同的处理逻辑:
(1) MAP_STRING_WILDCARD类型时,调用MultipartFormContentProcessor.process()方法进行编码,包括:参数封装、头部设置,请求体设置等。
public void process(RequestTemplate template, Charset charset, Map data) throws Exception {
String boundary = Long.toHexString(System.currentTimeMillis());
Output output = new Output(charset);
Iterator var6 = data.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = (Entry)var6.next();
Writer writer = this.findApplicableWriter(entry.getValue());
writer.write(output, boundary, (String)entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
output.write("--").write(boundary).write("--").write("\r\n");
String contentTypeHeaderValue = this.getSupportedContentType().getHeader() + "; charset=" + charset.name() + "; boundary=" + boundary;
template.header("Content-Type", new String[]{contentTypeHeaderValue});
template.body(output.toByteArray(), (Charset)null);
output.close();
} (2) 其他类型时,调用SpringEncoder的encode()方法进行编码处理,在此过程中遍历消息转换器对参数进行编码转换。
public void encode(Object requestBody, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate request)
throws EncodeException {
// template.body(conversionService.convert(object, String.class));
if (requestBody != null) {
Class requestType = requestBody.getClass();
Collection contentTypes = request.headers().get("Content-Type");
MediaType requestContentType = null;
if (contentTypes != null && !contentTypes.isEmpty()) {
String type = contentTypes.iterator().next();
requestContentType = MediaType.valueOf(type);
}
for (HttpMessageConverter messageConverter : this.messageConverters
.getObject().getConverters()) {
if (messageConverter.canWrite(requestType, requestContentType)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (requestContentType != null) {
log.debug("Writing [" + requestBody + "] as \""
+ requestContentType + "\" using ["
+ messageConverter + "]");
}
else {
log.debug("Writing [" + requestBody + "] using ["
+ messageConverter + "]");
}
}
FeignOutputMessage outputMessage = new FeignOutputMessage(request);
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
HttpMessageConverter 3.4.3 问题二:复杂参数
问题说明:
当采用问题一的解决代码处理问题二时,最后会调用SpringEncoder的encode()进行处理,由于参数中既包含属性,又包含文件,在编码过程中最后会报错:"Could not write request: no suitable HttpMessageConverter "。
问题分析:
(1) 针对问题二,可以借鉴MultipartFile的处理方法调用MultipartFormContentProcessor.process()方法进行编码处理;
(2) 考虑到后续其他复杂参数的使用,本文在3.4.2自定义了注解@FileFeignAnnotation来标记实体为复杂参数;
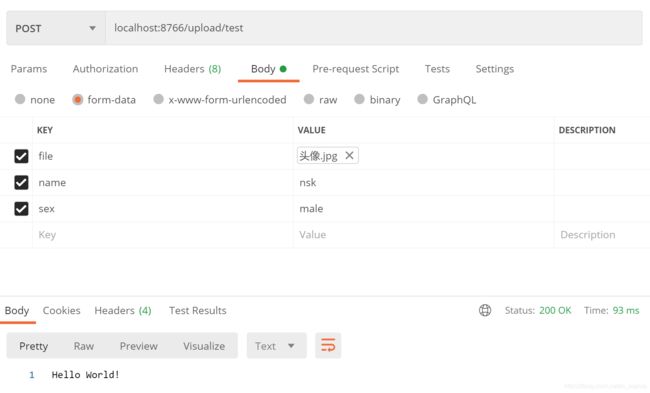
接口信息:
@RequestMapping(value = "/load/test", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE
, produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE})
String uploadInfo(UserInfo userInfo);自定义编码器DefinedSpringFormEncoder
public DefinedSpringFormEncoder(Encoder delegate) {
super(delegate);
MultipartFormContentProcessor processor = (MultipartFormContentProcessor) this.getContentProcessor(ContentType.MULTIPART);
processor.addWriter(new SpringSingleMultipartFileWriter());
processor.addWriter(new SpringManyMultipartFilesWriter());
}
@Override
public void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException {
if (!bodyType.equals(MultipartFile.class) && !isAnnotation(object)) {
super.encode(object, bodyType, template);
return;
}
if (isAnnotation(object)) {
Map data = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(object), new TypeReference>() {
});
try {
addNotSerializeField(data,object);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
super.encode(data, MAP_STRING_WILDCARD, template);
return;
}
MultipartFile file = (MultipartFile) object;
Map data = singletonMap(file.getName(), object);
super.encode(data, MAP_STRING_WILDCARD, template);
}
/**
* add these properties into map
* properties is not Serialize and annotation by @JSONField
* @param map
* @param object
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
private void addNotSerializeField(Map map, Object object) throws IllegalAccessException {
Field[] fields = object.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(JSONField.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String name = field.getName();
Object value = field.get(object);
map.put(name, value);
}
}
}
/**
* estimate if object is annotation by @FileFeignAnnotation
*
* @param object
* @return
*/
private boolean isAnnotation(Object object) {
Class objectClass = object.getClass();
FileFeignAnnotation annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(objectClass, FileFeignAnnotation.class);
return annotation != null;
}
核心代码为encode()方法:
(1) 对于非MultipartFile和非@FileFeignAnnotation的参数,调用SpringEncoder的encode()方法进行编码处理;
(2) 对于MultipartFile参数,调用MultipartFormContentProcessor.process()方法进行编码
(3) 对于@FileFeignAnnotation的实体参数,首先转换为Map,再将未序列化的参数添加到Map中,最后调用MultipartFormContentProcessor.process()方法进行编码。
测试结果:
4 小结
本文通过注入SpringFormEncoder编码器,解决了Feign服务间文件传输问题,测试结果正常;通过对源码进行分析,自定义编码器,解决了复杂参数传输问题,测试结果正常。