Spring如何注解式缓存redis
目录
1、Spring整合redis
1.1.导入pom依赖
1.2.添加相关配置
1.3.spring-redis.xml配置文件
2、redis的注解开发
3、redis击穿 穿透 雪崩 *
1、Spring整合redis
1.1.导入pom依赖
2.9.0
1.7.1.RELEASE
redis.clients
jedis
${redis.version}
org.springframework.data
spring-data-redis
${redis.spring.version}
1.2.添加相关配置
redis.properties:
redis.hostName=192.168.195.139
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
redis.timeout=10000
redis.maxIdle=300
redis.maxTotal=1000
redis.maxWaitMillis=1000
redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024
redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
redis.testOnBorrow=true
redis.testWhileIdle=true
redis.expiration=3600
1.3.spring-redis.xml配置文件
spring-redis.xml:
注意:redis.properties与jdbc.properties在与Spring做整合时会发生冲突;所以引入配置文件的地方要放到SpringContext.xml中!!!
2、redis的注解开发
注解式缓存
@Cacheable 配置在方法或类上,作用:本方法执行后,先去缓存看有没有数据,如果没有,从数据库中查找出来,给缓存中存一份,返回结果, 下次本方法执行,在缓存未过期情况下,先在缓存中查找,有的话直接返回,没有的话从数据库查找
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
package com.ycx.shiro;
import com.ycx.ssm.biz.ClazzBiz;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ClazzBizTest {
@Autowired
private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
}
@Test
public void test2(){
clazzBiz.deleteByPrimaryKey(10);
}
}@Cacheable 的测试代码
@Cacheable(value = "user-clz",key = "'clz:'+#cid",condition = "#cid < 5")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
@Test
public void test1(){
// 测试 Cacheable 中的value,以及缓存的应用体现
// System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(1));
// System.out.println("======================================");
// System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(1));
// 测试 Cacheable 中的 key
// System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(3));
// System.out.println("======================================");
// System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(3));
// 测试 Cacheable 中的 condition
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(4));
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(4));
}测试结果:redis中有数据,则访问redis;如果没有数据,则访问MySQL
@CachePut: 类似于更新操作,即每次不管缓存中有没有结果,都从数据库查找结果,并将结果更新到缓存,并返回结果
value 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个
key 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合
condition 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存
@CachePut测试代码
@CachePut(value = "user-clz-put")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
@Test
public void test2(){
// 测试 Cacheput 中的 key
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(4));
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(4));
}测试结果:只存不取
@CacheEvict 用来清除用在本方法或者类上的缓存数据(用在哪里清除哪里)
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
allEntries:true表示清除value中的全部缓存,默认为false
@CacheEvict测试代码
// @CacheEvict(value = "user-clz-put",key = "'clz:'+#cid") 删除指定的缓存数据
@CacheEvict(value = "user-clz-put",allEntries = true) // 删除以 user-clz-put开头的 缓存
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
@Test
public void test3(){
// 测试 CacheEvict 中的 key
clazzBiz.deleteByPrimaryKey(2);
}测试结果:可以配置删除指定缓存数据,也可以删除符合规则的所有缓存数据;
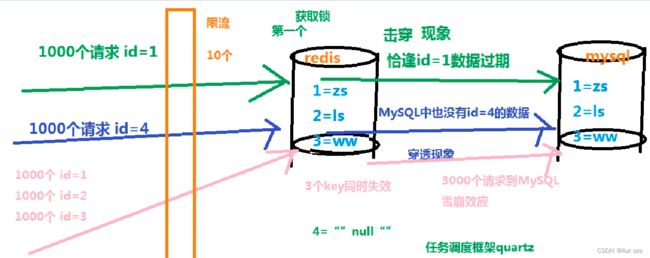
3、redis击穿 穿透 雪崩 *
击穿:高并发量的同时key失效,导致请求直接到达数据库
设置锁
1.获取 Redis 锁,如果没有获取到,则回到任务队列继续排队
2.获取到锁,从数据库拉取数据并放入缓存中
3.释放锁,其他请求从缓存中拿到数据限流:请求redis之前做流量削峰
穿透: 很多请求都在访问数据库一定不存在的数据,造成请求将缓存和数据库都穿透的情况
规则排除
可以增加一些参数检验。例如数据库数据 id 一般都是递增的,如果请求 id = -10 这种参数,势必绕过Redis。避免这种情况,可以对用户真实性检验等操作。null值填充
当缓存穿透时,redis存入一个类似null的值,下次访问则直接缓存返回空,当数据库中存在该数据的值则需要把redis存在的null值清除并载入新值,此方案不能解决频繁随机不规则的key请求
雪崩: 雪崩和击穿类似,不同的是击穿是一个热点 Key 某时刻失效,而雪崩是大量的热点 Key 在一瞬间失效
给不同的热点key设置不同的缓存策略