顺序表(2)
目录
Test.c主函数
test5
test6
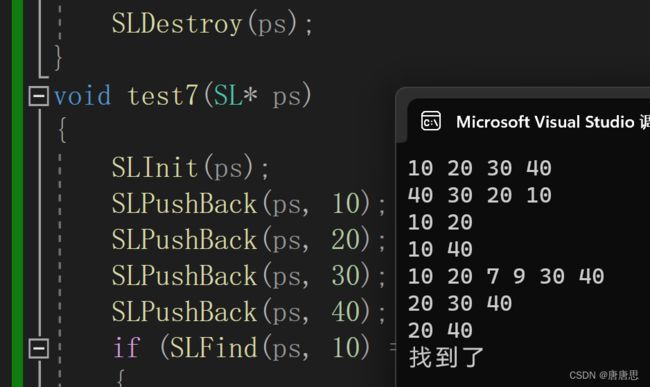
test7
菜单
Test.c总代码
SeqList.h头文件&函数声明
头文件
函数声明
SeqList.h总代码
SeqList.c函数实现
查找SeqListFind
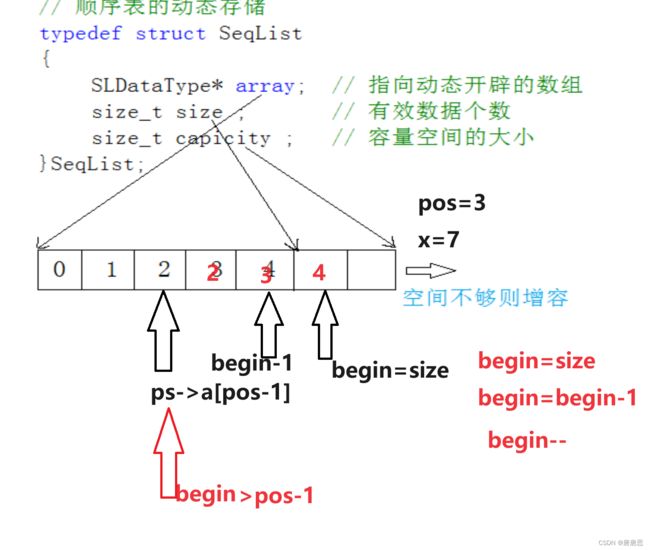
某位置插入SeqListInsert
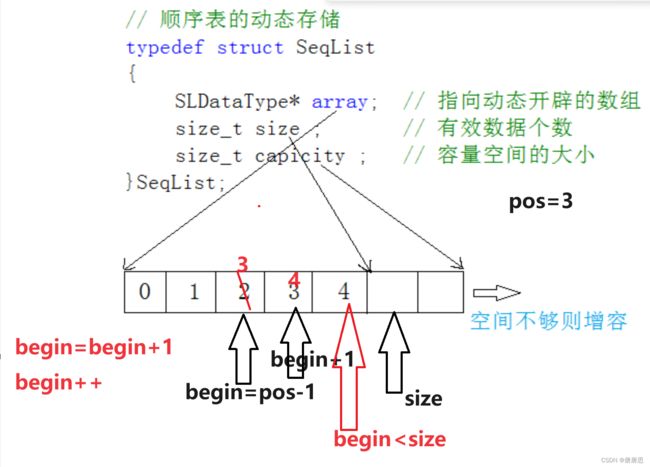
某位置删除SeqListErase
SeqList.c总代码
顺序表的问题及其思考
多文件调试小技巧
今天接着顺序表
Test.c主函数
int main()
{
SL ps;//创建一个结构题变量-传地址调用-形参是实参的一份临时拷贝
test5(&ps);//任意位置插入
test6(&ps);//任意位置删除
test7(&ps);//查找
return 0;
}test5
void test5(SL* ps)//测试在任意位置插入数据
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLInsert(ps, 3, 7);
SLInsert(ps, 4, 9);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}test6
void test6(SL* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLErase(ps, 1);
SLPrint(ps);
SLErase(ps, 2);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}test7
void test7(SL* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
if (SLFind(ps, 10) == 1)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
{
printf("未能找到\n");
}
SLDestroy(ps);
}菜单
在前面我们写过【通讯录】的多文件代码,有人询问为什么这里不先写【菜单】建议是:最后把所有功能测试成功,再去写【菜单】,这样好【调试】。
写菜单可以使用:switch&case 或 if&else
如果我们要把用户输入的数据分布放到每个函数实现内部,菜单中代码会微少,用switch&case
如果我们要把用户输入的数据放到菜单里面,菜单中代码会多,用if&else
因为我们之前【三子棋】&【扫雷】&【通讯录】都使用switch&case,这里我们就用if&else写。还有补充,在数据结构当中我们一般是不写菜单的,只要功能正确即可。建议,写好函数,先单个测试,没问题,最后在写菜单。
void menu()
{
printf("*******************************\n");
printf("1、尾插数据 2、尾删数据\n");
printf("3、头插数据 4、头删数据\n");
printf("5、打印数据 0、退出 \n");
printf("*******************************\n");
}
int main()
{
SL s;
SLInit(&s);
int option = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请输入你的选择:>");
scanf("%d", &option);
if (option == 1)//尾插
{
printf("请依次输入你的要尾插数据个数和数据:>");
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPushBack(&s, x);
}
}
else if (option == 2)//尾删
{
printf("请依次输入你的要尾删数据个数和数据:>");
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPopBack(&s, x);
}
}
else if (option == 3)//头插
{
printf("请依次输入你的要头插数据个数和数据:>");
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPushFront(&s, x);
}
}
else if (option == 4)//头删
{
printf("请依次输入你的要头删数据个数和数据:>");
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPopFront(&s, x);
}
}
else if (option == 5)//打印
{
SLPrint(&s);
}
else if (option == 0)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("无此选项,请重新输入\n");
}
} while (option != 0);
SLDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}
/*printf("请输入你的要尾插的数据,以-1结束:>");
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x != -1)
{
SLPushBack(&s, x);
scanf("%d", &x);
}*/Test.c总代码
#include"SeqList.h"
void test1(SL*ps)//测试尾插
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test2(SL*ps)//测试头插
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushFront(ps, 10);
SLPushFront(ps, 20);
SLPushFront(ps, 30);
SLPushFront(ps, 40);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test3(SL*ps)//测试头删
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLPopBack(ps);
SLPopBack(ps);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test4(SL*ps)//测试尾删//
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLPopFront(ps);
SLPopFront(ps);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test5(SL* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLInsert(ps, 3, 7);
SLInsert(ps, 4, 9);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test6(SL* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
SLErase(ps, 1);
SLPrint(ps);
SLErase(ps, 2);
SLPrint(ps);
SLDestroy(ps);
}
void test7(SL* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
SLPushBack(ps, 10);
SLPushBack(ps, 20);
SLPushBack(ps, 30);
SLPushBack(ps, 40);
if (SLFind(ps, 10) == 1)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
{
printf("未能找到\n");
}
SLDestroy(ps);
}
int main()
{
SL ps;//创建一个结构题变量-传地址调用-形参是实参的一份临时拷贝
test1(&ps);//测试尾插
test2(&ps);//测试头插
test3(&ps);//测试尾删
test4(&ps);//测试头删
test5(&ps);//任意位置插入
test6(&ps);//任意位置删除
test7(&ps);//查找
return 0;
}SeqList.h头文件&函数声明
头文件
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include//断言 函数声明
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//查找void SLInsert(SL* ps);//任意位置插入void SLErase(SL* ps);//任意位置删除SeqList.h总代码
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include//断言
//声明一个结构体
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;//如果后期a的类型改变就很方便
int size;//有效数据
int capacity;//空间容量
}SL;//SL是这个结构体的类型,用typedef定义更加方便了
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//释放销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
//展示
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//头删
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos, SLDataType x);//任意位置插入
void SLErase(SL* ps,int pos);//任意位置删除
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//查找 SeqList.c函数实现
查找SeqListFind
- 遍历一遍数组去查找元素
//元素查找
//找到了返回1
//没有找到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return 1;
}
}
return -1;
}某位置插入SeqListInsert
- pos是指我们从第一个位置往后数(数组下标是从0开始)
- 数据往后挪动,从后往前依次向后挪动
- 在pos-1的下标位置处放入元素,不要忘记size++哦
- size是数据个数,看作下标的话,它是最后一个数据的下一个位置。
//任意位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int begin = ps->size;
while (begin >= pos - 1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin - 1];
begin--;
}
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
ps->size++;
}某位置删除SeqListErase
- pos是指我们从第一个位置往后数(数组下标是从0开始)
- 数据往前挪动,从前往后依次向前挪动
- 在pos-1的下标位置处放入元素,不要忘记size++哦
//任意位置删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int begin = pos - 1;
while (begin < ps->size-1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];//会越界,注意循环条件
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}SeqList.c总代码
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
//关于初始化 可以首先置为NULL 也可以首先放点值
// memset一般用于数组初始化 直接初始化更加清晰
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->a != NULL)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
//展示
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)//容量满了需要扩容的条件
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (ps->capacity);
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("CheckCapacity");//
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//扩容
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)//注意可以等于0 size为1 但是不能为负数会越界访问
{
ps->a[end+1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size);//本质问题就是害怕这个顺序表空了还在删除
ps->size--;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size);
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
//任意位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int begin = ps->size;
while (begin >= pos - 1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin - 1];
begin--;
}
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//任意位置删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int begin = pos - 1;
while (begin < ps->size-1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];//会越界注意循环条件
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
//元素查找
//找到了返回1
//没有找到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return 1;
}
}
return -1;
}顺序表的问题及其思考
- 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
多文件调试小技巧
- 连带错误❌
- 退出码不为0❌
- 不要每个函数都去查看,要找到具体错误地方再去一步步调试❌
- 指针断言❌
- free报错是 越界访问的问题---开了这么多访问多❌
- 指向的释放位置错误----没开这么多以为有这么多❌
- realloc报错是 越界访问的问题❌
- 越界访问错误不一定会被检查出来,大概率会被检查出来而已❌(类比查酒驾)
最后为什么数组的下标从0开始?? 【指针和数组是相互融洽的】
思考:如何解决以上顺序表的问题?下章博客我们将介绍链表的结构来看看。
代码---------→【唐棣棣 (TSQXG) - Gitee.com】
联系---------→【邮箱:[email protected]】