算法学习|单调栈
学习材料声明
所有知识点都来自互联网,进行总结和梳理,侵权必删。
引用来源:基本参考代码随想录的刷题顺序和讲解。
理论基础
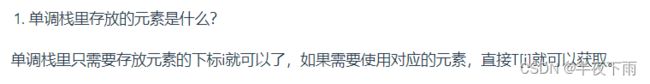
单调栈是什么?
应用场景:通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了。时间复杂度为O(n)。
本质:单调栈的本质是空间换时间,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素高的元素,优点是整个数组只需要遍历一次。
要确定的东西:存放什么?栈内元素递增or递减?三种情况如何操作?(截图来自代码随想录)
整个代码模型
设置栈,确定入栈的三种情况。
习题
1|739. 每日温度
非常直观可暴力。但是不够优美呀。
单调栈做法:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temperatures) {
// 递增栈
stack<int> st;
vector<int> result(temperatures.size(), 0);
for(int i=0; i<temperatures.size(); i++){
if(st.empty()){
st.push(i);
continue;
}
while(!st.empty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[st.top()]){
result[st.top()] = i-st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
2|496.下一个更大元素 I
相比于上一题,多一个查找的过程。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
// 递增栈
stack<int> st;
vector<int> result(nums2.size(), -1);
for(int i=0; i<nums2.size(); i++){
if(st.empty()){
st.push(i);
continue;
}
while(!st.empty()&&nums2[i]>nums2[st.top()]){
result[st.top()] = nums2[i];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
for(int j=0; j<nums2.size(); j++){
cout<<result[j]<<" ";
}
vector<int> result2(nums1.size(), -1);
for(int i=0; i<nums1.size(); i++){
for(int j=0; j<nums2.size(); j++){
if(nums1[i]==nums2[j]){
result2[i] = result[j];
}
}
}
return result2;
}
};
代码随想录:用到了map的映射。
// 版本二
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
stack<int> st;
vector<int> result(nums1.size(), -1);
if (nums1.size() == 0) return result;
unordered_map<int, int> umap; // key:下标元素,value:下标
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); i++) {
umap[nums1[i]] = i;
}
st.push(0);
for (int i = 1; i < nums2.size(); i++) {
while (!st.empty() && nums2[i] > nums2[st.top()]) {
if (umap.count(nums2[st.top()]) > 0) { // 看map里是否存在这个元素
int index = umap[nums2[st.top()]]; // 根据map找到nums2[st.top()] 在 nums1中的下标
result[index] = nums2[i];
}
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
----------------------------------------------------------------------------2023年11月02日----------------------------------------------------------
3| 503.下一个更大元素II
还是挺难的,做了45min,怎么结束循环啊。我是直接让他循环三次。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {
stack<int> stk;
vector<int> ans(nums.size(), -1);
vector<int> flag(nums.size(), 0);
if(nums.size()==1){
return ans;
}
stk.push(0);
for(int i=1, j=1; j<3*nums.size() ;j++,i=j%nums.size()){
while(!stk.empty()&&(nums[i]>nums[stk.top()])){
if(flag[stk.top()]==1){
ans[stk.top()] = nums[i];
}else{
flag[stk.top()]=1;
}
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
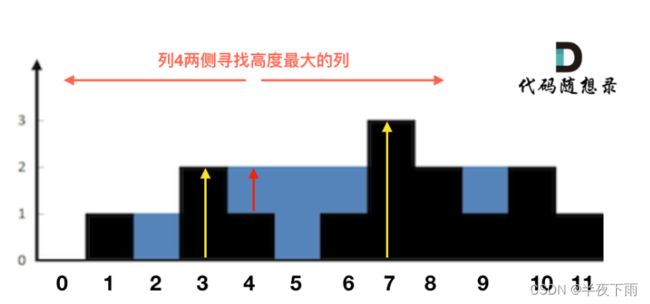
4|42. 接雨水
脑子有点转换不过来了。
代码随想录解法1(每一列计算),超时了:
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int ans=0, tmp=0;
for(int i=0; i<height.size(); i++){
if(i==0||i==height.size()-1){
continue;
}
int lheight = height[i];
for(int n=i-1; n>=0; n--){
if(height[n]>lheight){
lheight = height[n];
}
}
int rheight = height[i];
for(int m=i+1; m<height.size(); m++){
if(height[m]>rheight){
rheight = height[m];
}
}
tmp = min(lheight, rheight)-height[i];
if(tmp>0){
ans+=tmp;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
解法二:双指针策略,用空间换取每次左右遍历的时间。
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
if (height.size() <= 2) return 0;
vector<int> maxLeft(height.size(), 0);
vector<int> maxRight(height.size(), 0);
int size = maxRight.size();
// 记录每个柱子左边柱子最大高度
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
maxLeft[i] = max(height[i], maxLeft[i - 1]);
}
// 记录每个柱子右边柱子最大高度
maxRight[size - 1] = height[size - 1];
for (int i = size - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
maxRight[i] = max(height[i], maxRight[i + 1]);
}
// 求和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int count = min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i];
if (count > 0) sum += count;
}
return sum;
}
};
解法三:单调栈解法。代码来自代码随想录:
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
if (height.size() <= 2) return 0; // 可以不加
stack<int> st; // 存着下标,计算的时候用下标对应的柱子高度
st.push(0);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < height.size(); i++) {
if (height[i] < height[st.top()]) { // 情况一
st.push(i);
} if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 情况二
st.pop(); // 其实这一句可以不加,效果是一样的,但处理相同的情况的思路却变了。
st.push(i);
} else { // 情况三
while (!st.empty() && height[i] > height[st.top()]) { // 注意这里是while
int mid = st.top();
st.pop();
if (!st.empty()) {
int h = min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[mid];
int w = i - st.top() - 1; // 注意减一,只求中间宽度
sum += h * w;
}
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return sum;
}
};
----------------------------------------------------------------------------2023年11月03日----------------------------------------------------------
4|84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
维持一个单调递增的栈,然后小于的情况进行计算。
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int maxArea = 0, left, right, fixHeight, tempArea, tempIdx;
stack<int> stk;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++){
if(stk.empty()){
stk.push(i);
}
else if( !stk.empty() && heights[i] >= heights[stk.top()]){
stk.push(i);
}else if(!stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[stk.top()]){
right = i;
while( !stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[stk.top()])
{
tempIdx = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if(!stk.empty()){
left = stk.top();
}
else{
left = -1;
}
tempArea = heights[tempIdx] * (right - left-1);
if(maxArea < tempArea){
maxArea = tempArea;
}
//cout<}
stk.push(i);
}
}
right = stk.top();
while(!stk.empty()){
tempIdx = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if(!stk.empty()){
left = stk.top();
}
else{
left = -1;
}
tempArea = heights[tempIdx] * (right - left);
if(maxArea < tempArea){
maxArea = tempArea;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
----------------------------------------------------------------------------2023年11月04日----------------------------------------------------------