Map和Set(JAVA)
本篇文章建议在了解了哈希表和二叉搜索树后食用更佳。
链接: 二叉搜索树 和 哈希表 (JAVA)
Map和Set都是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。
Map接口
- Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap;
Map<Integer,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Integer> map2 = new TreeMap<>();
Map接口并没有继承Collection,该类中存储的是
Map中的数据是以Key-Value 模型来存储的。
一般搜索的数据被称为Key,而它的值被成为Value。
例如:用Key-Value 模型来统计单词出现的次数就可以存储为:<单词,单词出现的次数>。
Map中的一些常用方法:
put(key, value)
如果不存在 Key 就插入当前 key-value 键值对,如果存在当前 Key 则更新 key 对应的 value值。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
System.out.println(map);
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
map.put("zhangsan", 10);
System.out.println(map);
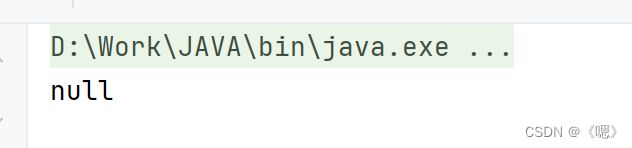
get(Key)
返回 key 对应的 value;如果没有对应的 Key 则返回 null。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
System.out.println(map.get("zhangsan"));
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
System.out.println(map.get("zll"));
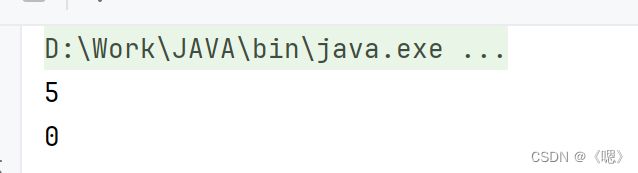
getOrDefault(key, defaultValue)
返回 key 对应的 value,key 不存在,返回 defaultValue 。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("zhangsan", 0));
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("llll", 0));
remove(key)
删除 key 对应的映射关系(删除 Key 和它对应的 Value) ,并返回 Value,如果当前 key 不存在就返回 null 。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
map.put("lisi", 5);
map.put("wangwu", 5);
System.out.println(map);
//删除“zhangsan”返回5
System.out.println(map.remove("zhangsan"));
//因为不存在“zhangsan”返回null
System.out.println(map.remove("zhangsan"));
System.out.println(map);
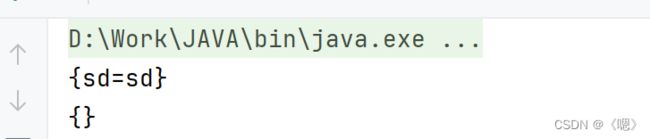
void clear()
删除集合中的所有键值对
Map<String,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("sd","sd");
System.out.println(map);
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
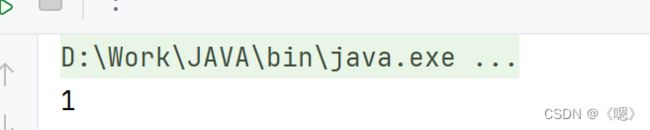
size()
返回map中的键值对的数量。
Map<String,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("sd","sd");
System.out.println(map.size());
Set < K > keySet()
返回包含所有 key 的一个集合对象。
此方法的返回值是 Set 类型的集合,该集合中包含当前类中的所有 key 关键字(Set 中不能存储重复的值)。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
map.put("lisi", 5);
map.put("wangwu", 5);
System.out.println(map);
Set<String> tmp = map.keySet();
System.out.println(tmp);
boolean isEmpty()
判断当前map集合中是否为空。
空就返回true;否则返回false。
Map<String,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
map.put("sd","sd");
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
Collection< V > values()
返回所有 value 的可重复集合。
和上面的 keySet() 方法差不多,这个方法是返回 Values 组成的集合。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
map.put("lisi", 5);
map.put("wangwu", 5);
System.out.println(map);
Collection<Integer> tmp = map.values();
System.out.println(tmp);
containsKey(key)
判断是否包含该 key,返回类型是boolean类型。
containsValue(value)
判断是否包含该 value,返回类型是boolean类型。
Set> entrySet()
返回所有的 key-value 映射关系。
在了解这个方法前先了解一下 Map.Entry
Map.Entry
Map 其实你可以想象成一个链表它里面的每一个 key-value 键值对都是以节点的形式来存储的而Map.Entry
在 Map.Entry
- getKey(): 返回 entry 中的 key
- getValue(): 返回 entry 中的 value
- setValue(V value): 将键值对中的value替换为指定value
此时再来看 entrySet() 方法:
entrySet() 方法其实就是返回 map 集合中的所有节点然后将其作为一个整体存放在 Set 类型的集合中。
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("zhangsan", 5);
map.put("lisi", 5);
map.put("wangwu", 5);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> tmp = map.entrySet();
//第一种遍历方式
System.out.println(tmp);
System.out.println("===========");
//第二种遍历方式
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> a:map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key:"+a.getKey()+" "+"Value"+a.getValue());
}
Map 的一些注意事项
- Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap;
- Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的;
- 在TreeMap中插入键值对时,key不能为空,否则就会抛NullPointerException异常,value可以为空。但是HashMap的key和value都可以为空;
- Map中键值对的Key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将该key删除掉,然后再来进行重新插入。
TreeMap和HashMap的区别:
| TreeMap | HashMap | |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 插入/删除/查找时间 | O(log2N) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于Key有序 | 无序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 插入/删除/查找区别 | 需要进行元素比较 | 通过哈希函数计算哈希地址 |
| 比较与覆写 | key必须能够比较,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常 | 自定义类型需要覆写equals和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要Key有序场景下 | Key是否有序不关心,需要更高的时间性能 |
Set 接口
Set相比于Map要简单很多。
- Set是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeSet或者HashSet。
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> set2 = new TreeSet<>();
Set与Map主要的不同有两点:Set是继承自Collection的接口类,Set中只存储了 Key
Set中的一些常用方法:
boolean add(Object o)
添加元素
添加成功返回true;失败返回false。
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
System.out.println(set.add("asd"));
//因为该元素已经存在了,所以不会添加成功,返回false
System.out.println(set.add("asd"));
boolean addAll(Collectionc)
将集合c中的元素添加到set中,可以达到去重的效果
void clear()
清空集合
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
set.add("d");
set.add("g");
System.out.println(set);
//删除所有元素
set.clear();
System.out.println(set);
boolean contains(Object o)
判断 o 是否在集合中
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
set.add("d");
set.add("g");
System.out.println(set.contains("s"));
System.out.println(set.contains("hhh"));
Iterator iterator()
返回一个迭代器
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
set.add("d");
set.add("g");
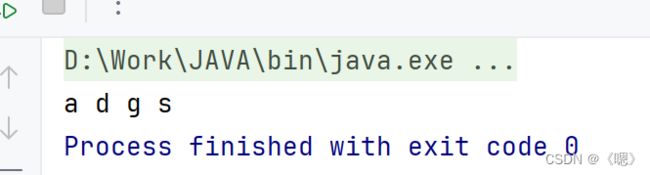
//利用迭代器进行集合的遍历
Iterator<String> tmp = set.iterator();
while (tmp.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(tmp.next()+" ");
}
boolean remove(Object o)
删除集合中的 o
成功删除返回true;失败返回false。
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
set.add("d");
set.add("g");
System.out.println(set.remove("a"));
//因为集合中不存在“asd”所以删除失败,返回false
System.out.println(set.remove("asd"));
int size()
返回set集合中元素的个数
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
set.add("d");
set.add("g");
System.out.println(set.size());
boolean isEmpty()
检测set是否为空,空返回true,否则返回false
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
Object[] toArray()
将set中的元素转换为数组返回
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
Object[] tmp =set.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println(tmp[i]);
}
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("s");
//此处不能进行强制类型转换
String[] tmp =(String[]) set.toArray();
System.out.println(tmp);
boolean containsAll(Collection c)
集合c中的元素是否在set中全部存在,是返回true,否则返回false
Set 的一些注意事项
- Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类;
- Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一;
- TreeSet的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的;
- Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重;
- 实现Set接口的常用类有TreeSet和HashSet,还有一个LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是在HashSet的基础上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序;
- Set中的Key不能修改,如果要修改,先将原来的删除掉,然后再重新插入
- TreeSet中不能插入null的key,HashSet可以。
TreeSet和HashSet的区别:
| TreeSet | HashSet | |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 插入/删除/查找时间 | O(log2N) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于Key有序 | 不一定有序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 插入/删除/查找区别 | 按照红黑树的特性来进行插入和删除 | 先计算key哈希地址 然后进行插入和删除 |
| 比较与覆写 | key必须能够比较,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常 | 自定义类型需要覆写equals和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要Key有序场景下 | Key是否有序不关心,需要更高的时间性能 |