基于Python+OpenCV图像识别的连连看辅助工具(深度学习+机器视觉)含全部工程源码及视频演示
目录
- 前言
- 总体设计
-
- 系统整体结构图
- 系统流程图
- 运行环境
-
- Python 环境
- Pycharm 环境
- 模块实现
-
- 1. 获取句柄
- 2. 图像划分
- 3. 建立矩阵
- 4. 矩阵求解
- 系统测试
- 工程源代码下载
- 其它资料下载
前言
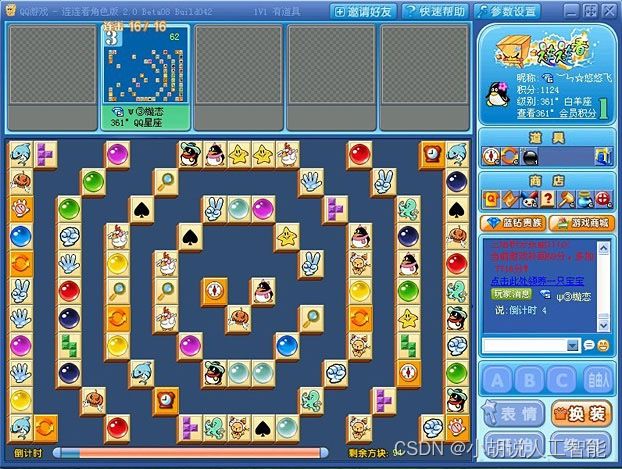
本项目目标是利用pywin32来获取游戏图像信息,并利用OpenCV进行识别和处理,从而实现QQ连连看游戏中相同图形的连通。
QQ连连看是一款非常受欢迎的游戏,通过连接相同花色的两张牌来消除它们,规则简单易懂。在我上大学的时候,QQ连连看风靡一时,我也是其中的狂热玩家之一。如果当时我会这个项目,我相信我早就成为了神眼 4000000级别的高手了!
这个项目不仅可以帮助玩家提高连连看的技能,还可以作为一个有趣的学习项目,深入研究图像处理和计算机视觉的应用。无论是解锁更高级别的成就,还是探索图像处理的奥秘,这个项目都将给你带来无尽的乐趣和挑战!
总体设计
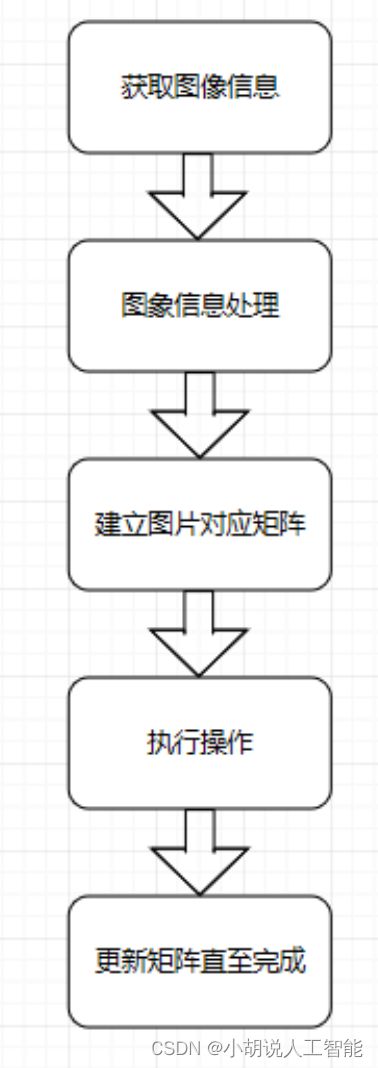
本部分包括系统整体结构图和系统流程图。
系统整体结构图
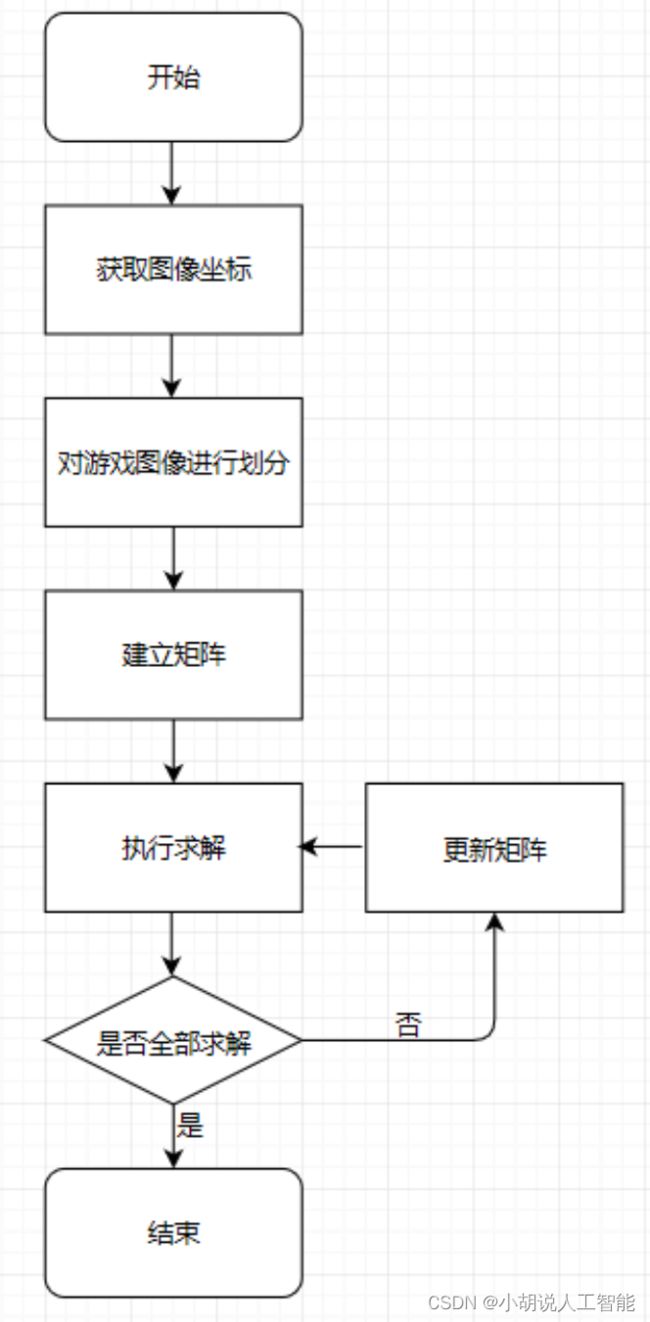
系统流程图
系统流程如图所示。
运行环境
本部分包括 Python 环境、Pycharm 环境配置和 安装相关库。
Python 环境
需要 Python 3.6 及以上配置
Pycharm 环境
通过 https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ 下载pywin32、matplotlib、numpy、OpenCV、Pillow。
进入相关环境后,可使用如下模版进行库的安装:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ 相关库名
模块实现
本项目包括本项目包括 4 个模块:获取句柄、图像划分、建立矩阵,矩阵求解,下面分别给出各模块的功能介绍及相关代码。
1. 获取句柄
QQ 游戏连连看的游戏区图像水平方向有 19 列,竖直方向有 11 行。确定连连看图像的坐标进行划分建立矩阵,通过获取游戏窗口句柄来实现,相关代码如下:
window_title = 'QQ游戏 - 连连看角色版'
num_grid_per_row = 19
num_grid_per_col = 11
screen_width = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(0)
screen_height = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(1)
hwnd = win32gui.FindWindow(win32con.NULL,window_title)
#获取游戏窗口句柄
if hwnd == 0 :
error_exit('%s not found' % window_title)
window_left,window_top,window_right,window_bottom = win32gui.GetWindowRect(hwnd)
print(window_left,window_top,window_right,window_bottom)
if min(window_left,window_top) < 0\
or window_right > screen_width\
or window_bottom > screen_height:
error_exit('window is at wrong position')
window_width = window_right - window_left
window_height = window_bottom - window_top
game_area_left = window_left + 14.0 / 800.0 * window_width
game_area_top = window_top + 181.0 / 600.0 * window_height
game_area_right = window_left + 603 / 800.0 * window_width
game_area_bottom = window_top + 566 / 600.0 * window_height
#确定游戏区图像坐标
game_area_width = game_area_right - game_area_left
game_area_height = game_area_bottom - game_area_top
grid_width = game_area_width / num_grid_per_row
grid_height = game_area_height / num_grid_per_col
2. 图像划分
获得游戏图像坐标,可准确地捕捉图像信息,将游戏图像进行区分处理。
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#最简单的以灰度直方图作为相似比较的实现
def classify_gray_hist(image1,image2,size = (256,256)):
#先计算直方图
#几个参数必须用方括号括起来
#直接用灰度图计算直方图,使用第一个通道
#进行通道分离后,得到多个通道的直方图
#bins 取为16
image1 = cv2.resize(image1,size)
image2 = cv2.resize(image2,size)
hist1 = cv2.calcHist([image1],[0],None,[256],[0.0,255.0])
hist2 = cv2.calcHist([image2],[0],None,[256],[0.0,255.0])
#可以比较直方图
plt.plot(range(256),hist1,'r')
plt.plot(range(256),hist2,'b')
plt.show()
#计算直方图的重合度
degree = 0
for i in range(len(hist1)):
if hist1[i] != hist2[i]:
degree = degree + (1 - abs(hist1[i]-hist2[i])/max(hist1[i],hist2[i]))
else:
degree = degree + 1
degree = degree/len(hist1)
return degree
#计算单通道直方图的相似值
def calculate(image1,image2):
hist1 = cv2.calcHist([image1],[0],None,[256],[0.0,255.0])
hist2 = cv2.calcHist([image2],[0],None,[256],[0.0,255.0])
#计算直方图的重合度
degree = 0
for i in range(len(hist1)):
if hist1[i] != hist2[i]:
degree = degree + (1 - abs(hist1[i]-hist2[i])/max(hist1[i],hist2[i]))
else:
degree = degree + 1
degree = degree/len(hist1)
return degree
#通过得到每个通道的直方图来计算相似度
def classify_hist_with_split(image1,image2,size = (256,256)):
#将图像resize后,分离为三个通道,再计算每个通道的相似值
image1 = cv2.resize(image1,size)
image2 = cv2.resize(image2,size)
sub_image1 = cv2.split(image1)
sub_image2 = cv2.split(image2)
sub_data = 0
for im1,im2 in zip(sub_image1,sub_image2):
sub_data += calculate(im1,im2)
sub_data = sub_data/3
return sub_data
#平均哈希算法计算
def classify_aHash(image1,image2):
image1 = cv2.resize(image1,(8,8))
image2 = cv2.resize(image2,(8,8))
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(image1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(image2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
hash1 = getHash(gray1)
hash2 = getHash(gray2)
return Hamming_distance(hash1,hash2)
def classify_pHash(image1,image2):
image1 = cv2.resize(image1,(32,32))
image2 = cv2.resize(image2,(32,32))
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(image1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(image2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#将灰度图转为浮点型,再进行dct变换
dct1 = cv2.dct(np.float32(gray1))
dct2 = cv2.dct(np.float32(gray2))
#取左上角的8*8,代表图片的最低频率
#这个操作等价于C++中利用OpenCV实现的掩码操作
#在Python中进行掩码操作,可以直接取出图像矩阵的某一部分
dct1_roi = dct1[0:8,0:8]
dct2_roi = dct2[0:8,0:8]
hash1 = getHash(dct1_roi)
hash2 = getHash(dct2_roi)
return Hamming_distance(hash1,hash2)
#输入灰度图,返回hash
def getHash(image):
avreage = np.mean(image)
hash = []
for i in range(image.shape[0]):
for j in range(image.shape[1]):
if image[i,j] > avreage:
hash.append(1)
else:
hash.append(0)
return hash
#计算汉明距离
def Hamming_distance(hash1,hash2):
num = 0
for index in range(len(hash1)):
if hash1[index] != hash2[index]:
num += 1
return num
if __name__ == '__main__':
img1 = cv2.imread('row_0-col_16.jpg')
cv2.imshow('img1',img1)
img2 = cv2.imread('row_1-col_17.jpg')
cv2.imshow('img2',img2)
#degree = classify_gray_hist(img1,img2)
degree = classify_hist_with_split(img1,img2)
#degree = classify_aHash(img1,img2)
#degree = classify_pHash(img1,img2)
print(degree)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#编写compare_image
def same_grid(image_a,image_b): #定义相同网格
numpy_array_a = numpy.array(image_a)
numpy_array_b = numpy.array(image_b)
#足够小,不需要resize
if 0.95 < compare_image.classify_hist_with_split(numpy_array_a,numpy_array_b,
size=image_a.size):
return True
return False
3. 建立矩阵
对游戏图像信息处理完毕后转化为数字矩阵,相同的图案转化成相同的数字,来帮助计算机进行运算执行。
def game_area_image_to_matrix(image_,grid_width,grid_height):
#将图片转化为网格
pos_to_image = {}
for row in range(11):
pos_to_image[row] = {}
for col in range(19):
grid_left = col * grid_width
grid_top = row * grid_height
grid_right = grid_left + grid_width
grid_bottom = grid_top + grid_height
grid_image = copy_part_image(image_,
grid_left,grid_top,
grid_right,grid_bottom)
pos_to_image[row][col] = grid_image
#区分网格
pos_to_type_id = {}
known_type_image = []
for row in range(11):
pos_to_type_id[row] = {}
for col in range(19):
this_image = pos_to_image[row][col]
if is_empty_grid(this_image):
pos_to_type_id[row][col] = 0
continue
found = False
for index in range(len(known_type_image)):
if same_grid(known_type_image[index],this_image):
id = index + 1
pos_to_type_id[row][col] = id
found = True
break
#对网格进行编号
if not found:
known_type_image.append(this_image)
id = len(known_type_image)
pos_to_type_id[row][col] = id
return pos_to_type_id
4. 矩阵求解
相关代码如下:
def execute_one_step(one_step,
game_area_left,game_area_top,
grid_width,grid_height):
from_row,from_col,to_row,to_col = one_step
from_x = game_area_left + (from_col + 0.5) * grid_width
from_y = game_area_top + (from_row + 0.5) * grid_height
to_x = game_area_left + (to_col + 0.5) * grid_width
to_y = game_area_top + (to_row + 0.5) * grid_height
pyautogui.moveTo(from_x,from_y)
pyautogui.click()
pyautogui.moveTo(to_x,to_y)
pyautogui.click()
#使用pyautogui实现自动化鼠标单击图案
def print_matrix(matrix):
for row in range(11):
line = str()
for col in range(19):
if matrix[row][col] == 0:
id = ' '
else:
id = '%02d' % matrix[row][col]
line+='%s ' % id
print(line)
while True:
print('\n\n\n---------')
game_area_image = grab_screen(game_area_left,game_area_top,
game_area_right,game_area_bottom)
#捕捉游戏画面
id_matrix = game_area_image_to_matrix(game_area_image,
grid_width,
grid_height)
#get matrix of grid_type_id
print_matrix(id_matrix)
#打印矩阵
def solve_matrix_one_step(matrix):
matrix_row = len(matrix)
matrix_col = len(matrix[0])
for row in range(matrix_row):
for col in range(matrix_col):
if matrix[row][col] == 0:
continue
target_row,target_col = DFS(row,col,
target_number=matrix[row][col],
empty_number=0,
matrix=matrix,
matrix_row=matrix_row,matrix_col=matrix_col,
path=str(),
first_step=True)
if target_row:
return row,col,target_row,target_col
#判断求解成功,否则无解
for row in range(matrix_row):
for col in range(matrix_col):
if matrix[row][col] != 0:
#无解
error_exit('no solution??')
#全空则求解完毕
return None
while True:
print('---one step---')
print_matrix(id_matrix)
one_step = solve_matrix_one_step(id_matrix)
#找出相同的一组进行相连求解
if not one_step:
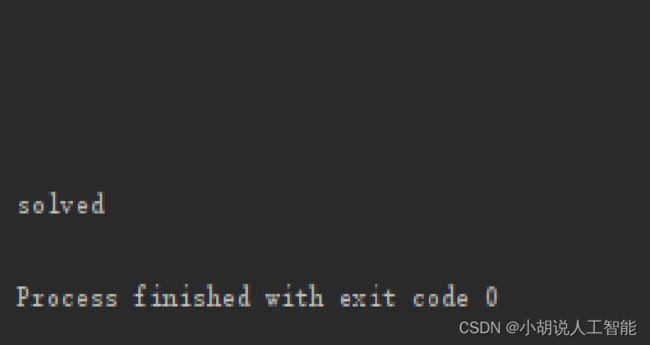
print('solved')
exit(0)
print(one_step)
execute_one_step(one_step,
game_area_left,game_area_top,
grid_width,grid_height)
from_row,from_col,to_row,to_col = one_step
id_matrix[from_row][from_col] = 0
id_matrix[to_row][to_col] = 0
time.sleep(args.interval)
系统测试
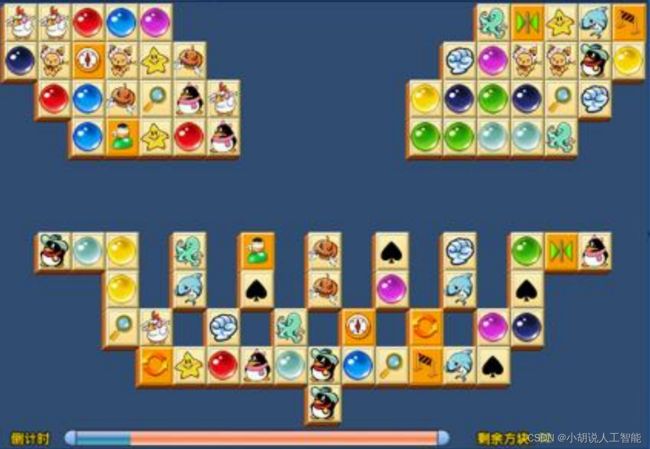
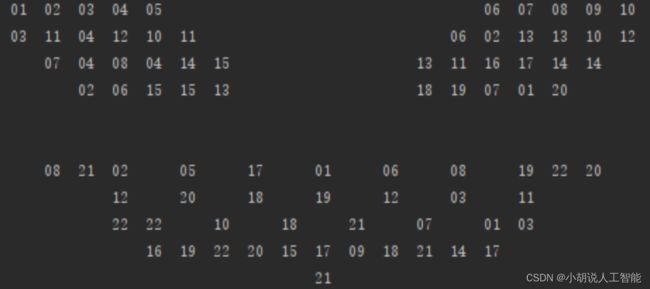
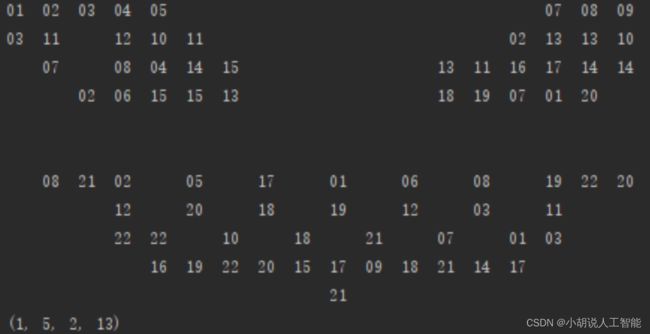
将截取获得的游戏图像转化成数字矩阵,如图 1 和图 2 所示,数字矩阵如图 3 所示,测试效果如图 4 所示。
工程源代码下载
详见本人博客资源下载页
其它资料下载
如果大家想继续了解人工智能相关学习路线和知识体系,欢迎大家翻阅我的另外一篇博客《重磅 | 完备的人工智能AI 学习——基础知识学习路线,所有资料免关注免套路直接网盘下载》
这篇博客参考了Github知名开源平台,AI技术平台以及相关领域专家:Datawhale,ApacheCN,AI有道和黄海广博士等约有近100G相关资料,希望能帮助到所有小伙伴们。