【无标题】
使用 Spring Boot 3 和 Spring Cloud 的微服务
本文将教您如何使用 Spring Boot 3 和 Spring Cloud 组件构建微服务。一旦 Spring Boot 的新主要版本发布,我就描述这个主题是一种传统。您可能知道,Spring Boot 3.0从 2022 年 11 月底开始全面可用。
总的来说,将在本文中涵盖以下主题:
- 在云原生开发中使用 Spring Boot 3
- 使用 Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka为所有微服务提供服务发现 。这是 Spring Cloud 中仍然可用的最后一个 Netflix 微服务组件
- 服务间通信中的Spring Cloud OpenFeign
- 使用Spring Cloud Config进行分布式配置
- 带有Spring Cloud Gateway的 API 网关模式包括带有Springdoc项目的全局 OpenAPI 文档
- 使用 Micrometer OpenTelemetry 和 Zipkin 收集痕迹
幸运的是,从 Spring Boot 2 迁移到 3 并不是一个痛苦的过程。
运行环境
目前运行 Spring Boot 微服务的首选平台是 Kubernetes。,你也可能正在开始迁移你的应用程序,或者至少它正在进行中。当然,可能会有一些例外,但我考虑的是绝大多数。
在 Kubernetes 生态系统也发生了很大变化。您可以轻松地将许多有用的工具和平台服务集成到您的应用程序中。我们至少可以提到 Kubernetes 本机解决方案,如服务网格(例如 Istio)或无服务器(例如 Knative)。这里的主要问题是:如果我在 Kubernetes 上运行微服务,Spring Cloud 组件是否仍然相关?答案是:大多数情况下不会。当然,你仍然可以使用 Eureka 进行服务发现,使用 Spring Cloud Config 进行分布式配置,或者使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 进行 API 网关模式。但是,您可以轻松地将它们替换为 Kubernetes 内置机制和其他平台服务。
总而言之,本文不针对 Kubernetes用户。它展示了如何在任何地方轻松运行微服务架构。
源代码
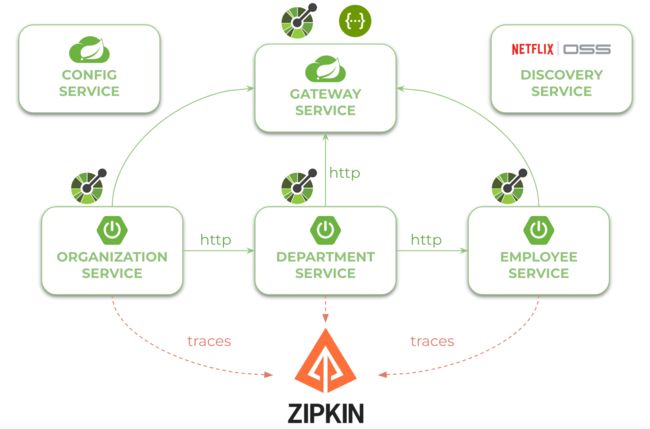
在继续查看源代码之前,让我们看一下下图。它说明了我们示例系统的架构。我们有三个独立的 Spring Boot 3 微服务,它们在服务发现中注册自己,从配置服务中获取属性,并相互通信。整个系统隐藏在API网关的后面。我们的 Spring Boot 3 微服务使用 Micrometer OTEL 项目将跟踪发送到 Zipkin 实例。
使用的版本 Spring Cloud 2022.0.1 。这个版本 spring-cloud-dependencies 应该被声明为 BOM 用于依赖管理。
org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-dependencies 2022.0.1 pom import
第 1 步:使用 Spring Cloud Config 配置服务器
要为应用程序启用 Spring Cloud Config 功能,我们应该首先将 spring-cloud-config-server 依赖项包含到您的项目中。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
然后启用在应用程序启动使用注释期间运行嵌入式配置服务器 @EnableConfigServer 。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(ConfigApplication.class).run(args);
}
}默认情况下,Spring Cloud Config Server 将配置数据存储在 Git 存储库中。我们将通过激活模式来改变这种行为 native 。在这种模式下,Spring Cloud Config Server 从类路径中读取属性源。我们将所有 YAML 属性文件放在 src/main/resources/config . 这是配置服务器 application.yml 文件。它激活该 native 模式并将默认端口覆盖到 8088 .
server:
port: 8088
spring:
profiles:
active: nativeYAML 文件名将与服务名称相同。例如,的 YAML 文件 discovery-service 位于此处: src/main/resources/config/discovery-service.yml 。除了默认配置文件外,我们还将定义自定义 docker 配置文件。因此配置文件的名称将包含后缀 docker 。 localhost 在默认配置文件中,我们通过动态分配的端口连接服务。因此,默认配置文件的典型配置文件如下所示:
server:
port: 0
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8061/eureka/下面是默认配置文件的典型配置文件:
server:
port: 8080
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://discovery-service:8061/eureka/为了在客户端连接配置服务器,我们需要在 Maven 依赖项中包含以下模块:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
根据运行环境( localhost 或 docker),我们需要为配置服务器提供不同的地址:
application.yml
spring:
config:
import: "optional:configserver:http://config-service:8088"
activate:
on-profile: docker
---
spring:
application:
name: discovery-service
config:
import: "optional:configserver:http://localhost:8088"第 2 步:使用 Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka 的发现服务器
当然,您可以将 Eureka 替换为 Spring Cloud 支持的任何其他发现服务器。可以是Consul,也可以是阿里巴巴Nacos,也可以是Zookeeper。运行 Eureka 服务器的最佳方式就是将其嵌入到 Spring Boot 应用程序中。为此,我们首先需要包含以下 Maven 依赖项:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
然后我们需要 @EnableEurekaServer 在主类上设置注解。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class DiscoveryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(DiscoveryApplication.class).run(args);
}
}这不是什么新鲜事。正如我已经提到的,配置文件 discovery-service.yml or discovery-service-docker.yml 应该放在 config-service 模块中。我们已将 Eureka 的运行端口从默认值 (8761) 更改为 8061。对于独立的 Eureka 实例,我们必须禁用注册并省略获取注册表。我们只想激活一个单节点的演示发现服务器。
server:
port: 8061
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/成功启动应用程序后,您可以访问地址下的 Eureka Dashboard http://localhost:8061/ 。
第 3 步:使用 Spring Boot 3 和 Spring Cloud 构建应用程序
让我们看一下我们的微服务所需的 Maven 模块列表。每个应用程序都必须从 中获取配置 config-service ,并且需要在 中注册自己 discovery-service 。它还公开 REST API,自动生成 API 文档,并将跟踪信息导出到 Zipkin 实例。我们使用 springdoc-openapi 专用于 Spring Boot 3 的 v2 库。它生成路径下可用的 JSON 和 YAML 格式的文档 v3/api-docs (或 /v3/api-docs.yaml YAML 格式)。为了将跟踪导出到 Zipkin 服务器,我们将包含该 opentelemetry-exporter-zipkin 模块。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
io.micrometer
micrometer-tracing-bridge-otel
io.opentelemetry
opentelemetry-exporter-zipkin
org.springdoc
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-api
2.0.2
对于调用其他服务的应用程序,我们还需要包含一个声明式 REST 客户端。我们将使用 Spring Cloud OpenFeign。
org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
OpenFeign 客户端自动与服务发现集成。我们只是在注释里面设置它在 Eureka 中注册的名称 @FeingClient 。为了创建客户端,我们需要定义一个接口,其中包含它必须调用的所有端点。
@FeignClient(name = "employee-service")
public interface EmployeeClient {
@GetMapping("/organization/{organizationId}")
List findByOrganization(@PathVariable("organizationId") Long organizationId);
}
在演示期间,我们会将所有跟踪发送到 Zipkin。它需要将概率参数的值设置为 1.0 。为了覆盖 Zipkin 的默认 URL,我们需要使用该 management.zipkin.tracing.endpoint 属性。
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0
zipkin:
tracing:
endpoint: http://zipkin:9411/api/v2/spans
@RestController 这是in的实现 department-service 。它注入存储库 bean 与数据库交互,并注入 Feign 客户端 bean 与之通信 employee-service 。其余代码非常简单。
@RestController
public class DepartmentController {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DepartmentController.class);
DepartmentRepository repository;
EmployeeClient employeeClient;
public DepartmentController(DepartmentRepository repository, EmployeeClient employeeClient) {
this.repository = repository;
this.employeeClient = employeeClient;
}
@PostMapping("/")
public Department add(@RequestBody Department department) {
LOGGER.info("Department add: {}", department);
return repository.add(department);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Department findById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
LOGGER.info("Department find: id={}", id);
return repository.findById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/")
public List findAll() {
LOGGER.info("Department find");
return repository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/organization/{organizationId}")
public List findByOrganization(@PathVariable("organizationId") Long organizationId) {
LOGGER.info("Department find: organizationId={}", organizationId);
return repository.findByOrganization(organizationId);
}
@GetMapping("/organization/{organizationId}/with-employees")
public List findByOrganizationWithEmployees(@PathVariable("organizationId") Long organizationId) {
LOGGER.info("Department find: organizationId={}", organizationId);
List departments = repository.findByOrganization(organizationId);
departments.forEach(d -> d.setEmployees(employeeClient.findByDepartment(d.getId())));
return departments;
}
}
如您所见,Spring Boot 2 和 3 之间的应用程序实现几乎没有差异。您唯一需要做的就是将所有的更改 javax.persistence 为 jakarta.persistance .
第 4 步:使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 的 API 网关
A gateway-service 是我们使用 Spring Boot 3 的微服务架构中的最后一个应用程序。从 Spring Boot 2 开始,Spring Cloud Gateway 取代了 Netflix Zuul。我们也可以使用例如 VMWare Tanzu 提供的 Helm 图表将其安装在 Kubernetes 上。
我们将使用嵌入式网关创建一个单独的应用程序。为此,我们需要在 Maven 依赖项中包含 Spring Cloud Gateway Starter。由于我们的网关要与发现和配置服务进行交互,因此它还包括 Eureka Client Starter 和 Spring Cloud Config Starter。我们不想仅仅将它用作下游服务的代理,而且我们还公开了所有应用程序生成的 OpenAPI 文档。由于 Spring Cloud Gateway 构建在 Spring WebFlux 之上,我们需要包含专用于该项目的 Springdoc 启动器。
org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-gateway org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-config io.micrometer micrometer-tracing-bridge-otel io.opentelemetry opentelemetry-exporter-zipkin org.springdoc springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-api 2.0.2 org.springdoc springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-ui 2.0.2
为了从多个 v3/api-docs 端点公开 OpenAPI 文档,我们需要使用该 GroupedOpenApi 对象。 employee-service 它应该提供一种在, department-service 和生成的文档之间切换的方法 organization-service 。这些服务在动态地址(或至少是随机端口)上运行。在那种情况下,我们将使用该 RouteDefinitionLocator bean 来获取每个服务的当前 URL。然后我们只需要过滤一个路由列表,只找到与我们的三个微服务相关的路由。最后,我们创建 GroupedOpenApi 包含服务名称和路径的 。
@SpringBootApplication
public class GatewayApplication {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(GatewayApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
RouteDefinitionLocator locator;
@Bean
public List apis() {
List groups = new ArrayList<>();
List definitions = locator
.getRouteDefinitions().collectList().block();
assert definitions != null;
definitions.stream().filter(routeDefinition -> routeDefinition
.getId()
.matches(".*-service"))
.forEach(routeDefinition -> {
String name = routeDefinition.getId()
.replaceAll("-service", "");
groups.add(GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.pathsToMatch("/" + name + "/**").group(name).build());
});
return groups;
}
}
下面是 的配置 gateway-service 。我们应该通过将属性设置 spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.enabled 为来启用与发现服务器的集成 true 。然后我们可以继续定义路由规则。我们使用 Path Route Predicate Factory 来匹配传入的请求,并使用 RewritePath GatewayFilter Factory 来修改请求的路径以使其适应下游服务公开的格式。该 uri 参数指定在发现服务器中注册的目标服务的名称。例如, 由于谓词 ,在路径 organization-service 下的网关上可用 ,重写路径从 到. /organization/** Path=/organization/** /organization/** /**
应用.ymlspring:
output:
ansi:
enabled: always
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
routes:
- id: employee-service
uri: lb://employee-service
predicates:
- Path=/employee/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/employee/(?.*), /$\{path}
- id: department-service
uri: lb://department-service
predicates:
- Path=/department/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/department/(?.*), /$\{path}
- id: organization-service
uri: lb://organization-service
predicates:
- Path=/organization/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/organization/(?.*), /$\{path}
- id: openapi
uri: http://localhost:${server.port}
predicates:
- Path=/v3/api-docs/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/v3/api-docs/(?.*), /$\{path}/v3/api-docs
springdoc:
swagger-ui:
urls:
- name: employee
url: /v3/api-docs/employee
- name: department
url: /v3/api-docs/department
- name: organization
url: /v3/api-docs/organization
正如您在上面看到的,我们还为 Springdoc OpenAPI 创建了一个专用路由。它重写上下文的路径 /v3/api-docs 以在 Swagger UI 中正确地提供它。
第 5 步:运行 Spring Boot 3 微服务
最后,我们可以运行我们所有的微服务。使用存储库中的当前配置,您可以直接在笔记本电脑上或使用 Docker 容器启动它们。
选项 1:直接在笔记本电脑上启动
总共有 6 个应用程序要运行:3 个微服务、一个发现服务器、一个配置服务器和一个网关。我们还需要运行 Zipkin 来收集和存储服务之间通信的痕迹。在第一步中,我们应该启动 config-service . 我们可以为此使用 Spring Boot Maven 插件。只需转到 config-service 目录和以下命令即可。它暴露在 8088 端口上。
$ mvn spring-boot:run
我们应该对所有其他应用程序重复相同的步骤。正在 discovery-service 监听端口 8061 ,而在端口 gateway-service 上 8060 。由于 server.port=0 配置中的属性,微服务将在动态生成的端口号上启动。在最后一步中,我们可以通过以下命令使用其 Docker 容器运行 Zipkin:
$ docker run -d --name zipkin -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin
选项 2:构建镜像并使用 Docker Compose 运行它们
在第一步中,我们将为所有应用构建整个 Maven 项目和 Docker 镜像。我创建了一个配置文件 build-image ,需要激活它才能构建图像。它主要使用 build-image Spring Boot Maven Plugin 提供的步骤。但是, config-service 我 discovery-service 正在使用 Jib,因为它建立在已安装的基本映像之上 curl 。对于这两种服务,Docker compose 都需要在启动其他容器之前验证健康检查。
$ mvn clean package -Pbuild-image
docker-compose.yml 在存储库根目录中可用。整个文件如下所示。我们需要 config-service 在所有其他应用程序之前运行,因为它提供了属性源。其次,我们应该开始 discovery-service 。在这两种情况下,我们都定义了一个健康检查,使用容器内的 curl 测试 HTTP 端点。一旦我们启动并验证 config-service , discovery-service 我们就可以运行 gateway-service 所有微服务。由于 SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE 环境变量,所有应用程序都在激活 docker Spring 配置文件的情况下运行。它对应于 spring.profiles.active 可以在配置属性中定义的参数。
docker-composer.ymlversion: "3.7"
services:
zipkin:
container_name: zipkin
image: openzipkin/zipkin
ports:
- "9411:9411"
config-service:
image: piomin/config-service:1.1-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8088:8088"
healthcheck:
test: curl --fail http://localhost:8088/employee/docker || exit 1
interval: 5s
timeout: 2s
retries: 3
discovery-service:
image: piomin/discovery-service:1.1-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8061:8061"
depends_on:
config-service:
condition: service_healthy
links:
- config-service
healthcheck:
test: curl --fail http://localhost:8061/eureka/v2/apps || exit 1
interval: 4s
timeout: 2s
retries: 3
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker
employee-service:
image: piomin/employee-service:1.2-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8080"
depends_on:
discovery-service:
condition: service_healthy
links:
- config-service
- discovery-service
- zipkin
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker
department-service:
image: piomin/department-service:1.2-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8080"
depends_on:
discovery-service:
condition: service_healthy
links:
- config-service
- discovery-service
- employee-service
- zipkin
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker
organization-service:
image: piomin/organization-service:1.2-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8080"
depends_on:
discovery-service:
condition: service_healthy
links:
- config-service
- discovery-service
- employee-service
- department-service
- zipkin
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker
gateway-service:
image: piomin/gateway-service:1.1-SNAPSHOT
ports:
- "8060:8060"
depends_on:
discovery-service:
condition: service_healthy
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker
links:
- config-service
- discovery-service
- employee-service
- department-service
- organization-service
- zipkin
最后,让我们使用 Docker Compose 运行所有应用程序:
$ docker-compose up
测试
启动所有应用程序后,您可以通过 gateway-service . 它在端口上监听 8060 。启动时会自动生成一些测试数据。您可以调用以下端点来测试它们之间的所有服务和通信:
$ curl http://localhost:8060/employee/
$ curl http://localhost:8060/department/organization/1
$ curl http://localhost:8060/department/organization/1/with-employees
$ curl http://localhost:8060/organization/
$ curl http://localhost:8060/organization/1/with-departments以下是应用程序在上面可见的调用期间生成的日志:
让我们显示在网关上公开的 Swagger UI。您可以轻松地在所有三个微服务的上下文之间切换,如下所示:
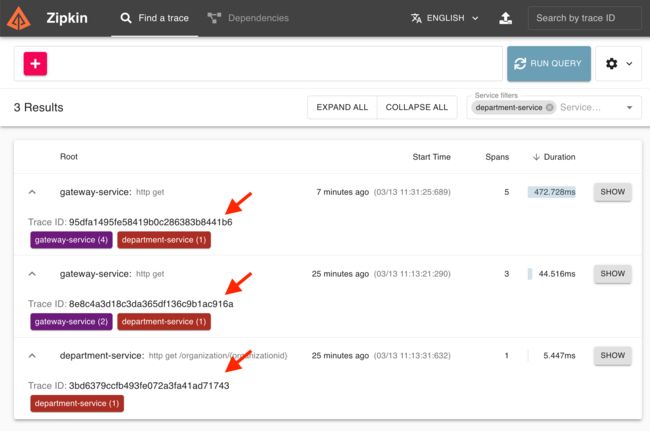
我们可以去 Zipkin 仪表板验证收集到的痕迹:
总结
演示项目更新到 Spring Boot 3 会很容易,这里只是做一个简单的入门体验。但是一旦您尝试更新真正的企业系统,它就会变得更加困难,所以在不充分了解业务和新技术的情况下,请勿尝试把现有的项目升级,否则会付出生产上的沉重代价。