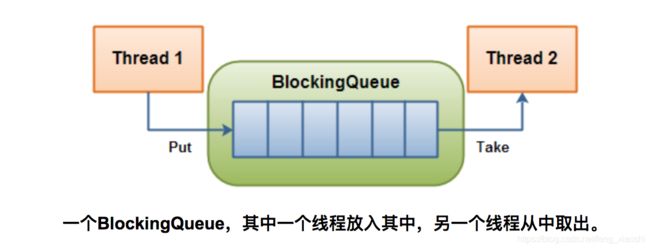
多线程08--阻塞队列
上一篇:https://blog.csdn.net/fengxianaa/article/details/124427373
1. 整体介绍
/**
* BlockingQueue
* 高效且线程安全的阻塞队列,适合多线程之间数据共享,比如:生产消费模型
*
* 主要实现类
* ArrayBlockingQueue
* 数组实现的有界阻塞队列,先进先出(FIFO)
*
* LinkedBlockingQueue
* 链表结构组成的有界队列,此队列的默认长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,又被称为无界,先进先出
*
* PriorityBlockingQueue
* 支持元素排序的无界队列
*
* DelayQueue
* 延迟获取的无界队列,
* 在增加元素时,可以指定一个时间。只有到期后后才能从队列中获取元素。
*
* SynchronousQueue
* 长度为0的阻塞队列,每一个put操作会阻塞,直到另一个take操作
*
*/
public class Queue01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}2. ArrayBlockingQueue
/**
* ArrayBlockingQueue
* 数组实现的有界阻塞队列,先进先出(FIFO)
*
* 主要方法:
* offer(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 成功:true
* 失败:false,表示队列已满
*
* offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
* 跟offer(E e)类似,如果队列已满,在指定时间,等到队列可用
* 等待时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* add(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 如果队列已满,抛 IllegalStateException
*
* take()
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,阻塞,直到队列中有值
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* put(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果队列已满,阻塞,直到队列可用
* 如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* poll()
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,返回null
*
* poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,阻塞,在指定时间,等到队列有值,时间到了仍然没有,返回null
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* peek()
* 从队列头拿到一个元素,但是不会把元素从队列中删除
* 如果队列为空,返回null
*
* drainTo(Collection c)
* 一次性取出所有元素放到指定的集合中,返回元素个数
* 如果参数是null,抛 NullPointerException
* 如果参数是该队列自己,抛 IllegalArgumentException
*
* drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements)
* 最多取出maxElements元素,放到指定的集合中
*
*/
public class Queue02_ArrayBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
System.out.println(queue.offer("feng"));
// System.out.println(queue.offer("feng"));
// System.out.println(queue.offer("feng", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// System.out.println(queue.add("feng"));
// new Thread(() -> {
// try {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"阻塞。。。。。。");
// String s = queue.take();
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"结束。。。。。。"+s);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }).start();
//
// ThreadHelper.sleep(3000);
// queue.offer("feng");
// queue.put("feng");
// System.out.println("主线程结束。。。。。。");
// System.out.println(queue.poll());
// System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// System.out.println(queue.peek());//不会删除队列中的元素
// System.out.println(queue.peek());
// List list = new ArrayList<>();
// queue.drainTo(list);
// System.out.println(list);
}
} 3. LinkedBlockingQueue
/**
* LinkedBlockingQueue
* 链表结构组成的有界队列,如果不指定容量,长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,又被称为无界,先进先出
* 建议:使用时,还是指定容量
*
* 主要方法:
* offer(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 成功:true
* 失败:false,表示队列已满
*
* offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
* 跟offer(E e)类似,如果队列已满,在指定时间,等到队列可用
* 等待时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* add(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 如果队列已满,抛 IllegalStateException
*
* take()
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,阻塞,直到队列中有值
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* put(E e)
* 向队列尾部插入元素,如果队列已满,阻塞,直到队列可用
* 如果元素为null,抛 NullPointerException
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* poll()
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,返回null
*
* poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
* 从队列头取出一个元素,如果队列为空,阻塞,在指定时间,等到队列有值,时间到了仍然没有,返回null
* 阻塞时被打断,抛 InterruptedException
*
* peek()
* 从队列头拿到一个元素,但是不会把元素从队列中删除
* 如果队列为空,返回null
*
* drainTo(Collection c)
* 一次性取出所有元素放到指定的集合中,返回元素个数
* 如果参数是null,抛 NullPointerException
* 如果参数是该队列自己,抛 IllegalArgumentException
*
* drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements)
* 最多取出maxElements元素,放到指定的集合中
*
*
* 跟 ArrayBlockingQueue 不同之处
* 1. ArrayBlockingQueue是有界的初始化必须指定大小,而LinkedBlockingQueue可以不指定
* 2. ArrayBlockingQueue是数组,而LinkedBlockingQueue是链表
* 3. ArrayBlockingQueue添加、移除 是同一个ReenterLock,LinkedBlockingQueue添加是putLock,移除是takeLock,
* 能大大提高队列的吞吐量
*
*/
public class Queue03_LinkedBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue(1);
// System.out.println(queue.offer("feng"));
// System.out.println(queue.offer("feng"));
// System.out.println(queue.offer("feng", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// System.out.println(queue.add("feng"));
// new Thread(() -> {
// try {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"阻塞。。。。。。");
// String s = queue.take();
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"结束。。。。。。"+s);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }).start();
//
// ThreadHelper.sleep(3000);
// queue.offer("feng");
queue.put("feng");
// System.out.println("主线程结束。。。。。。");
// System.out.println(queue.poll());
// System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// System.out.println(queue.peek());//不会删除队列中的元素
// System.out.println(queue.peek());
// List list = new ArrayList<>();
// queue.drainTo(list);
// System.out.println(list);
}
} 4. PriorityBlockingQueue
/**
* PriorityBlockingQueue
* 数组结构,无界队列,
* 默认按照元素的自然顺序排序,添加的对象必须实现 comparable 接口
*/
public class Queue04_PriorityBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
PriorityBlockingQueue queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue();
queue.add(new Person());
// PriorityBlockingQueue queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(1);
// System.out.println(queue.offer(2));
// System.out.println(queue.offer(1));//队列会自动扩容,容量小于64则翻倍后再加2,容量大于64则增加一半
//
// System.out.println(queue.take());
}
} 5. DelayQueue
/**
* DelayQueue
* 延迟获取的无界队列,添加的元素必须实现 Delayed 接口
* 在增加元素时,可以指定一个时间,只有到期后后才能从队列中获取元素。
*/
class DelayDemo implements Delayed{
long delayTime;//过期时间
long time;//多少秒过期
public DelayDemo(int time){
this.time = time;
// 如果time=3,System.currentTimeMillis()= 1616056291000 ,那么就是 1616056294000 时过期
this.delayTime = time*1000 + System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 返回还有多久到期,DelayQueue队列内部会不停的调用这个方法
* @param unit
* @return 返回值<=0 表示到期了
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return delayTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 排序使用,过期时间短的排到前面
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int) (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.SECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DelayDemo{" +
"delayTime=" + delayTime +
", time=" + time +
'}';
}
}
public class Queue05_DelayQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DelayQueue queue = new DelayQueue();
queue.add(new DelayDemo(3));
queue.add(new DelayDemo(2));
queue.add(new DelayDemo(5));
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
}
} 6. SynchronousQueue
/**
* SynchronousQueue
* 长度为0的阻塞队列,每一个put操作会阻塞,直到另一个take操作
* 线程池中 newCachedThreadPool 用到这个队列
*
*/
public class Queue06_SynchronousQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("put 1 。。。。。。");
queue.put("1");
System.out.println("put 2 。。。。。。");
queue.put("2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
ThreadHelper.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("take "+queue.take()+" 。。。。。。");
ThreadHelper.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("take "+queue.take()+" 。。。。。。");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}