java解析xml文件
JDK API中提供了3种方式解析XML,分别为DOM、SAX、XPath。
目录:
- DOM
- XPath:Mybaties中采用XPath方式解析XML文件的配置信息。
- SAX:Spring使用SAX读取xml文件
- 使用第三方
- JDOM
仅适用具体类而不使用接口
API大量使用了Collections类 - dom4j :Java dom4j生成和解析XML_ouyangjun__的博客-CSDN博客_dom4j解析xml步骤
注意:如何使用dom4j解析带冒号的节点 - jsoup,简单的要命:jsoup系列教材 (一)- 简介
- JDOM
- 总结
- SAX
- 优点
- 采用事件驱动模式,对内存消耗比较小
- 适用于只需要处理xml中数据时
- 缺点
- 不易编码
- 很难同时访问同一个xml中的多处不同数据
- 优点
- DOM
- 优点
- 形成了树结构,直观好理解,代码更易编写
- 解析过程中树结构保存在内存中,方便修改
- 缺点
- 当xml文件较大时,对内存消耗比较大,容易影响解析性能并造成内存溢出
- 优点
- JDOM
- 仅适用具体类而不使用接口
- API大量使用了Collections类
- dom4j
- jdom的一种智能分支,它合并了许多超出基本xml文档表示的功能
- dom4j使用接口和抽象基本类方法,是一个优秀的Java XML API
- 具有性能优异、灵活性好、功能强大和极端易用的特点
- 是一个开源软件
- SAX
一.DOM
studentx.xml
John
B
12
Mary
A
11
Simon
A
18
XMLParser.java
import java.io.File;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class XMLParser {
public void getAllUserNames(String fileName) {
try {
//1.获得一个文档解析器工厂:定义工厂API,使应用程序能够从XML文档获取生成DOM对象树的解析器
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//2.获得一个文档解析器:定义从XML文档获取DOM文档实例的API。 使用这个类,应用程序员可以从XML获得一个Document 。
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
File file = new File(fileName);
if (file.exists()) {
//3.解析器解析xmL文件,获得一个DOM文档
Document doc = db.parse(file);
//4.通过DOM文档获取根结点元素,并打印
Element docEle = doc.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println("Root element of the document: "+ docEle.getNodeName());
//5.通过DOM文档根据标签名获取所有其对应的结点,并将其存储在NodeList抽象集合中
NodeList studentList = docEle.getElementsByTagName("student");
System.out.println("Total students: " + studentList.getLength());
//6.打印"student"结点下所有的结点信息
if(studentList != null && studentList.getLength() > 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < studentList.getLength(); i++) {
//7.遍历一个"student"结点
Node node = studentList.item(i);
//8.node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE,表示node结点是一个Element(一组)
if(node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
System.out.println("=====================");
Element e = (Element) node;
NodeList nodeList = e.getElementsByTagName("name");
System.out.println("Name: "+ nodeList.item(0).getChildNodes().item(0).getNodeValue());
nodeList = e.getElementsByTagName("grade");
System.out.println("Grade: "+nodeList.item(0).getChildNodes().item(0) .getNodeValue());
nodeList = e.getElementsByTagName("age");
System.out.println("Age: "+ nodeList.item(0).getChildNodes().item(0).getNodeValue());
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
XMLParser parser = new XMLParser();
parser.getAllUserNames("./src/students.xml");
}
}三.XPath方式
users.xml
张三
2018-10-15
123
10086
阿毛
李四
2018-10-15
234
12306
二狗子
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class UserEntity {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Date createTime;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String nickName;
static UserEntity buildUserEntity(String id, String name, String createTime, String password, String phone,
String nickName) throws ParseException {
UserEntity user=new UserEntity();
user.id=Long.valueOf(id);
user.name=name;
user.createTime=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse(createTime);
user.password=password;
user.nickName=nickName;
return user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
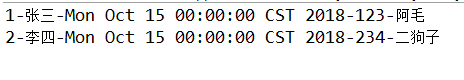
return id+"-"+name+"-"+createTime+"-"+password+"-"+nickName;
}
}
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.xpath.XPath;
import javax.xml.xpath.XPathConstants;
import javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class XMLParser {
public void getAllUserNames(String fileName) {
try {
//1.获得一个文档解析器工厂:定义工厂API,使应用程序能够从XML文档获取生成DOM对象树的解析器
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//2.获得一个文档解析器:定义从XML文档获取DOM文档实例的API。 使用这个类,应用程序员可以从XML获得一个Document 。
DocumentBuilder builder = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
File file=new File(fileName);
//3.通过解析器解析xml文件,获得一个文档对象
Document document=builder.parse(file);
//4.获取新的XPathFactory实例
XPathFactory xpathFactory=XPathFactory.newInstance();
//5.一个XPathFactory实例可以用来创建XPath对象
XPath xpath=xpathFactory.newXPath();
//6.xpath根据根结点"users"标签解析document文档
NodeList nodeList=(NodeList) xpath.evaluate("/users/*", document,XPathConstants.NODESET);
//7.获取一个ArrayList实例用来存储UserEntity对象
List userList=new ArrayList();
//8.获取所有的user结点
for(int i=1;i 四.dom4j
1.引入依赖
dom4j
dom4j
1.6.1
2.application.xml
3.BeanDefine.java
public class BeanDefine {
private String id;
private String className;
public BeanDefine(String id, String className) {
this.id = id;
this.className = className;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "id:"+id+",className:"+className;
}
}4.测试
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 读取xml文件,转换成Document结点
Document document = null;
// 创建一个SAXReader解析器
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
document = saxReader.read(classLoader.getResourceAsStream("configAnnotation.xml"));
Element beans = document.getRootElement();
for (Iterator beansList = beans.elementIterator();beansList.hasNext();) {
Element element = beansList.next();
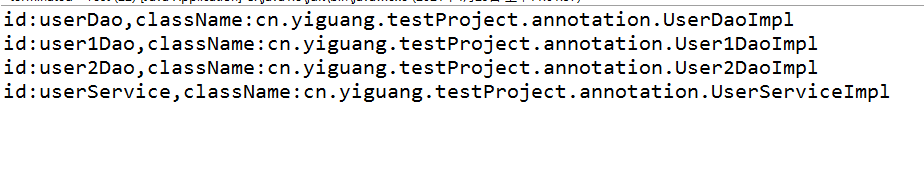
BeanDefine bean = new BeanDefine(element.attributeValue("id"), element.attributeValue("class"));
System.out.println(bean.toString());
}
}catch (DocumentException e){
System.out.println("解析配置文件出错......");
}
}
} 结果:
注意:如何使用dom4j解析带冒号的节点?
比如:applicationContext.xml
第一步:
需要添加一行:
为什么需要添加这一行呢?
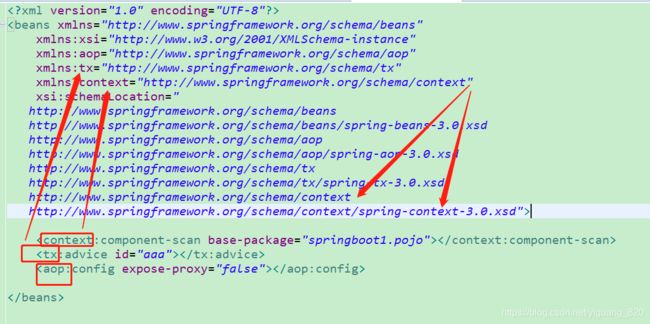
当没有添加这一行的时候,一直提示:
因为是在模仿spring注解,因此参考spring的xml配置文件,添加这一行就可以了,具体为什么能行,可以细入深究?
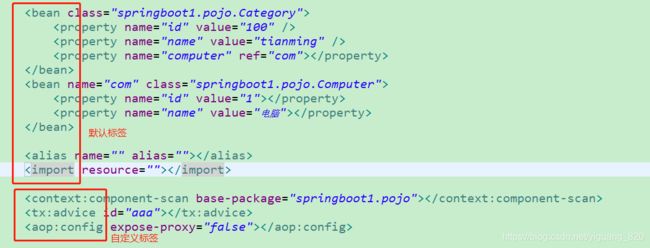
spring的xml文件中有两种标签,一种是默认标签,一种是自定义标签。带了节点带了冒号的就是自定义标签,自定义标签都需要如上面所示,需要指定解析标签的地址
第二步:此步不需要也可
添加:root.element("context");
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException {
Document document = null;
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
document = saxReader.read(classLoader.getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml"));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
root.element("context"); // 此步不需要也可
for (Iterator beansList = root.elementIterator();beansList.hasNext();) {
Element element = beansList.next();
System.out.println(element.getName());
System.out.println(element.attributeValue("base-package"));
}
}
} 结果: