工厂模式详解及实战案例分析
文章目录
- 工厂模式
-
- 简单工厂
- 案例
-
- 优化一 抽离方法
- 优化二 抽离成类
- 优化三 map
- 工厂方法
-
- 业务中使用
- 枚举方案-->(工厂中的工厂)
- 抽象工厂
- 优缺点
- 简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂的区别
- 框架中的工厂模式
工厂模式
工厂模式分为三种更加细分的类型:简单工厂、工厂方法和抽象工厂,其中简单工厂、工厂方法在实际的项目中也比较常用。属于创建型
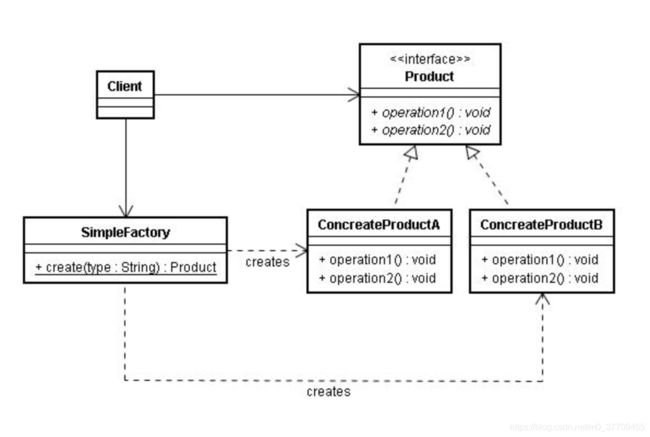
简单工厂
简单工厂是产品的工厂
案例
在下面这段代码中,我们根据配置文件的后缀(json、xml、yaml、properties),选择不 同的解析器(JsonRuleConfigParser、XmlRuleConfigParser…),将存储在文件中的 配置解析成内存对象 RuleConfig。
public class RuleConfigSource {
public RuleConfig load(String ruleConfigFilePath) {
String ruleConfigFileExtension = getFileExtension(ruleConfigFilePath);
IRuleConfigParser parser = null;
if ("json".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)) {
parser = new JsonRuleConfigParser();
} else if ("xml".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)) {
parser = new XmlRuleConfigParser();
} else if ("yaml".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)){
parser = new YamlRuleConfigParser();
} else if ("properties".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)){
parser = new PropertiesRuleConfigParser();
} else {
throw new InvalidRuleConfigException("Rule config file format is not supported: " + ruleConfigFilePath);
}
String configText = "";
//从ruleConfigFilePath文件中读取配置文本到configText中
RuleConfig ruleConfig = parser.parse(configText);
return ruleConfig;
}
private String getFileExtension(String filePath) {
//...解析文件名获取扩展名,比如rule.json,返回json
return "json";
}
}
优化一 抽离方法
上述代码逻辑不清晰,我们要将相对独立的代码封装成函数,将parser抽离出来
public RuleConfig load(String ruleConfigFilePath) {
String ruleConfigFileExtension = getFileExtension(ruleConfigFilePath);
IRuleConfigParser parser = createParser(ruleConfigFileExtension);
if(parser == null) {
throw new InvalidRuleConfigException("Rule config file format is not supported: " + ruleConfigFilePath);
}
... 省略其他方法
//封装成一个方法
private IRuleConfigParser createParser(String configFormat) {
IRuleConfigParser parser = null;
if ("json".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)) {
parser = new JsonRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("xml".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)) {
parser = new XmlRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("yaml".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)){
parser = new YamlRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("properties".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)){
parser = new PropertiesRuleConfigParser();
}
return parser;
}
优化二 抽离成类
- 让类的职责更加单一、代码更加清晰
public RuleConfig load(String ruleConfigFilePath) {
String ruleConfigFileExtension = getFileExtension(ruleConfigFilePath);
//调用工厂方法
IRuleConfigParser parser = RuleConfigParserFactory.createParser(ruleConfigFileExtension);
if(parser == null) {
throw new InvalidRuleConfigException("Rule config file format is not supported: " + ruleConfigFilePath);
}
... 省略其他方法
}
//工厂类
public class RuleConfigParserFactory {
//封装成一个方法
public IRuleConfigParser createParser(String configFormat) {
IRuleConfigParser parser = null;
if ("json".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)) {
parser = new JsonRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("xml".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)) {
parser = new XmlRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("yaml".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)){
parser = new YamlRuleConfigParser();
}else if ("properties".equalsIgnoreCase(configFormat)){
parser = new PropertiesRuleConfigParser();
}
return parser;
}
- 注意类名和方法名,大部分工厂类都是以“Factory”这个单词结尾,工厂类中创建对象的方法一般都是 create 开头
优化三 map
去if 使用map
//工厂类
public class RuleConfigParserFactory {
private static final Map<String, RuleConfigParser> cachedParsers = new HashMap();
static{
cachedParsers.put("json", new JsonRuleConfigParser());
cachedParsers.put("xml", new XmlRuleConfigParser());
cachedParsers.put("yaml", new YamlRuleConfigParser());
cachedParsers.put("properties", new PropertiesRuleConfigParser());
}
public static IRuleConfigParser createParser(String configFormat) {
if (configFormat == null || configFormat.isEmpty()) {
return null;//返回null还是IllegalArgumentException全凭你自己说了算
}
IRuleConfigParser parser = cachedParsers.get(configFormat.toLowerCase());
return parser;
}
}
工厂方法
工厂的工厂
- 工厂方法是将逻辑条件交给客户端,并应用到继承和多态
// 定义创建解析器接口
public interface IRuleConfigParserFactory {
IRuleConfigParser createParser();
}
// json实现
public class JsonRuleConfigParserFactory implements RuleConfigParserFactory {
@Override
public IRuleConfigParser createParser() {
return new JsonRuleConfigParser();
}
}
// xml实现
public class XmlRuleConfigParserFactory implements IRuleConfigParserFactory {
@Override
public IRuleConfigParser createParser() {
return new XmlRuleConfigParser();
}
}
// yaml实现
public class YamlRuleConfigParserFactory implements IRuleConfigParserFactory {
@Override
public IRuleConfigParser createParser() {
return new YamlRuleConfigParser();
}
}
// properties实现
public class PropertiesRuleConfigParserFactory implements IRuleConfigParserFactory{
@Override
public IRuleConfigParser createParser() {
return new PropertiesRuleConfigParser();
}
}
业务中使用
public class RuleConfigSource {
public RuleConfig load(String ruleConfigFilePath) {
String ruleConfigFileExtension = getFileExtension(ruleConfigFilePath);
IRuleConfigParserFactory parserFactory = null;
if ("json".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)) {
parserFactory = new JsonRuleConfigParserFactory();
}else if ("xml".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)) {
parserFactory = new XmlRuleConfigParserFactory();
}else if ("yaml".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)) {
parserFactory = new YamlRuleConfigParserFactory();
}else if ("properties".equalsIgnoreCase(ruleConfigFileExtension)){
parserFactory = new PropertiesRuleConfigParserFactory();
}else {
throw new InvalidRuleConfigException("Rule config file format is not supported: " + ruleConfigFilePath);
}
IRuleConfigParser parser = parserFactory.createParser();
String configText = "";
//从ruleConfigFilePath文件中读取配置文本到configText中
RuleConfig ruleConfig = parser.parse(configText);
return ruleConfig;
}
private String getFileExtension(String filePath) {
//...解析文件名获取扩展名,比如rule.json,返回json
return "json";
}
}
- 还是嵌套了很多if,并耦合了,如果新增一个php后缀的信息则需要修改load中的方法。那如何使其优雅呢?
枚举方案–>(工厂中的工厂)
与简单工厂中的map方案类似 但操作更骚
//工厂枚举
public enum RuleConfigParserFactoryEnum {
/**
* 定义具体工厂
*/
JSON("json", new JsonRuleConfigParserFactory()),
XML("xml", new XmlRuleConfigParserFactory()),
YAML("yaml", new YamlRuleConfigParserFactory()),
PROPERTIES("properties", new PropertiesRuleConfigParserFactory());
RuleConfigParserFactoryEnum(String key, IRuleConfigParserFactory ruleConfigParserFactory) {
this.key = key;
this.ruleConfigParserFactory = ruleConfigParserFactory;
}
// 为试代码可读性高 这里使用的是key 而非type
private String key;
private IRuleConfigParserFactory ruleConfigParserFactory;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* 获取工厂
* @param type
* @return
*/
public static IRuleConfigParserFactory getParserFactory(@NonNull String type) {
for (RuleConfigParserFactoryEnum ruleConfigParserFactoryEnum : RuleConfigParserFactoryEnum.values()) {
if(ruleConfigParserFactoryEnum.key.equals(type)){
return ruleConfigParserFactoryEnum.ruleConfigParserFactory;
}
}
return null;
}
}
优点: 如果增加一种解析那么只需要增加对应的工厂类及工厂枚举中的常量而不用修改业务逻辑.基本上符合开闭原则
缺点: 对于某些可以形成产品族的情况处理比较复杂。
抽象工厂

抽象工厂模式的应用场景比较特殊,没有前两种常用。所以不展开讲。抽象工厂可以让一个工厂负责创建多个不同类型的对象,比如以上场景:如果我们未来在规则配置解析的基础上还要增加一种系统配置解析,那么出现两种IRuleConfigParser和ISystemConfigParser
public interface IConfigParserFactory {
IRuleConfigParser createRuleParser();
ISystemConfigParser createSystemParser();
}
public class JsonConfigParserFactory implements IConfigParserFactory {
// 规则配置解析(原有)
@Override
public IRuleConfigParser createRuleParser() {
return new JsonRuleConfigParser();
}
// 系统配置解析
@Override
public ISystemConfigParser createSystemParser() {
return new JsonSystemConfigParser();
}
}
如果后续还要加入IBizConfigParser,并不需要增加对应的工厂,直接在IConfigParserFactory工厂中加入其产品就可以。
优缺点
- 缺点: 如果新增产品,那么会导致动一发而牵全身。所以工厂模式适用不经常改动且比较复杂、重复代码较多的场景
- 优点: 高聚合、使用者无需关心内部实现逻辑、符合开闭原则。
简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂的区别
- 简单工厂接受了一个参数,通过不同的参数实例化不同的产品类。
用来生产同一等级结构中的任意产品。(不支持拓展增加产品)
- 工厂方法是针对每一种产品提供一个工厂类。通过不同的工厂实类来创建不同的产品实例。(支持拓展增加产品)
用来生产同一等级结构中的固定产品。(支持拓展增加产品)
- 抽象工厂是应对产品族概念的。工厂方法模式是一种极端情况的抽象工厂模式(即只生产一种产品的抽象工厂模式),而抽象工厂模式可以看成是工厂方法模式的一种推广。(不支持拓展增加产品;支持增加产品族)
用来生产不同产品族的全部产品。(支持增加产品族)
框架中的工厂模式
BeanFactory/LoggerFactory