【Java进阶】字符串和常见集合
文章目录
-
- 1. 字符串
-
- 1.1 String类常用方法
- 1.2 ==和equals的区别
- 1.3 String的不可变性
- 1.4 StringBuilder类概述
- 1.5 StringBuilder类方法
- 2. 常见集合
-
- 2.1 集合初始
- 2.2 List集合
-
- ① ArrayList
- ② LinkedList
- ③ 三种集合遍历方式
- 2.3 Set集合
-
- ① HashSet**基本使用**
- ② hashCode()
- ③ HashSet与TreeSet存储原理
- ④ LinkedHashSet
- ⑤ TreeSet
- 2.4 Map集合
-
- ① HashMap
- ② LinkedHashMap
- ③ TreeMap
- ④ 三种集合遍历方式
- 2.5 Collections实现集合排序
1. 字符串
1.1 String类常用方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
int length() |
返回当前字符串的长度 |
int indexOf(int ch) |
查找ch字符在该字符串中第一次出现的位置 |
int indexOf(String str) |
查找str子字符串在该字符串中第一次出现的位置 |
int lastIndexOf(int ch) |
查找ch字符在该字符串中最后一次出现的位置 |
int lastIndexOf(String str) |
查找str子字符串在该字符串中最后一次出现的位置 |
String substring(int beginIndex) |
获取从beginIndex位置开始到结束的子字符串 |
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) |
获取 [beginInde, endIndex) 的子字符串 |
String trim() |
返回去除了前后空格的字符串 |
boolean equals(Object obj) |
将该字符串与指定对象比较,返回true或false |
String toLowerCase() |
将字符串转换为小写 |
String toUpperCase() |
将字符串转换为大写 |
char charAt(int index) |
获取字符串中指定位置的字符 |
Stringp[] split(String regex, int limit) |
将字符串分割为子字符串,返回字符串数组 |
byte[] getBytes() |
将该字符串转换为byte数组 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str = new String ("我是哈哈哈,你好!");
byte[] arrs1 = str.getBytes();
String str1 = new String(arrs1, "GBK");
System.out.println(str1);
byte[] arrs2 = str.getBytes("UTF-8");
String str2 = new String(arrs2, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(str2);
}
1.2 ==和equals的区别
==判断地址是否相同,equals判断内容是否相同
因此str1 == str2为true,str1 == str3和str3 == str4均为false
互相之间.equals均为ture
1.3 String的不可变性
String对象一旦被创建,则不能修改,是不可变的
所谓的修改其实是创建了新的对象,所指向的内存空间不变
1.4 StringBuilder类概述
String具有不可变性,StringBuilder不具备
建议当频繁操作字符串时,使用StringBuilder
StringBuilder和StringBuffer二者基本相似,但StringBuffer是线程安全的,StringBuilder则没有,因此性能略高,单线程下建议使用StringBuilder
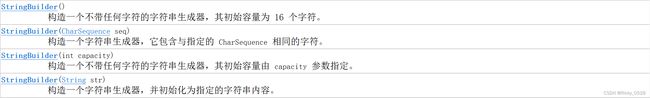
1.5 StringBuilder类方法
package com.ricky.str;
public class StringBuilderUse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("你好");
// 给字符串添加内容
System.out.println(sb.append(",").append("我是hhh哈"));
// 字符串替换
// System.out.println(sb.delete(5, 8).insert(5, "HHH"));
System.out.println(sb.replace(5, 8, "HHH"));
// 字符串截取
System.out.println(sb.substring(5, 8));
}
}
2. 常见集合
2.1 集合初始
Java集合是一种有用的工具类,可用于存储数量不等的对象
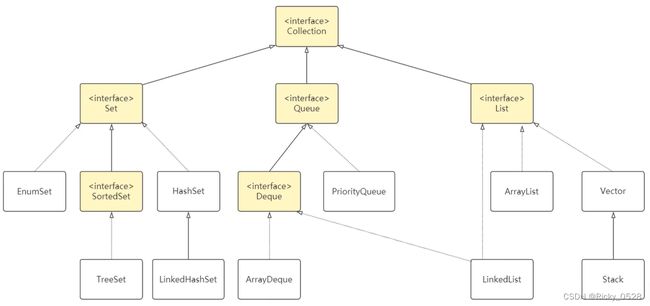
Java集合包含List、Set、Map,以及JDK1.5推出的Queue四种体系
Java的集合类主要有两个接口派生而出:Collection和Map
四种存储结构
- List代表有序、可重复集合
- Queue代表队列特性
- Set代表无序、不可重复集合
- Map代表存储映射关系的集合
Collection接口及实现
Map接口及实现
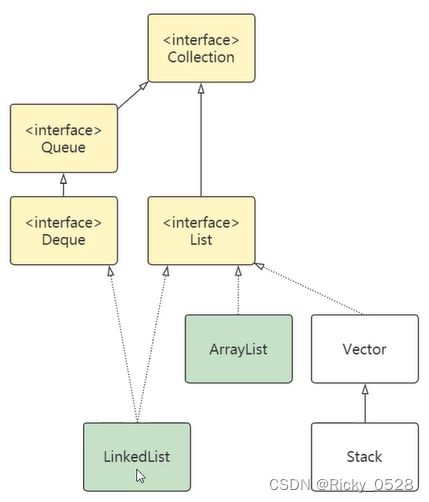
2.2 List集合
- List集合代表一个元素有序、可重复的集合,集合中每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引
- List集合允许使用重复元素,通过索引访问指定位置的元素
- List集合默认按元素添加顺序设置元素的索引
① ArrayList
- ArrayList基于数组实现的List类,是Java数组的有效替代品
- ArrayList会自动对容量进行扩容,多数情况下无序指定最大长度
- ArrayList的数据在内存中是连续紧密存储的,基于数据访问速度快
package com.ricky.collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化ArrayList集合
ArrayList<String> bookList = new ArrayList<String>();
bookList.add("三国演义"); // “ctrl+shift+回车”自动增加结尾分号
bookList.add("水浒传");
// bookList.add("三国演义");
System.out.println(bookList);
String bookName1 = bookList.get(1);
System.out.println(bookName1);
// bookList.get(10);
bookList.add(1,"红楼梦");
System.out.println(bookList);
// add方法返回值代表List集合是否发生变化
boolean result1 = bookList.add("西游记");
System.out.println("列表是否发生变化:" + result1);
// set方法用于更新指定索引的数据,返回值是更新前的原数据
String before = bookList.set(3,"西游记后传");
System.out.println(before);
System.out.println(bookList);
// remove方法有两种形式
// 按数据删除,传入数据,返回是否删除成功的布尔类型
boolean result2 = bookList.remove("西游记后传");
System.out.println(result2);
System.out.println(bookList);
// 按索引位置删除,返回被删除的数据
String item = bookList.remove(0);
System.out.println(item);
System.out.println(bookList);
// size方法用于获取List集合的总长度
int count = bookList.size();
System.out.println(count);
// 更新最后一个数据
bookList.set(bookList.size() - 1, "测试数据");
System.out.println(bookList);
// 删除最后一个数据
bookList.remove(bookList.size() - 1);
System.out.println(bookList);
}
}
② LinkedList
- LinkedList同时实现了List与Deque两个接口
- LinkedList在保障有序、允许重复的前提下,也可以作为队列在队首、队尾快速追加数据
- LinkedList的数据在内存中是分散存储的,基于链表,拥有良好的数据插入速度,但数据访问速度低于ArrayList
package com.ricky.collection.list;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> bookList = new LinkedList<String>();
bookList.add("三国演义");
bookList.add(0,"水浒传");
bookList.add("西游记");
bookList.add("红楼梦");
System.out.println(bookList);
bookList.addFirst("蒸汽革命");
bookList.addLast("黄金时代");
System.out.println(bookList);
}
}
③ 三种集合遍历方式
- for循环遍历
- forEach方法遍历
- Iterator迭代器遍历
package com.ricky.collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListLoopSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<String>();
bookList.add("三国演义");
bookList.add("水浒传");
bookList.add("西游记");
bookList.add("红楼梦");
// 方式1:通过标准for循环对每一个List元素赋值给book进行循环处理
for(String book : bookList) {
System.out.println(book);
}
// 方式2:利用forEach方法+Lambda表达式简化循环过程
bookList.forEach(book->{
System.out.println(book);
});
// 方式3:利用Iterator迭代器对象循环输出
Iterator<String> itr = bookList.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String book = itr.next(); // 提取出下一个元素,同时将指针向后移动
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}
2.3 Set集合
- Set集合代表一个元素无序、不可重复的集合
- Set集合与List集合使用方法基本相同,只是处理行为略有不同
- Set集合常用的实现类是:HashSet与TreeSet
① HashSet基本使用
package com.ricky.collection.set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSetSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化Set集合
Set<String> mobileSet = new HashSet<String>();
// 通过add方法增加新的元素
mobileSet.add("13311112222");
mobileSet.add("13333334444");
mobileSet.add("13355556666");
// Set集合不允许出现重复,add方法返回值代表是否真正在集合中插入数据
boolean isChanged = mobileSet.add("13377778888");
System.out.println("Set集合是否发生改变:" + isChanged);
// 对于已有的数据,再次调用add方法写入将返回false
isChanged = mobileSet.add("13377778888");
System.out.println("Set集合是否发生改变:" + isChanged);
System.out.println(mobileSet);
// Set集合可以使用所有Collection接口定义的方法
int count = mobileSet.size();
boolean result = mobileSet.contains("13377778888");
System.out.println(result);
// 需要额外注意的是,get等以索引获取数据的方法属于List接口,因此Set实现类无法使用
// mobileSet.get(0);
}
}
② hashCode()
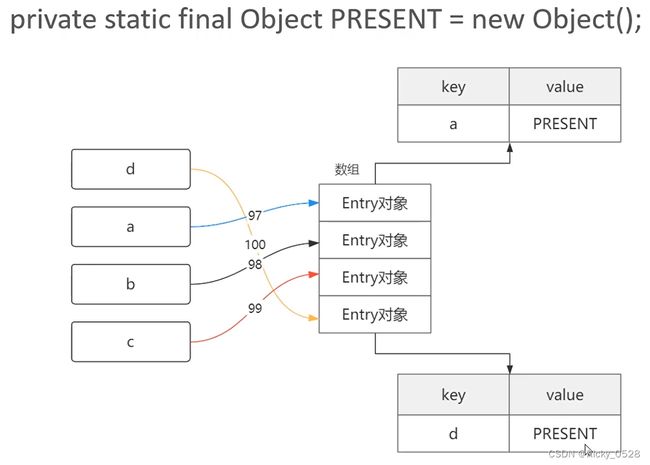
每一个类都会提供一个hashCode()方法
Set集合如何确保数据的唯一性
- Set集合在新增数据时先判断数据的hashCode()是否已经存在
- 若hashCode()在Set集合存在再调用equals()进行值比较
- hashCode()与equals()都存在的情况下,Set集合才认为数据已经存在,不予新增
为什么要先使用对象的hashCode(),而不是直接用equals()
- 出于执行效率考虑
- hashCode()返回的整数结果决定了Set集合中的存放位置,hashCode()计算速度很快,但可能出现哈希碰撞
- equals()则对值进行比较,处理速度相对较慢
对象的hashCode()与equals()都可以进行重载,使其在插入Set集合时能按照预定的规则不重复的插入
③ HashSet与TreeSet存储原理
Hash,一般翻译做散列、杂凑或音译为哈希,是把任意长度的数据通过散列算法变换成固定的输出,该输出就是散列值
HashSet
- HashSet是Set接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用Set集合时就是使用这个实现类
- HashSet按Hash算法来决定集合元素的顺序,具有很好的查找性能
- 当向HashSet集合中存入一个元素时,根据该对象的hashCode值决定该对象在HashSet中的存储位置
LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,除HashSet的特性外,它同时使用链表维护元素的次序,可以保障按插入顺序提取数据
- LinkedHashSet需要维护元素的插入顺序,因此性能略低于HashSet的性能
- 迭代访问Set里的全部元素时将有很好的性能,因为它以链表来维护内部顺序
TreeSet
- TreeSet是SortedSet接口的实现类,TreeSet可以确保集合元素处于排序状态
- TreeSet采用红黑树的数据结构来存储集合元素
- TreeSet默认采用自然排序对元素升序排列,也可以实现Comparable接口自定义排序方式
④ LinkedHashSet
注意,并不是存储时按照顺序存储的,存储仍然跟HashSet一样,只是增加了链表的结构,使其可以有序访问
package com.ricky.collection.set;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class LinkedHashSetSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> mobileSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
mobileSet.add("13377778888");
mobileSet.add("13311112222");
mobileSet.add("13333334444");
mobileSet.add("13355556666");
System.out.println(mobileSet);
}
}
⑤ TreeSet
可以自定义排序规则,需要重写Comparator接口中的compare方法
package com.ricky.collection.set;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetSample {
class IntegerComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1; // 降序排列,如果要升序,反过来即可
}
}
public void sort() {
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<Integer>(new IntegerComparator());
set.add(100);
set.add(140);
set.add(180);
set.add(200);
System.out.println(set);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TreeSetSample().sort();
}
}
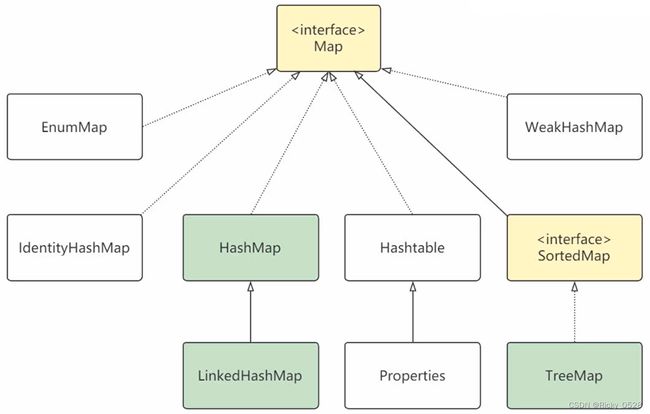
2.4 Map集合
Map映射特点
- Map用于保存具有映射关系的数据,每组映射都是Key(键)与Value(值)组合而成
- Key与Value可以是任何引用数据类型,但是Key通常是String
- Map中的Key不允许重复,重复为同一个Key设置Value,后者Value会覆盖前者Value
Java是现有Map后有Set,HashSet从HashMap精简而来
HashMap
HashSet
① HashMap
package com.ricky.collection.map;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化HashMap,HashMap同样存储在java.util包下
// 泛型可以只写在左边,右边泛型可以省略
HashMap<String, Object> student = new HashMap<>();
// put方法向Map放入键值对
student.put("name", "张三");
// 多次为同一个key赋值,新的value会覆盖旧value,同时将旧value返回
String name = (String)student.put("name", "李四");
System.out.println(name + "已被替换为李四");
// Map可以存储多组键值对,且value可以是不同类型
student.put("age", 18);
student.put("height", 182);
student.put("weight", 60);
System.out.println(student);
// 利用get方法获取指定key的value
String n = (String)student.get("name");
System.out.println(n);
// containsKey用于判断传入的key是否存在
boolean r1 = student.containsKey("name");
System.out.println(r1);
// containsValue用于判断传入的value是否存在
boolean r2 = student.containsValue(61);
System.out.println(r2);
// size方法返回当前键值对的总数
int count = student.size();
System.out.println(count);
// remove方法将指定的键值对删除,并将value返回
Integer w = (Integer)student.remove("weight");
System.out.println("weight项已被移除,其值为:" + w);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
HashMap:Value的类型写成Object这样可以支持多种数据类型
如果存进去的是int则会被自动转换为它的包装类型,其它的类似
② LinkedHashMap
取数据时按存入顺序取出,其余与HashMap一样
package com.ricky.collection.map;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LinkedHashMapSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> student = new LinkedHashMap<>();
student.put("name", "张三");
student.put("age", 18);
student.put("height", 182);
student.put("weight", 60);
//按插入顺序提取数据
System.out.println(student);
}
}
③ TreeMap
- TreeMap存储key-value对时,需要根据key对节点进行排序
- TreeMap支持两种Key排序:自然排序与定制排序
- 与TreeSet相同,TreeMap也是基于红黑树结构对数据进行排序的
package com.ricky.collection.map;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapSample {
// 按自定义规则对TreeMap进行排序
class RecordComparator implements Comparator<String>{
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1); // o2按字典序比o1大则返回大于0的数字,这样写则为降序
}
}
public void sort(){
Map<String, Object> record = new TreeMap<>(new RecordComparator());
record.put("A1", "1");
record.put("C3", "2");
record.put("B5", "3");
record.put("X1", "4");
record.put("C1", "5");
record.put("B1", "6");
System.out.println(record);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMapSample sample = new TreeMapSample();
sample.sort();
}
}
重写compare时,o2在前则为降序,在后则为升序
④ 三种集合遍历方式
package com.ricky.collection.map;
import java.util.*;
public class LoopSample {
// 利用for循环遍历所有key,再获取value
public void doForLoop(Map map){
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
for(String k : keys){
System.out.println(k + ":" + map.get(k));
}
}
// 利用forEach方法+Lambda表达式循环遍历(推荐)
public void doForEach(Map map){
map.forEach((key,value) -> {
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
});
}
// 使用迭代器对象Iterator循环遍历每一个Entry对象,通过Entry对象获取键值对
public void doIterator(Map map){
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Object>> itr = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Object> entry = itr.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> student = new LinkedHashMap<>();
student.put("name", "张三");
student.put("age", 18);
student.put("height", 182);
student.put("weight", 60);
System.out.println(student);
LoopSample loopSample = new LoopSample();
loopSample.doForLoop(student);
loopSample.doForEach(student);
loopSample.doIterator(student);
}
}
Map中一对键值对为一个Entry对象
2.5 Collections实现集合排序
package com.ricky.collection.list;
import java.util.*;
public class ListSort {
class ListComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
// 结果 > 0,则交换位置
// 结果 = 0 或小于 0,则位置不变
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
}
public List<Integer> listSorter(List<Integer> list) {
// 利用Collections.sort方法实现对List、Set进行排序,默认为升序
Collections.sort(list, new ListComparator());
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(4);
list.add(1);
list.add(6);
list.add(2);
list.add(10);
list.add(7);
list.add(5);
System.out.println(list);
ListSort ls = new ListSort();
List<Integer> sortedList = ls.listSorter(list);
System.out.println(sortedList);
}
}