耗时一个月总结出来的Netty实战笔记
目录
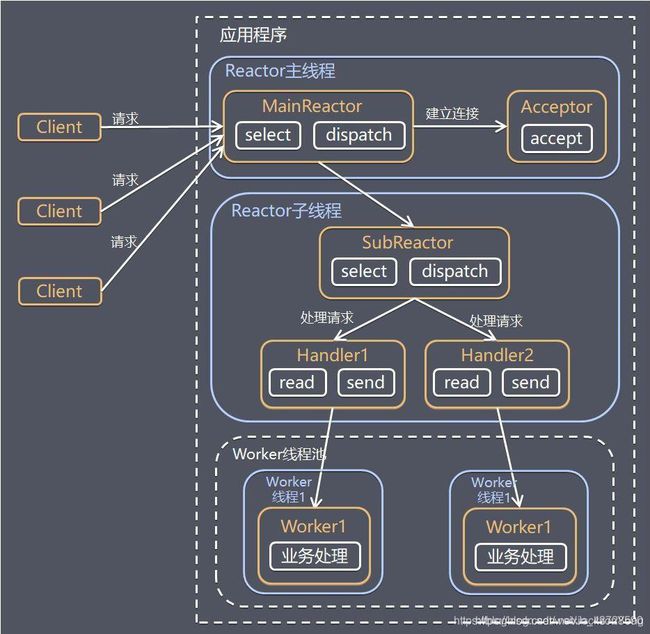
1.Netty体系图
2.Java的三种IO流
1)BIO:
2)NIO:
3).AIO:图略。不常用
3.IO实例
1).BIO:
2).NIO:
(1).Buffer:
(2).Channel:
(3).Selector:
3).零拷贝:
3.线程模型
1)Reactor模式:
4.Netty模型
入门案例:
5.源码分析
任务队列中的Task使用场景:
6.异步模型
1)Future说明:
2)Netty异步模型示意图:
3)Future-Listener机制
7.unpooled类
8.Netty应用实例
(1)群聊系统:
(2)心跳处理器:
9.WebSocket长连接开发
10.Protobuf
11.Handler链调用机制
12.TCP粘包和拆包
13.Netty调用Dubbo RPC
1.Netty体系图
2.Java的三种IO流
1)BIO:
简单示意图:
适用于:连接数量少而且架构固定的架构。
2)NIO:
简单示意图:
适用于:连接数量多而且连接比较短的架构,比如聊天服务器、弹幕系统和服务器之间的通信等。
(1)可以将buffer转成只读型buffer。
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();(2) MappedByteBuffer可直接在内存(堆外内存)修改文件,操作系统不需要再拷贝一次。
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
//获取对应的通道
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
//arg1:此处使用读写模式,arg2:可以修改的起始位置,arg3:映射内存的大小,即多少个字节映射到内存中
MappedByteBuffer map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);//下标范围为[0,5)
map.put(0,(byte) 'H');
map.put(3,(byte) '9');
randomAccessFile.close();Selector、Channel 和 Buffer是NIO的三大核心组件,
关系图:
文字说明:
(1)每个 Thread都会对应一个 Selector,每个 Channel 都会对应一个 Buffer。
(2)一个Thread对应多个 Channel。
(3)程序切换到哪个 Channel 是由事件决定的。
(4)Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换。
(5)Buffer 就是一个内存块,底层是一个数组。
(6)BIO 中的数据流是单向的,要么是输入流,或者是输出流,但是 NIO 的 Buffer 是可以读也可以写,需要 flip 方法切换 Channel ,是双向的。
3).AIO:图略。不常用
适用于:连接数目比较多且连接比较长的架构。
3.IO实例
1).BIO:
思路:1.创建一个线程池
2.如果有客户端连接,就创建一个线程与之通讯(单独写一个方法)
代码:
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//创建ServerSocket
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务器启动了");
while (true) {
//监听,等待客户端连接
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接到一个客户端");
//创建线程与之通讯
newCachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
handler(socket);
}
});
}
}
//和客户端通讯
public static void handler(Socket socket){
try{
System.out.println("线程信息id="+Thread.currentThread().getId()+",线程名字="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//通过socket获取输入流
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//循环读取客户端发送的数据
while (true){
System.out.println("线程信息id="+Thread.currentThread().getId()+",线程名字="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
if(read !=1 ){
//输出客户端发送的数据
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,read));
}else {
break;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试:win+r,用telnet 127.0.0.1 6666,ctrl+]进入编辑页面,send内容,测试结果。
2).NIO:
(1).Buffer:
代码:
public class BaseBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个buffer,大小(长度)为5
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
for (int i=0;i结果:0 2 4 6 8
(2).Channel:
Demo1:创建文件
public class NIOChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "hello,world";
//创建输入流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file01.txt");
//获取FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将str放入byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
//将byteBuffer的数据写入fileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileChannel.close();
}
}Demo2:读取文件
public class NIOChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件输入流
File file = new File("d:\\file01.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
//获取FileChannel,类似于FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());
//将通道的数据写入Buffer
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//将字节数据转换成String
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}Demo3:复制文件
public class NIOChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileChannel channel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel channel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true){//循环次数
byteBuffer.clear();//这里一定要清空buffer,不然的话后面当position=limit时,read就会变成0
int read = channel01.read(byteBuffer);
if(read == -1){//表示读完
break;
}
//将buffer中的数据写入到channel02,即2.txt中
byteBuffer.flip();
channel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}Demo4:拷贝文件transferFrom方法
public class NIOChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建相关流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.jpg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\b.jpg");
//获取对应流的FileChannel
FileChannel sourceCh = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//使用transferFrom完成拷贝
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh,0,sourceCh.size());
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}(3).Selector:
Selector、SelectionKey、ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel的关系(步骤):
1.当客户端连接时,会通过ServerSocketChannel得到SocketChannel。
2.Selector使用select()方法监听,返回有事件发生的通道个数。
3.将SocketChannel注册到Selector上,使用register(Selector sel,int ops),一个selector上可以注册多个SocketChannel。
4.注册后返回一个SelectionKey,会和该Selector关联。
5.进一步得到各个SelectionKey(有事件发生)
6.通过SelectionKey反向获取SocketChannel,使用channel()方法。
7.得到channel,完成业务处理。
Demo1:
服务器端:
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建ServerSocketChannel -> ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//得到一个Selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//绑定端口6666,在服务器端监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将serverSocketChannel注册到selector
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//循环等待客户端连接
while (true){
if(selector.select(1000) == 0){
System.out.println("服务器等待了1秒,无连接");
continue;
}
//如果返回>0,就获得相关的SelectionKey集合
//通过selectionKeys反向获取通道
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()){
//获取到SelectionKey
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//根据key对应的通道发生的事件做相应处理
if(key.isAcceptable()){//如果是OP_ACCEPT,表示有新的客户端连接
//该客户端生成一个socketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接成功,生成了一个socketChannel" + socketChannel.hashCode());
//将得到的socketChannel设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将socketChannel注册到selector,同时给socketChannel关联一个Buffer
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if(key.isReadable()){//发生OP_ACCEPT
//通过key反向获取到对应的channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//获取到该channel关联的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("form 客户端" + new String(buffer.array()));
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
} 客户端:
public class BINClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//提供服务器端的Ip和端口号
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",6666);
//连接服务器
if(!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("连接需要时间,但是客户端不会阻塞,可以做其它工资...");
}
}
String str = "hello,world";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
//发送数据,将buffer数据写入channel
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();
}
}Demo2:群聊系统
服务器端:
public class GroupChatServer {
//定义属性
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel listenChannel;
private static final int PORT = 6667;
//在构造器里面初始化工作
public GroupChatServer() {
try{
//得到选择器
selector = Selector.open();
listenChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
listenChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
//设置非阻塞模式
listenChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将listenChannel注册到selector
listenChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//监听
public void listen(){
try{
while (true){
int count = selector.select(2000);
if(count > 0){//有事件处理
Iterator iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//监听到accept
if(key.isAcceptable()){
SocketChannel sc = listenChannel.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//将sc注册到selector
sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(sc.getRemoteAddress()+"上线");
}if(key.isReadable()){
readData(key);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}else {
System.out.println("等待.......");
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
//读取客户端消息
private void readData(SelectionKey key){
SocketChannel channel = null;
try{
channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if(count > 0){
//把缓冲区的内容转成字符串
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println("from 客户端"+msg);
//向其它客户端转发消息,要排除给自己
sendInfoToOtherClients(msg,channel);
}
}catch (IOException e){
try {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress()+"离线了...");
key.cancel();
channel.close();
}catch (IOException e2){
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//向其它客户端转发消息,要排除给自己
private void sendInfoToOtherClients(String msg,SocketChannel self) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器转发消息中.......");
for(SelectionKey key : selector.keys()){
//通过key取出对应的Channel
Channel targetChannel = key.channel();
//排除自己
if(targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != self){
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;
//将msg存储到buffer中
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
//将buffer写入通道
dest.write(buffer);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建服务器对象
GroupChatServer chatServer = new GroupChatServer();
chatServer.listen();
}
} 客户端:
public class GroupChatClient {
private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private final int PORT = 6667;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
public GroupChatClient() throws IOException {
selector = Selector.open();
//连接服务器
socketChannel = socketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将channel注册到selector
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//得到username
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println(username + "is ready....");
}
//向服务器发送消息
public void sendInfo(String info){
info = username + "说:" + info;
try{
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes()));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读取服务器回复的消息
public void readInfo(){
try{
int readChannels = selector.select();
if(readChannels > 0 ){//有可用的通道
Iterator iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if(key.isReadable()){
//得到相关的通道
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//得到buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
sc.read(buffer);
//将读到缓冲区的数据转成字符串
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
iterator.remove();//删除当前的SelectionKey,防止重复操作。
}else {
System.out.println("没有可用的通道");
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动客户端
final GroupChatClient chatClient = new GroupChatClient();
//每隔三秒启动线程,读取服务器发来的数据
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while (true){
chatClient.readInfo();
try{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
//发送数据给服务器端
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String s = scanner.nextLine();
chatClient.sendInfo(s);
}
}
} 3).零拷贝:
概念:在内核缓冲区之间,没有数据重复,只有kernel buffer一份数据。
3.线程模型
1)Reactor模式:
原理:一个或多个客户发送请求给服务器端处理器,服务器端处理器处理完请求后,使用IO复用监听事件,将请求同步发送给相应的线程。一个线程可以处理多个事件,执行非阻塞操作。
(1)单Reactor单线程:服务器端用一个线程通过多路复用技术来搞定所有的IO操作。
例子:前面的群聊系统。
使用场景:客户端有限的情况下。
结合生活打个比喻:前台和服务员是同一个人,全程只服务一个客户。
(2)单Reactor多线程:由reactor处理所有事件的监听和处理,是单线程运行的。
结合生活打个比喻:一个前台,多名服务员,前台只负责接待客户,将客户带去给服务员。
(3)主从Reactor多线程:
结合生活打个比喻:多名前台和多名服务员,服务多名客户。
4.Netty模型
文字说明:(1)Netty抽象出两组线程池BossGroup和WorkGroup,前者负责连接客户端,后者负责读写网络,但两种线程池的类型都是NioEventLoopGroup。
(2)NioEventLoopGroup相当于一个事件循环组,组中含有多个事件循环,每一个事件循环是NioGroupLooop。
(3)NioGroupLooop表示一个不断循环的执行处理任务的线程,每一个NioGroupLooop都有一个selector,用于监听绑定在其上的socket网络通信。
(4)可以有多个NioEventGroup。
(5)每个NioEventGroup循环时,先轮询、处理accept事件,再与client建立连接,生成NioSocketChaneel,并将其注册到某个Worker NIOEventLoop上的selector,最后处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks。
(6)Worker NIOEventLoop,先轮询、处理read,write事件,交给对应的NioSocketChannel处理,最后处理任务队列的事件,runAllTasks。
(7)每个worker NIOEventLoop处理业务时,会使用pipeline(管道),里面包含了channel。
入门案例:
TCP服务:
先导入Maven:
服务器端:
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建两个线程组,都是无限循环的
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//bossGroup处理连接请求
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//workGroup处理客户端业务
try {
//创建服务器的启动对象,配置参数
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//使用链式编程来进行设置
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)//设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//使用NioSctpServerChannel作为服务器的通道实现
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//设置线程队列得到的连接个数
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)//设置保持活动的连接状态
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});//给workGroup对应的EventLoop对应的管道设置处理器
System.out.println("Server is ready.......");
//启动服务器并绑定端口
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync();
//对关闭通道进行监听
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
//自定义一个handler
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//arg1为上下文对象,含有管道、通道和地址
//agr2为客户端发送的数据
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("客户端发送消息是:"+buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("客户端地址"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
//读取完毕
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,Server",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
//处理异常关闭通道
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}客户端:
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//客户端需要一个事件循环组
NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//设置相关参数
bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)//设置线程组
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//设置客户端通道的实现类
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler());//加入处理器
}
});
System.out.println("client is ready......");
//启动客户端连接服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6668).sync();
//监听关闭通道
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
} public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//当通道就绪时就会触发此方法
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,server", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
//当通道有读取事件时会触发此事件
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:"+buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器的地址:"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
运行结果:
5.源码分析
(1) BossGroup和WorkerGroup默认都是八核的,含有子线程的个数为八个,等于实际的CPU核数 * 2。
(2) pipeline的本质是一个双向链表。
任务队列中的Task使用场景:
(1)用户自定义的普通任务。提交该channel到NIOEventLoop的takeQueue中。
(2)用户自定义定时任务。 该任务提交到scheduleTakeQueue中。
(3)非当前的Reactor线程调用Channel的各种方法
6.异步模型
当发出异步过程调用后,调用者不能立即得到结果,而是通过Future-Listener机制,用户可以方便主动获取或者通过通知机制获得IO操作结果。Netty中所有的I/O操作是异步的。
1)Future说明:
(1)表示异步的结果,可以通过它提供的方法来检测是否完成。
(2)ChannelFuture是一个接口,可以添加监听器,当监听的事件发生时,就会通知监听器。
2)Netty异步模型示意图:
3)Future-Listener机制
当Future对象刚刚创建时,处于非完成状态,调用者可以通过返回的ChannelFuture来获取操作执行的状态,注册监听事件函数来执行完成操作。
7.unpooled类
netty提供专门用来操作缓冲区的工具类。
注意:(1)在netty的buffer中,不需要使用flip方法进行读写反转,因为底层委会了了readerIndex和writerIndex。
(2)通过readerIndex、writerIndex和capacity,将buffer分成三个区域:
| 范围 | 含义 |
| 0-readerIndex | 表示已经读取的区域 |
| readerIndex- writerIndex | 可读区域 |
| writerIndex-capacity | 可写区域 |
8.Netty应用实例
(1)群聊系统:
服务器端:
public class GroupChatServer {
private int port;//端口号
public GroupChatServer(int port){
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
//创建两个线程组
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
try{
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//获取到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//向pipeline加入解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder());
//向pipeline加入编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder());
//加入自己的业务处理handler
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty服务器启动");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new GroupChatServer(7000).run();
}
} public class GroupChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
//定义一个channel组,管理所有的channel
//GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE 是全局事件执行器,是一个单例
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//该方法表示建立一旦连接,第一个被执行
//将当前channel加入到channelGroup中
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//将客户加入聊天的信息推送给其它在线的客户端
//writeAndFlush方法会将channelGroup中所有的channel遍历,并发送消息
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端]"+channel.remoteAddress()+"加入聊天"+sdf.format(new Date())+"\n");
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
//将xx用户断开信息推送给其它在线用户
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端]"+channel.remoteAddress()+"离开了"+sdf.format(new Date())+"\n");
}
//表示channel处于活动的状态,提示xx上线了
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"上线了"+sdf.format(new Date())+"\n");
}
//当channel处于非活动状态,提示xx下线了
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"下线了......."+sdf.format(new Date())+"\n");
}
//读取数据
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, final String msg) throws Exception {
//获取到当前的channel
final Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//遍历channelGroup,根据不同的情况,回送不同的消息
channelGroup.forEach(ch ->{
if(channel != ch){
ch.writeAndFlush("[客户]"+channel.remoteAddress()+"发送了消息"+msg+"\n");
}else{
ch.writeAndFlush("[自己]发送了消息"+msg+"\n");
}
});
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//关闭
ctx.close();
}
} 客户端:
public class GroupChatClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public GroupChatClient(String host,int port){
this.host=host;
this.port=port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//得到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//向pipeline加入解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder());
//向pipeline加入编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder());
//加入自己的业务处理handler
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
//得到channel
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("--------"+channel.localAddress()+"--------");
//客户端需要输入信息,创建一个扫描器
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
//通过channel发送到服务器端
channel.writeAndFlush(msg+"\r\n");
}
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
new GroupChatClient("127.0.0.1",7000).run();
}
} public class GroupChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
} (2)心跳处理器:
服务器端:
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//设置读写时间
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3,5,7, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
//启动服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally{
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
} public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 事件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if(evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent)evt;
String eventType = null;
switch (event.state()){
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "读空闲";
break;
case READER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
break;
}
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"---超时时间---"+eventType);
//发生异常就关闭
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}服务器端:同上面的
运行结果:
9.WebSocket长连接开发
后台核心代码:
//使用http的编码和解码器
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//以块的方式写,添加ChunkedWriteHandler处理器
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
//http在传输过程中是分段的,而HttpObjectAggregator可以将多段合起来
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
//websocket是以帧的方式传输的,浏览器请求 wc://localhost:7000/hello 表示请求的url
//WebSocketServerProtocolHandler可以将http协议升级为tcp协议,保持长连接
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello"));10.Protobuf
流程图:
编译的命令:
protoc.exe --java_out=.xxxx.proto11.Handler链调用机制
过程图:
总结:
无论是解码器handler还是编码器handler,接收的数据类型要和待处理的数据类型保持一致,否则不会被执行。
ps:在解码器进行解码时,要判断缓冲区(ByteBuf)的数据是否足够,否则接收的结果和期望结果可能不一致。
ReplayingDecoder不需要判断数据是否足够,其内部会进行处理,当并不是所有的ByteBuf都支持ReplayingDecoder。
12.TCP粘包和拆包
产生的原因:TCP无消息保护边界,需要再接收端处理消息边界问题。简单来讲,就是服务器会多读或少读数据。
解决方案:使用自定义协议+编解码器。
13.Netty调用Dubbo RPC
RPC:远程过程调用,是一种计算机通信协议。使得两个或多个部署到不同的服务器上应用程序之间的调用像在本地调用一样。
RPC调用流程图: