5-Servlet
5-Servlet
文章目录
- 5-Servlet
- Servlet概述
-
- 补充概念:静态资源和动态资源
- Servlet简介
- Servlet开发流程
-
- 开发方式1--XML配置
-
- 步骤1:新建一个module,并将其改为Web类型
- 步骤2:开发一个Java类,名为:UserServlet
- 步骤3:在web.xml中为UserServlet配置请求的映射路径
- 步骤4:开发一个HTML的form表单并绑定servlet对应的url,发送一个get请求并携带username参数
- 映射关系图解
- 开发方式2--@WebServlet注解
- Servlet生命周期
-
- 什么是Servlet生命周期?
- Servlet主要的生命周期
- Servlet生命周期测试
- Servlet生命周期测试结论
- Servlet继承结构
-
- 总的继承图解
- 继承体系介绍
- 继承体系中各成员的基本方法
-
- 顶层-Servlet接口
- 次顶层-GenericServlet抽象类
- 次次顶层-HttpServlet抽象类
- 次次次顶层-自定义Servlet
- Servlet初始化配置参数和获取上下文信息
-
- ServletConfig
-
- 什么是ServletConfig?
- ServletConfig常用API
- ServletConfig的XML配置初始化
- ServletConfig的注解配置初始化
- ServletConfig的API使用示例
- ServletContext
-
- 什么是ServletContext?
- 域的概念
- ServletContext常用API
- ServletContext的XML配置初始化
- ServletContext的API调用用法
- Servlet-处理和响应浏览器请求
-
- HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse与请求、响应之间的关系
- HttpServletRequest常用API
-
- 获取请求行信息相关
- 获得请求头信息相关
- 获得请求(体内的)参数相关
- HttpServletResponse常用API
-
- 设置响应行相关
- 设置响应头相关
- 设置响应体相关
- 其他API
- MIME类型
- 请求转发和响应重定向
-
- 整体概述
- 请求转发
-
- 1-逻辑图
- 2-请求转发特点(背诵)
- 3-代码实现
- 响应重定向
-
- 1-逻辑图
- 2-请求重定向特点
- 3-代码实现
- 总结
- Web乱码问题
-
- 乱码根源
- 乱码Case--HTML乱码
- 乱码Case--Tomcat控制台乱码
- 乱码Case--请求乱码
-
- Get请求乱码
- Post请求乱码
- 乱码Case--响应乱码
- 路径问题
-
- 概念:相对路径和绝对路径
- 路径演示--前端项目示例
- 前端路径问题
-
- 相对路径分析
- 绝对路径分析
- base标签使用
- 究极操作:缺省项目上下文路径
- 响应重定向的路径问题
-
- 目标
- Servlet-相对路径写法
- Servlet-绝对路径写法
- HTML-请求项目内其他静态资源
- 请求转发的路径问题
-
- 目标
- Servlet-相对路径写法
- HTML-目标资源内相对路径处理
- Servlet-绝对路径写法
- HTML-目标资源内绝对路径处理
Servlet概述
补充概念:静态资源和动态资源
静态资源
-
无需在程序运行时通过代码运行生成的资源,在程序运行之前就写好的资源
-
例如:html css js img ,音频文件和视频文件
动态资源
- 需要在程序运行时通过代码运行生成的资源,在程序运行之前无法确定的数据,运行时动态生成。
- 例如Servlet,Thymeleaf … …
理解
- 去蛋糕店买蛋糕,直接买柜台上已经做好的:静态资源
- 去蛋糕店买蛋糕,和柜员说要求后现场制作:动态资源
Servlet简介
概念
- Servlet (server applet) 是运行在服务端(tomcat)的Java小程序,是sun公司提供一套定义动态资源规范;从代码层面上来讲Servlet就是一个接口
用途
-
用来接收、处理客户端请求、响应给浏览器的动态资源
-
在整个Web应用中,Servlet主要负责接收处理请求、协同调度功能以及响应数据,可以把Servlet称为Web应用中的控制器
补充
- 不是所有的Java类都能用于处理客户端请求,能处理客户端请求并做出响应的一套技术标准就是Servlet
- Servlet是运行在服务端的,所以 Servlet必须在WEB项目中开发且在Tomcat这样的服务容器中运行
Servlet开发流程
开发方式1–XML配置
步骤1:新建一个module,并将其改为Web类型
- 参考网上视频
步骤2:开发一个Java类,名为:UserServlet
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求中的参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
if("atguigu".equals(username)){
//通过响应对象响应信息
resp.getWriter().write("NO");
}else{
resp.getWriter().write("YES");
}
}
}
- 类要继承HttpServlet,且重写service方法
- service方法参数用tomcat传递调配
- HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的理解见下边,内容上分别包含请求和响应中的信息
步骤3:在web.xml中为UserServlet配置请求的映射路径
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>userServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.UserServletservlet-class>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>userServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/userServleturl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
- 一个servlet可以对应多个不同的url-pattern,但是一个url-pattern只能对应一个servlet
- url-pattern中可以使用一些通配写法:
| 通配方法 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| /name | http://localhost:8080/name | 通配特定name的路径资源 |
| / | http://localhost:8080/xxx http://localhost:8080/aaa http://localhost:8080/bbb |
表示通配所有资源,都会访问到该servlet 不包括jsp文件,即http://localhost:8080/test.jsp,不会进入到该servlet |
| /* | 同 / | 解释同 / ,且寻找jsp文件也会进入到该servelt |
| /a/* | http://localhost:8080/a/xxx http://localhost:8080/a/aaa http://localhost:8080/a/bbb/ccc/ddd/eee |
解释同 / ,且*表示任意,具体文件,或者更深层次的路径,都会进入到该servlet中 |
| *.action | http://localhost:8080/a/xxx.action http://localhost:8080/a/aaa.action http://localhost:8080/a/bbb/ccc/ddd/eee.action |
所有以.action结尾的资源访问,都会进入到该servlet |
步骤4:开发一个HTML的form表单并绑定servlet对应的url,发送一个get请求并携带username参数
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="userServlet">
请输入用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /> <br>
<input type="submit" value="校验">
form>
body>
html>
映射关系图解
开发方式2–@WebServlet注解
@WebServlet(
name = "userServlet",
//value = "/user",
urlPatterns = {"/userServlet1","/userServlet2","/userServlet"},
initParams = {@WebInitParam(name = "encoding",value = "UTF-8")},
loadOnStartup = 6
)
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String encoding = getServletConfig().getInitParameter("encoding");
System.out.println(encoding);
// 获取请求中的参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
if("atguigu".equals(username)){
//通过响应对象响应信息
resp.getWriter().write("NO");
}else{
resp.getWriter().write("YES");
}
}
}
注意:
- WebServlet注解和XML配置两者只能选择一个,不能对一个servlet使用两种开发方式
- WebServlet注解参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| name | 别名 |
| value | url-pattern,和urlPatterns互斥,两者给定一个即可 |
| urlPatterns | url-pattern,和value互斥,两者给定一个即可 |
| loadOnStartup | 当前servlet实例化顺序,尽量写6以后的数字 |
Servlet生命周期
什么是Servlet生命周期?
应用程序中的对象不仅在空间上有层次结构的关系,在时间上也会因为处于程序运行过程中的不同阶段而表现出不同状态和不同行为——这就是对象的生命周期
-
简单的叙述生命周期,就是对象在容器中从开始创建到销毁的过程
-
servlet对象由servlet容器创建,生命周期方法都是由容器(目前我们使用的是Tomcat)调用
Servlet主要的生命周期
| 生命周期 | 对应方法 | 执行时机 | 执行次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 构造对象 | 构造器 | 在第一次请求该servlet或者容器启动时构造(可配置) | 1 |
| 初始化 | init() | 对象构造完毕后 | 1 |
| 处理服务 | service(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp) | 每次请求 | 多次 |
| 销毁 | destory() | 容器关闭 | 1 |
Servlet生命周期测试
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ServletLifeCycle extends HttpServlet {
// 重写空参构造方法
public ServletLifeCycle(){
System.out.println("构造器");
}
// 重写初始化方法(框架内部真正起作用的是带参初始化方法,该方法用于给用户提供使用,且不影响正常的servlet初始化)
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
// 请求处理
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("service方法");
}
// 方法销毁
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
XML配置–初始化参数:load-on-startup
<servlet>
<servlet-name>servletLifeCycleservlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.ServletLifeCycleservlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>servletLifeCycleservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servletLiftCycleurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
- 该参数默认值为-1,即请求该servlet时才构造对象并初始化
- 当该参数值=正整数时,表示Tomcat容器启动时,就要构造对象并初始化,数值大小表示构造顺序
- Tomcat内置有其他的对象实例初始化,建议改值从6以后写
@WebServlet–初始化参数:loadOnStartup
- 参考上述:Servlet开发方式2-@WebServlet注解开发
Servlet生命周期测试结论
- servlet是单例模式,仅初始化一次,后续每次请求改servlet的时候,仅调用service方法处理请求
- 因此:尽量不要在service处理中改变公共变量的值,避免并发带来的错误问题
- 不采用锁来解决单例模式带来的问题,是因为加锁太影响性能
Servlet继承结构
总的继承图解
继承体系介绍
| 从父类到子类 | 关系 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| Servlet接口 | 顶层 | 提供Servlet规范,所有servlet均要实现该接口 |
| GenericServlet抽象类 | 实现Servlet | 对Servlet接口一些固定功能的粗糙实现以及对service方法的再次抽象声明,并定义了一些其他相关功能方法 |
| HttpServlet抽象类 | 继承GenericServlet | 除了基本的实现以外,增加了更多的基础功能 |
| 自定义Servlet | 继承HttpServlet | 重写service方法,完善具体业务逻辑 |
继承体系中各成员的基本方法
顶层-Servlet接口
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
// 初始化方法,容器在构造servlet对象后,自动调用的方法,容器负责实例化一个ServletConfig对象,并在调用该方法时传入
// ServletConfig对象可以为Servlet 提供初始化参数
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
// 获取ServletConfig对象的方法,后续可以通过该对象获取Servlet初始化参数
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
// 处理请求并做出响应的服务方法,每次请求产生时由容器调用
// 容器创建一个ServletRequest对象和ServletResponse对象,容器在调用service方法时,传入这两个对象
public String getServletInfo();
// 获取ServletInfo信息的方法
public void destroy();
// Servlet实例在销毁之前调用的方法
次顶层-GenericServlet抽象类
private transient ServletConfig config;
// 初始化配置对象作为属性
public GenericServlet() { }
// 构造器,为了满足继承而准备
public void destroy() { }
// 销毁方法的平庸实现,即不写任何逻辑
public String getInitParameter(String name)
// 获取初始参数的快捷方法
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames()
// 返回所有初始化参数名的方法
public ServletConfig getServletConfig()
// 获取初始Servlet初始配置对象ServletConfig的方法
public ServletContext getServletContext()
// 获取上下文对象ServletContext的方法
public String getServletInfo()
// 获取Servlet信息的平庸实现
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException()
// 初始化方法的实现,并在此调用了init的空参重载方法,方便用户加入自己的逻辑,且不影响正常servlet初始化
public void init() throws ServletException
// 重载init方法,为了让我们自己定义初始化功能的方法
public void log(String msg)
public void log(String message, Throwable t)
// 打印日志的方法及重载
public abstract void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
// 服务方法再次声明
public String getServletName()
// 获取ServletName的方法
次次顶层-HttpServlet抽象类
private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE";
private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD";
private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET";
private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS";
private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST";
private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT";
private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE";
// 上述属性用于定义常见请求方式名常量值
public HttpServlet() {}
// 构造器,用于处理继承
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
// 对服务方法的实现
// 在该方法中,将请求和响应对象转换成对应HTTP协议的HttpServletRequest HttpServletResponse对象
// 调用重载的service方法
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
// 重载的service方法,被重写的service方法所调用
// 在该方法中,通过请求方式判断,调用具体的do***方法完成请求的处理
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
// 对应不同请求方式的处理方法
// 除了doOptions和doTrace方法, 其他的do*** 方法都在故意响应错误信息
次次次顶层-自定义Servlet
方法1:重写service方法,任何请求都进入该处理逻辑
public class demo1 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
......
}
}
方法2:重写doXXX方法,不同的请求方式,调用不同的业务处理逻辑
public class demo1 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
......
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
......
}
}
Servlet初始化配置参数和获取上下文信息
ServletConfig
什么是ServletConfig?
- 为Servlet提供初始配置参数的一种对象,每个Servlet都有自己独立唯一的ServletConfig对象
- 容器会为每个Servlet实例化一个ServletConfig对象,并通过Servlet生命周期的init方法传入给Servlet作为属性
ServletConfig常用API
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| getServletName() | 获取 |
| getServletContext() | 获取ServletContext对象 |
| getInitParameter() | 获取配置Servlet时设置的『初始化参数』,根据名字获取值 |
| getInitParameterNames() | 获取所有初始化参数名组成的Enumeration对象 |
ServletConfig的XML配置初始化
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>userServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.UserServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>param1param-name>
<param-value>value1param-value>
init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>param2param-name>
<param-value>value2param-value>
init-param>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>userServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/userServleturl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
ServletConfig的注解配置初始化
@WebServlet(
name = "userServlet",
//value = "/user",
urlPatterns = {"/userServlet1","/userServlet2","/userServlet"},
initParams = {@WebInitParam(name = "encoding",value = "UTF-8"),
@WebInitParam(name = "你好",value = "你也好")},
loadOnStartup = 6
)
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
......
}
}
ServletConfig的API使用示例
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletConfig servletConfig = this.getServletConfig();
// 根据参数名获取单个参数
String value = servletConfig.getInitParameter("param1");
System.out.println("param1:"+value);
// 获取所有参数名
Enumeration<String> parameterNames = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
// 迭代并获取参数名
while (parameterNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramaterName = parameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(paramaterName+":"+servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramaterName));
}
}
}
ServletContext
什么是ServletContext?
- ServletContext对象有称呼为上下文对象,或者叫应用域对象(后面统一讲解域对象)
- 容器会为每个app创建一个独立的唯一的ServletContext对象
- ServletContext对象为所有的Servlet所共享
- ServletContext可以为所有的Servlet提供初始配置参数
域的概念
- 域对象:一些用于存储数据和传递数据的对象,传递数据不同的范围,我们称之为不同的域,不同的域对象代表不同的域,共享数据的范围也不同
- ServletContext代表应用,所以ServletContext域也叫作应用域,是webapp中最大的域,可以在本应用内实现数据的共享和传递
- webapp中的三大域对象,分别是应用域,会话域,请求域
ServletContext常用API
普通API
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| servletContext.getRealPath(“资源在web目录中的路径”); | 获取资源在部署目录下的路径(不是工程目录下的路径) |
| servletContext.getContextPath(); | 获取上下文路径(暂时不知道怎么用) |
| getInitParameter() | 获取配置Servlet时设置的『初始化参数』,根据名字获取值 |
| getInitParameterNames() | 获取所有初始化参数名组成的Enumeration对象 |
域基本API(三大域都具有的API)
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void setAttribute(String key,Object value); | 向域中存储/修改数据 |
| Object getAttribute(String key); | 获得域中的数据 |
| void removeAttribute(String key); | 移除域中的数据 |
ServletContext的XML配置初始化
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>paramAparam-name>
<param-value>valueAparam-value>
context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>paramBparam-name>
<param-value>valueBparam-value>
context-param>
web-app>
ServletContext的API调用用法
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 从ServletContext中获取为所有的Servlet准备的参数
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String valueA = servletContext.getInitParameter("paramA");
System.out.println("paramA:"+valueA);
// 获取所有参数名
Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
// 迭代并获取参数名
while (initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramaterName = initParameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(paramaterName+":"+servletContext.getInitParameter(paramaterName));
}
System.out.println("你好");
System.out.println(getServletContext().getRealPath("BBB"));
System.out.println(getServletContext().getRealPath("\\AAA\\TTT"));
System.out.println(getServletContext().getRealPath("\\TTT\\BB"));
System.out.println(getServletContext().getRealPath(""));
System.out.println(getServletContext().getContextPath());
}
}
getRealPath
- 四个输出分别是:
- D:\GSF_Data\Github\Java\JavaWeb\Web-ALL\out\artifacts\web01_war_exploded\BBB
- D:\GSF_Data\Github\Java\JavaWeb\Web-ALL\out\artifacts\web01_war_exploded\AAA\TTT
- D:\GSF_Data\Github\Java\JavaWeb\Web-ALL\out\artifacts\web01_war_exploded\TTT\BB
- D:\GSF_Data\Github\Java\JavaWeb\Web-ALL\out\artifacts\web01_war_exploded\
- 参数所对应Web目录下的路径
- 参数所对应工程目录下的路径
- 所以该函数的作用就是:参数写入某个资源以web为基础目录所对应的相对位置,然后函数返回其在工程部署目录下对应的实际位置
getContextPath
- 函数输出:
- /web01
- 用途:暂时还没相关应用场景
Servlet-处理和响应浏览器请求
HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse与请求、响应之间的关系
请求、响应、报文、HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse之间的对应关系
HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletRequest是一个接口,其父接口是ServletRequest
- HttpServletRequest是Tomcat将请求报文转换封装而来的对象,在Tomcat调用service方法时传入
- HttpServletRequest代表客户端发来的请求,所有请求中的信息都可以通过该对象获得
HttpServletResponse
- HttpServletResponse是一个接口,其父接口是ServletResponse
- HttpServletResponse是Tomcat预先创建的,在Tomcat调用service方法时传入
- HttpServletResponse代表对客户端的响应,该对象会被转换成响应的报文发送给客户端,通过该对象我们可以设置响应信息
HttpServletRequest常用API
获取请求行信息相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| StringBuffer getRequestURL(); | 获取客户端请求的url |
| String getRequestURI(); | 获取客户端请求项目中的具体资源,即项目所在的资源路径(URI跟上边的URL不一样) |
| int getServerPort(); | 获取客户端发送请求时的端口 |
| int getLocalPort(); | 获取本应用在所在容器的端口 |
| int getRemotePort(); | 获取客户端程序的端口 |
| String getScheme(); | 获取请求协议 |
| String getProtocol(); | 获取请求协议及版本号 |
| String getMethod(); | 获取请求方式 |
获得请求头信息相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getHeader(String headerName); | 根据头名称获取请求头 |
| Enumeration getHeaderNames(); | 获取所有的请求头名字 |
| String getContentType(); | 获取content-type请求头 |
获得请求(体内的)参数相关
获取key-value类型的参数
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getParameter(String parameterName); | 根据请求参数名获取请求单个参数值 |
| String[] getParameterValues(String parameterName); | 根据请求参数名获取请求多个参数值数组(多选框,一个参数对应多个参数值) |
| Enumeration getParameterNames(); | 获取所有请求参数名 |
| Map |
获取所有请求参数的键值对集合 |
获取非key-value类型的参数,例如Json串、文件等
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException; | 获取读取请求体的字符输入流,Json串 |
| ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException; | 获取读取请求体的字节输入流,文件 |
| int getContentLength(); | 获得请求体长度的字节数 |
其他API
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getServletPath(); | 获取请求的Servlet的映射路径 |
| ServletContext getServletContext(); | 获取ServletContext对象 |
| Cookie[] getCookies(); | 获取请求中的所有cookie |
| HttpSession getSession(); | 获取Session对象 |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String encoding) ; | 设置请求体字符集 |
HttpServletResponse常用API
设置响应行相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void setStatus(int code); | 设置响应状态码 |
设置响应头相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void setHeader(String headerName, String headerValue); | 设置/修改响应头键值对 |
| void setContentType(String contentType); | 设置content-type响应头及响应字符集(设置MIME类型) |
设置响应体相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException; | 获得向响应体放入信息的字符输出流 |
| ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException; | 获得向响应体放入信息的字节输出流 |
| void setContentLength(int length); | 设置响应体的字节长度,其实就是在设置content-length响应头 |
其他API
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void sendError(int code, String message) throws IOException; | 向客户端响应错误信息的方法,需要指定响应码和响应信息 |
| void addCookie(Cookie cookie); | 向响应体中增加cookie |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String encoding); | 设置响应体字符集 |
MIME类型
- MIME类型,可以理解为文档的类型,用户表示传递的数据是属于什么类型的文档
- 浏览器可以根据MIME类型决定该用什么样的方式解析接收到的响应体数据
- 可以这样理解: 前后端交互数据时,告诉对方发给对方的是 html/css/js/图片/声音/视频/… …
- tomcat/conf/web.xml中配置了常见文件的拓展名和MIMIE类型的对应关系
- 常见的MIME类型举例如下
| 文件拓展名 | MIME类型 |
|---|---|
| .html | text/html |
| .css | text/css |
| .js | application/javascript |
| .png /.jpeg/.jpg/… … | image/jpeg |
| .mp3/.mpe/.mpeg/ … … | audio/mpeg |
| .mp4 | video/mp4 |
| .m1v/.m1v/.m2v/.mpe/… … | video/mpeg |
请求转发和响应重定向
整体概述
-
请求转发和响应重定向是在web应用中间接访问项目资源的两种手段,也是Servlet控制页面跳转的两种手段
-
请求转发通过HttpServletRequest实现,响应重定向通过HttpServletResponse实现
-
请求转发生活举例
- 张三找李四借钱,李四没有,李四找王五,让王五借给张三
-
响应重定向生活举例
- 张三找李四借钱,李四没有,李四让张三去找王五,张三自己再去找王五借钱
请求转发
1-逻辑图
2-请求转发特点(背诵)
- 请求转发通过HttpServletRequest对象获取请求转发器实现
- 请求转发是服务器内部的行为,对客户端是屏蔽的:
- 客户端只发送了一次请求,客户端地址栏不变
- 服务端只产生了一对请求和响应对象,这一对请求和响应对象会继续传递给下一个资源
- 因为全程只有一个HttpServletRequset对象,所以请求参数可以传递,请求域中的数据也可以传递
- 请求转发可以转发的对象有:
- 其他Servlet动态资源,也可以转发给一些静态资源以实现页面跳转
- 给WEB-INF下受保护的资源
- 请求转发不可以转发的对象:
- 不能转发到本项目以外的外部资源
3-代码实现
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求转发器
// 转发给servlet ok
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("servletB");
// 转发给一个视图资源 ok
//RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.html");
// 转发给WEB-INF下的资源 ok
//RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("WEB-INF/views/view1.html");
// 转发给外部资源 no (他会把这个当成内部的项目资源路径来访问,所以不行)
//RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("http://www.atguigu.com");
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
// 向请求域中添加数据
req.setAttribute("reqKey","requestMessage");
// 做出转发动作
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
- 图示为请求转发给外部资源对应的结果:即把外部资源当作内部资源的一个路径来访问,当然是不行的
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
// 获取请求域中的数据
String reqMessage = (String)req.getAttribute("reqKey");
System.out.println(reqMessage);
// 做出响应
resp.getWriter().write("servletB response");
}
}
响应重定向
1-逻辑图
2-请求重定向特点
- 响应重定向通过HttpServletResponse对象的sendRedirect方法实现
- 响应重定向是服务端通过302响应码和路径,告诉客户端自己去找其他资源,是在服务端提示下的,客户端的行为
- 客户端至少发送了两次请求,客户端地址栏是要变化的(可能出现多次重定向)
- 服务端产生了多对请求和响应对象,且请求和响应对象不会传递给下一个资源
- 因为全程产生了多个HttpServletRequset对象,所以请求参数不可以传递,请求域中的数据也不可以传递(应用域依旧可以)
- 重定向可以是:
- 可以是其他Servlet动态资源,也可以是一些静态资源以实现页面跳转
- 可以到本项目以外的外部资源
- 重定向不可以是:
- 给WEB-INF下受保护的资源
3-代码实现
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
// 向请求域中添加数据
req.setAttribute("reqKey","requestMessage");
// 响应重定向
// 重定向到servlet动态资源 OK 包含两步动作:
resp.sendRedirect("servletB");
// 重定向到视图静态资源 OK
//resp.sendRedirect("welcome.html");
// 重定向到WEB-INF下的资源 NO
//resp.sendRedirect("WEB-INF/views/view1");
// 重定向到外部资源 ok
//resp.sendRedirect("http://www.atguigu.com");
}
}
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
// 获取请求域中的数据
String reqMessage = (String)req.getAttribute("reqKey");
System.out.println(reqMessage);
// 做出响应
resp.getWriter().write("servletB response");
}
}
总结
-
针对页面跳转问题,能用响应重定向就不用转发(范围更广)
-
其他情况,以实际为准
Web乱码问题
乱码根源
乱码根本
- 数据的编码和解码不是一个字符集
- 使用了不支持某个语言文字的字符集
常见字符集的兼容性
乱码Case–HTML乱码
解决
-
查看文件的字符集、项目(开发软件)的字符集、视图文件(浏览器解析文件所用)的字符集
-
保证三者一致
文件字符集
开发软件字符集
视图文件字符集
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
中文
body>
html>
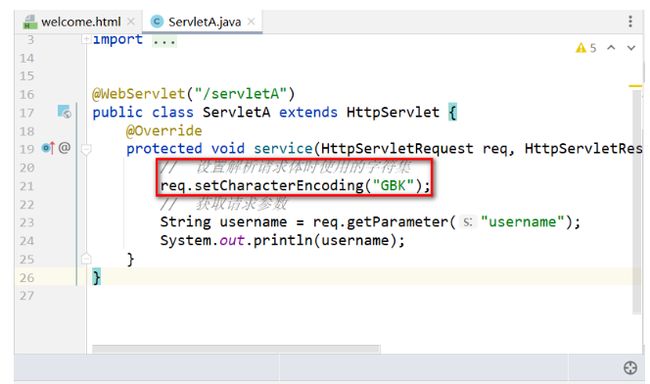
乱码Case–Tomcat控制台乱码
- 修改 tomcat/conf/logging.properties中,将所有的GBK用UTF-8替换
乱码Case–请求乱码
Get请求乱码
乱码情况分析
-
GET方式提交参数,将参数放在URL后面,对参数进行编码处理
- HTML的meta属性规定了提交URL参数时的编码方式
- Tomcat对URI的编码也有自己的方式
-
当两者的编码所有字符集不一样,就会产生乱码
乱码情况演示
- 浏览器解析的文档的
- GET方式提交时,会对数据进行URL编码处理 ,是将GBK 转码为 “百分号码”
- %表示分隔符,一个字节的开始
- GBK对中文的编码由两个字节组成
- 输入的小明,就转为了4个字节
- tomcat10.1.7 默认使用UTF-8对URI进行解析,造成前后端使用的字符集不一致,出现乱码
乱码情况解决
- 推荐:设置GET方式提交的编码和Tomcat10.1.7的URI默认解析编码一致即可
- 不推荐:设置Tomcat10.1.7的URI解析字符集和GET请求发送时所使用URL转码时的字符集一致即可,修改conf/server.xml中 Connecter 添加 URIEncoding=“GBK”
- 注意:该设置仅规定URI解析时候的编码方式
Post请求乱码
乱码情况分析
- 原理同于GET请求
- 数据放在请求体中,HTML上传时的编码方式和Tomcat的解析方式不同,导致乱码
乱码情况解决
- 推荐:请求时,使用UTF-8字符集提交请求体
- 不推荐:后端在获取参数前,设置解析请求体使用的字符集和请求发送时使用的字符集一致
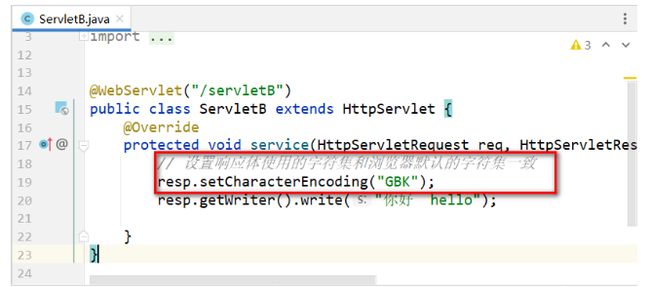
乱码Case–响应乱码
乱码情况分析
- 在Tomcat10.1.7中,向响应体中放入的数据默认使用了工程编码UTF-8
- 浏览器在接收响应信息时,使用了不同的字符集或者是不支持中文的字符集就会出现乱码
乱码情况演示
- 服务端通过response对象向响应体添加数据
- 浏览器接收数据解析乱码
乱码情况解决
- 不推荐:手动设定浏览器对本次响应体解析时使用的字符集
- 有的浏览器没有对应入口
- 不推荐:后端通过设置响应体的字符集和浏览器解析响应体的默认字符集一致
- 推荐:设置content-type响应头
路径问题
概念:相对路径和绝对路径
相对路径
- 规则是:以当前资源所在的路径为出发点去寻找目标资源
- 不以 / 开头
- 在file协议下,使用的是磁盘路径
- 在http协议下,使用的是url路径
- 可以使用 ./ 表示当前资源所在路径,可以省略不写
- 可以使用 …/ 表示当前资源所在路径的上一层路径,需要时要手动添加
绝对路径
- 规则是:使用以一个固定的路径做出出发点去寻找目标资源,和当前资源所在的路径没有关系
- 绝对路径要以 / 开头
- 绝对路径的写法中,不以当前资源的所在路径为出发点,所以不会出现 ./ 和 …/
- 不同的项目和不同的协议下,绝对路径的基础位置可能不同,要通过测试确定
- 绝对路径的好处就是:无论当前资源位置在哪,寻找目标资源路径的写法都一致
应用场景
- 前端代码中,href src action 等属性
- 请求转发和重定向中的路径
路径演示–前端项目示例
前端路径问题
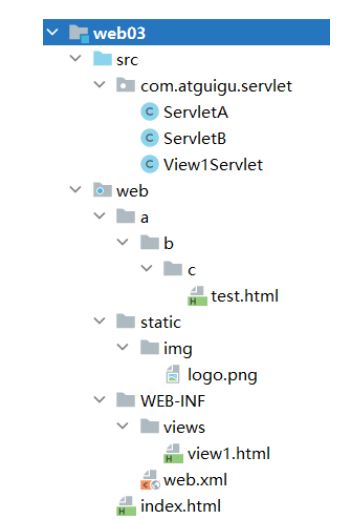
前端项目结构:
相对路径分析
case1:web/index.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问index.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/index.html |
| 当前资源为 | index.html |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
case2:web/a/b/c/test.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问index.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| 当前资源为 | test.html |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | …/…/…/static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="../../../static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
- 一个 …/ 抵消一层目录
case3:web/WEB-INF/views/view1.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
- 受保护目录下的资源,需要先通过请求转发来访问
@WebServlet("/view1Servlet")
public class View1Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("WEB-INF/views/view1.html");
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
- 分析
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问view1.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/view1Servlet |
| 当前资源为 | view1Servlet |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
绝对路径分析
case1:web/index.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问index.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/index.html |
| 绝对路径的基准路径为 | http://localhost:8080 |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | /web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
case2:web/a/b/c/test.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问index.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| 绝对路径的基准路径为 | http://localhost:8080 |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | /web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
case3:web/WEB-INF/views/view1.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
- 受保护目录下的资源,需要先通过请求转发来访问
@WebServlet("/view1Servlet")
public class View1Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("WEB-INF/views/view1.html");
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
- 分析
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问view1.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/view1Servlet |
| 绝对路径的基准路径为 | http://localhost:8080 |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| index.html中以相对路径定义的路径形式:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | /web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
base标签使用
所有相对路径内容前会补充base标签中,href里面的内容
- 即相对路径经过补充,变为了绝对路径
case1:web/index.html中引入web/static/img/logo.png
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问index.html的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/index.html |
| 当前资源为 | index.html |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| 相对路径的公共前缀 | /web03_war_exploded/ |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<base href="/web03_war_exploded/">
head>
<body>
<img src="static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
- base 标签定义的公共前缀只在相对路径上有效,绝对路径中无效。如果src相对路径开头有 ./ 或者…/修饰,则base标签对该路径无效
究极操作:缺省项目上下文路径
项目上下文路径变化问题
- 通过 base标签虽然解决了相对路径转绝对路径问题,但是base中定义的是项目的上下文路径
- 项目的上下文路径是可以随意变化的,一旦项目的上下文路径发生变化,所有base标签中的路径都需要改
解决方案
- 将项目的上下文路径进行缺省设置,设置为 /,所有的绝对路径中就不必填写项目的上下文了,直接就是/开头即可
响应重定向的路径问题
目标
由/x/y/z/servletA重定向到a/b/c/test.html
Servlet-相对路径写法
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问ServletA的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/y/z/servletA |
| 当前资源为 | servletA |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/x/z/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| ServletA重定向的路径 | …/…/…/a/b/c/test/html |
@WebServlet("/x/y/z/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 相对路径重定向到test.html
resp.sendRedirect("../../../a/b/c/test.html");
}
}
Servlet-绝对路径写法
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问ServletA的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/y/z/servletA |
| 绝对路径的基准路径为 | http://localhost:8080 |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| ServletA重定向的路径(不推荐) | /web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| ServletA重定向的路径(推荐) | getServletContext().getContextPath()+“/a/b/c/test.html” |
绝对路径中需要填写项目上下文路径,但是上下文路径是变换的
- 可以通过 ServletContext的getContextPath()获取上下文路径
- 可以将项目上下文路径定义为 / 缺省路径,那么路径中直接以/开头即可
@WebServlet("/x/y/z/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 绝对路径写法1:带有项目上下文路径
resp.sendRedirect("/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html");
// 绝对路径写法2:通过ServletContext对象动态获取项目上下文路径
resp.sendRedirect(getServletContext().getContextPath()+"/a/b/c/test.html");
// 绝对路径写法3:缺省项目上下文路径时,直接以/开头即可
resp.sendRedirect("/a/b/c/test.html");
}
}
HTML-请求项目内其他静态资源
- 响应重定向相当于重新发送请求
- 其html文件内访问对应资源路径的写法参考【前端路径问题】
请求转发的路径问题
目标
目标 :由x/y/servletB请求转发到a/b/c/test.html
Servlet-相对路径写法
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 访问ServletB的url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/y/servletB |
| 当前资源为 | servletB |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/x/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/a/b/c/test.html |
| ServletA请求转发路径:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | …/…/a/b/c/test/html |
@WebServlet("/x/y/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("../../a/b/c/test.html");
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
HTML-目标资源内相对路径处理
| 分析 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 当前示例下访问a/b/c/test.html的url路径 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/y/servletB |
| 当前资源为 | servletB |
| 当前资源的所在路径为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/x/x/ |
| 要获取的目标资源url为 | http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded/static/img/logo.png |
| img src写入值:**目标资源路径=当前所在资源路径+src属性值 ** | …/…/static/img/logo.png |
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="../../static/img/logo.png">
body>
html>
- 请求转发是服务器行为,浏览器不知道,地址栏不变化,所以当前资源所在路径是servletB所在的路径
Servlet-绝对路径写法
-
请求转发只能转发到项目内部的资源,其绝对路径无需添加项目上下文路径
- 除了请求转发,其他都是需要添加项目上下文路径的
-
请求转发绝对路径的基准路径相当于http://localhost:8080/web03_war_exploded
-
在项目上下文路径为缺省值时,也无需改变,直接以/开头即可
@WebServlet("/x/y/servletB") public class ServletB extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("/a/b/c/test.html"); requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp); } }
HTML-目标资源内绝对路径处理
- 处理逻辑同于:【前端路径问题–绝对路径分析】