mysql高阶语句
排序 分组 子查询 视图 多表连接查询(左连接 右连接 内连接)
创建库test
create database test;创建表info
create table info (
id int(4) primary key,
name varchar(10) not null,
score decimal(5,2),
address varchar(20),
sex char(3) not null
);往表里插入数据
使用select语句,用order by来对表进行排序
ASC:升序排列,默认就是升序,可以不加
desc:降序排列,需要添加
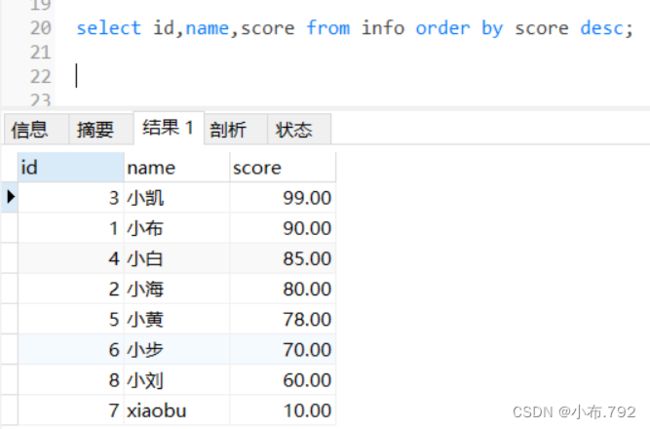
分数以高到低排序
select id,name,score from info order by score desc;order by 结合where条件过滤
select name,score from info where address='南京北部' order by score desc;查找姓名 成绩 ,根据性别=女,按照id进行降序排列
select id,name,score from info where sex ='女' order by id desc;select id,name,score from info where sex='女' order by score,id desc; 只有第一个参数出现相同值时,第二个才会按照
区间判断查询和去重查询 and/or 且 或 select * from info;
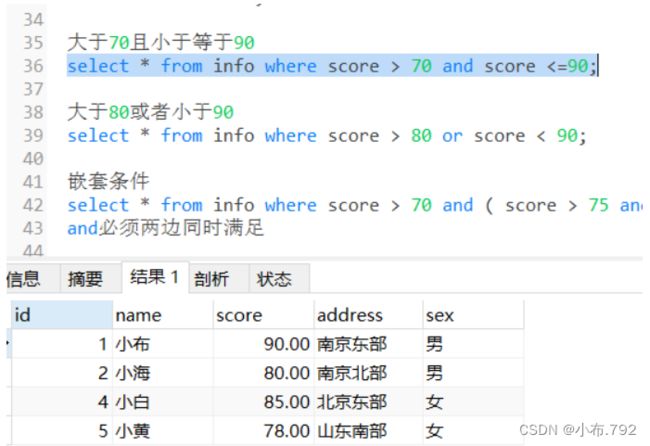
大于70且小于等于90
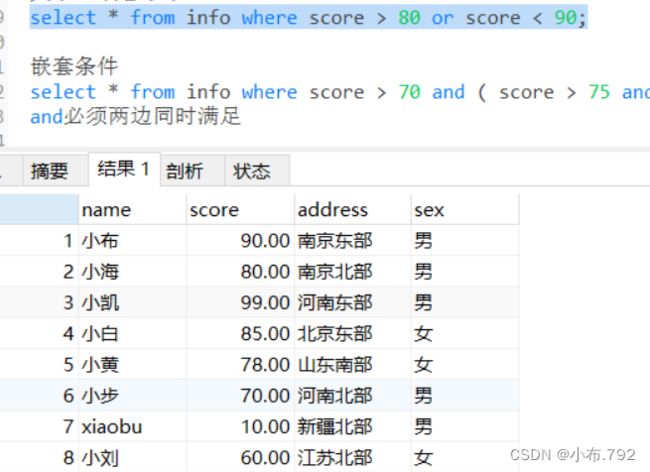
select * from info where score > 70 and score <=90;大于80或者小于90
select * from info where score > 80 or score < 90;嵌套条件
select * from info where score > 70 and ( score > 75 and score < 90);
and必须两边同时满足
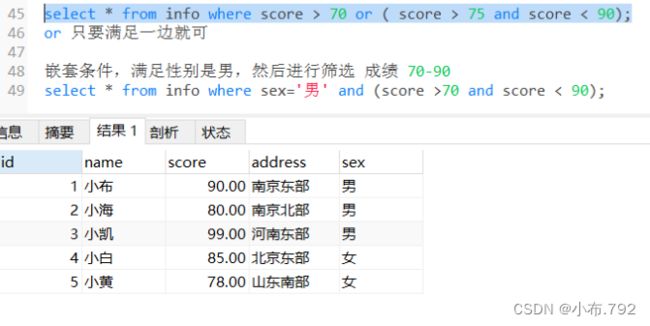
select * from info where score > 70 or ( score > 75 and score < 90);
or 只要满足一边就可
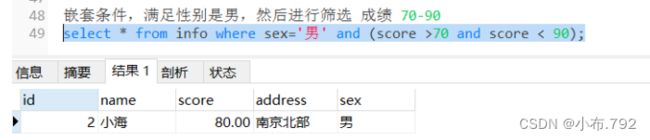
嵌套条件,满足性别是男,然后进行筛选 成绩 70-90
select * from info where sex='男' and (score >70 and score < 90);去重查询
select distinct address from info;
select distinct sex from info;根据地址去重,然后过滤出成绩=90且性别是男
select distinct address,name,score from info where score='90' and sex='男';对结果分组查询group by语句
一般是结合聚合函数一块
count()统计有多少行
sum() 列的值相加,求和
avg() 列的值求平均值
max() 过滤出列的最大值
min() 过滤出列的最小值
分组的可以按照一个字段,也可以按照多个字段对结果进行分组处理
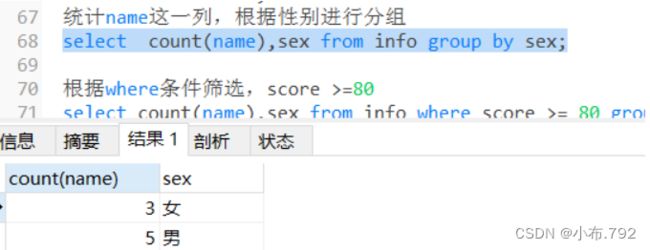
统计name这一列,根据性别进行分组
select count(name),sex from info group by sex;根据where条件筛选,score >=80
select count(name),sex from info where score >= 80 group by sex;求和 以地址为分组,对score求和
select sum(score),address from info group by address;
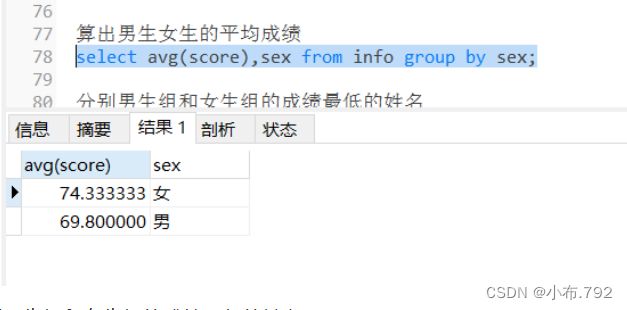
算出男生女生的平均成绩
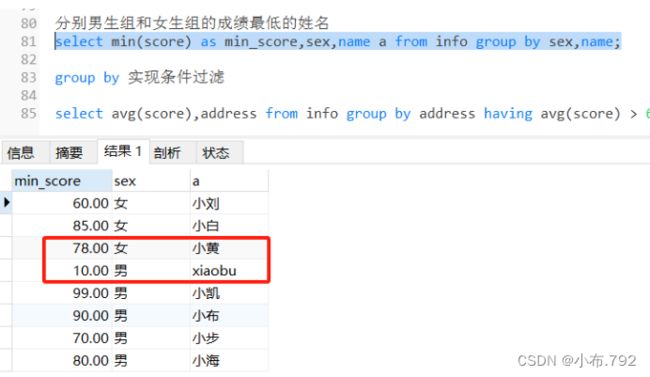
select avg(score),sex from info group by sex;分别男生组和女生组的成绩最低的姓名
select min(score) as min_score,sex,name a from info group by sex,name;group by 实现条件过滤
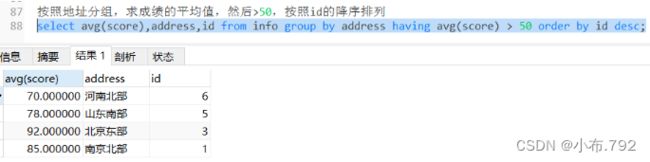
select avg(score),address from info group by address having avg(score) > 60;按照地址分组,求成绩的平均值,然后>50,按照id的降序排列
select avg(score),address,id from info group by address having avg(score) > 50 order by id desc;统计name行数,计算出学生的个数,把成绩也查出来,然后按照统计出来的学生个数,升序排列,按照地址分组,学生的成绩>=70
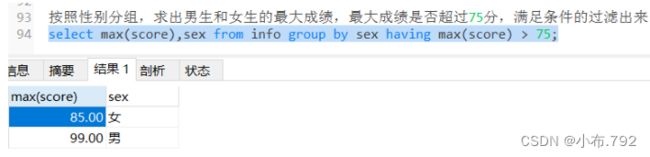
select count(name),score,address from info group by address having score >= 70 order by count(name);按照性别分组,求出男生和女生的最大成绩,最大成绩是否超过75分,满足条件的过滤出来
select max(score),sex from info group by sex having max(score) > 75;使用聚合函数必须要加group by 分组的条件,要选用有多个重复值的列,过滤条件要用having语句过滤
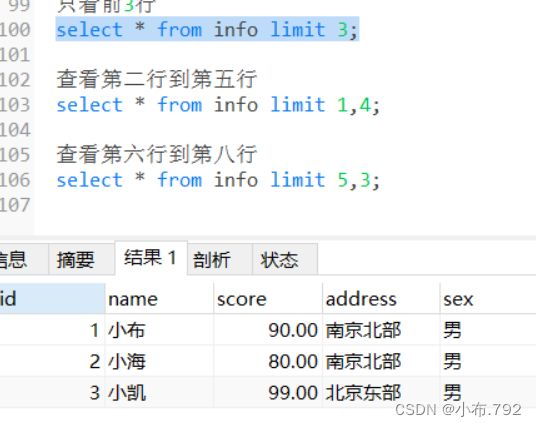
limit 限制输出的结果纪录,查看表中的指定行
只看前3行
select * from info limit 3;查看第二行到第五行
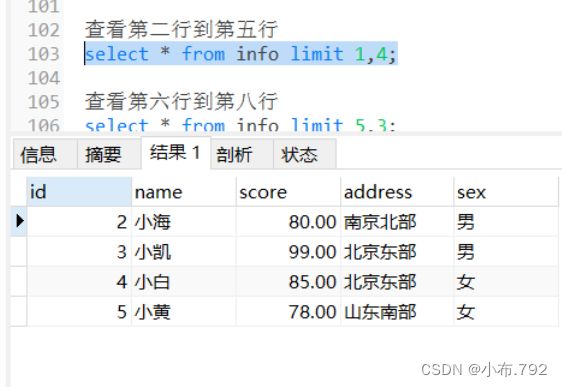
select * from info limit 1,4;查看第六行到第八行
select * from info limit 5,3;查看最后3行
select * from info order by id desc limit 3;通配符 通配符主要用于替换字符串中的部分字符,通过部分字符的匹配将先关的结果查询出来
通配符和like一起使用,使用where语句一起来完成查询
%:表示0个,1个,或者多个
_: 表示单个字符
以什么开头:c%
以什么结尾:%c
表示内容当中包含:%c%
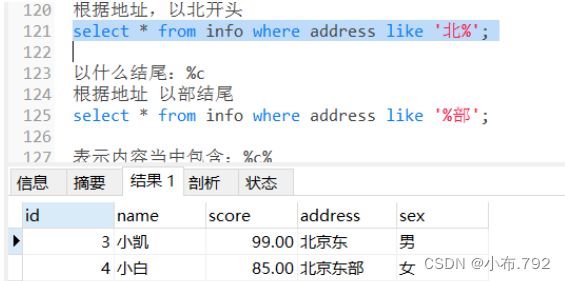
根据地址,以北开头
select * from info where address like '北%';通配符可以结合一起使用
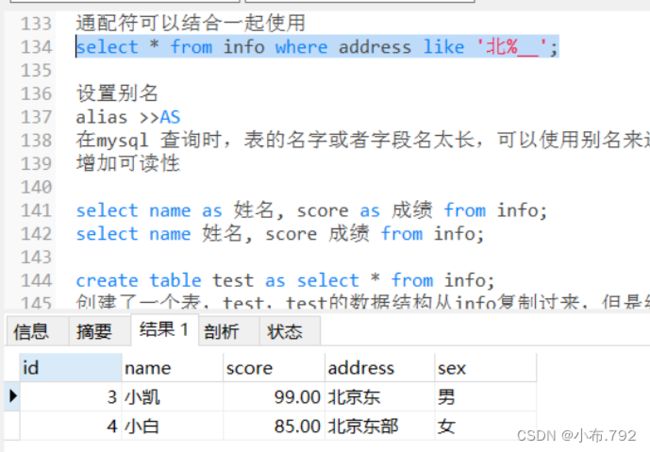
select * from info where address like '北%__';设置别名
alias >>AS
在mysql 查询时,表的名字或者字段名太长,可以使用别名来进行替代,方便书写
增加可读性
select name as 姓名, score as 成绩 from info;
select name 姓名, score 成绩 from info;create table test as select * from info;
创建了一个表,test,test的数据结构从info复制过来,但是约束不会被复制
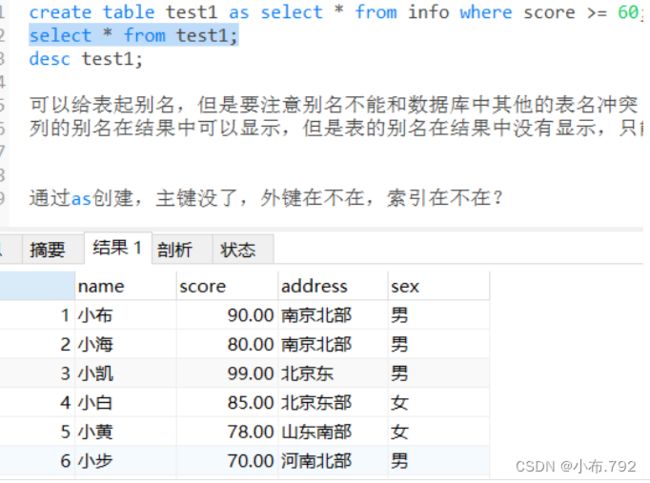
select * from test;create table test1 as select * from info where score >= 60;
select * from test1;子查询 内查询 嵌套查询
select ----(select)
括号里面的查询语句会先于主查询语句执行,然后再把子查询的结果作为条件返回给查询条件进行过滤
select name,score from info where id in (select id from info where score >80);子查询语句返回的结果,只能是一列不能是多列,多列会报错
where后条件是什么,子查询的列就是什么。
select id,name,score from info where id in (select id from test);根据两张表相同的name进行查询(多表联查,不要超过三张)
select id,name,score from info where name in (select name from test);取反
select id,name,score from info where id not in (select id from info where score > 80);子查询语句还可以用在insert update delete
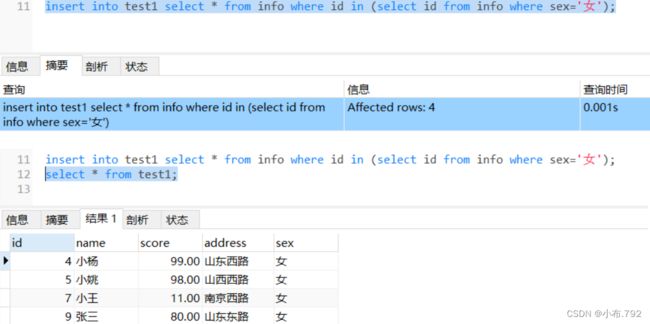
创建一个和info表一样的表test1
把info中性别为女的信息添加到test1表里
insert into test1 select * from info where id in (select id from info where sex='女');插入数据,要求按照地址,包含南京插入到xiaobu
insert into xiaobu select * from info where id in (select id from info where address like '南京%');通过子查询的方式修改info表
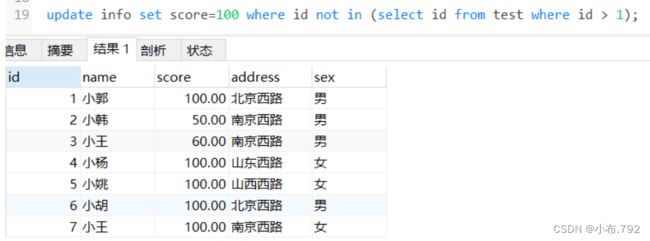
update info set score=50 where id in (select id from test where id =2);修改info表score=100,not in子查询的条件是id> 1
update info set score=100 where id not in (select id from test where id > 1);删除
delete from info where id in (select id test where score > 80);exists:关键字在子查询时,主要用于判断子查询的结果集是否为空,不为空,返回true为空,false
根据info表,查询大于80分的同学,然后统计多少个
select count(*) from info a where exists (select id from info where score > 80 and info.id=a.id );根据info表,查询小于80分的同学,然后统计多少个
select count(*) from info a where exists (select id from info where score < 80 and info.id=a.id );视图:MySQL当中的视图view
视图在MySQL当中是一个虚拟表,基于查询结果得出的一个虚拟表
在工作当中,我们查询的表未必是真表,有可能是基于真表查询结果的一个虚拟表
可以简化负载的查询语句,隐藏表的细节,提供安全的数据访问
创建视图表可以是一张表的结果集,也是多个表共同的查询的结果集
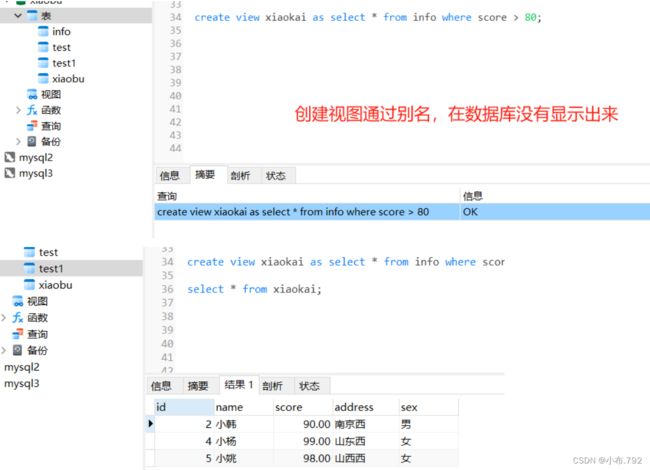
create view 表名 as select * from info wherescore >= 80;
select * from 表名;
desc 表名;查看视图表和真表的结构是不一样的,视图表没有主键
视图表和真表之间的区别
1、存储方式不一样的,真表存储实际数据,真正写在磁盘当中的,视图不存储任何数据仅仅是一个查询结果集的虚拟表
2、表可以增删改查但是视图一般情况下只能用于查,展示数据
3、占用空间,真表真实占用空间,视图不占用数据库空间
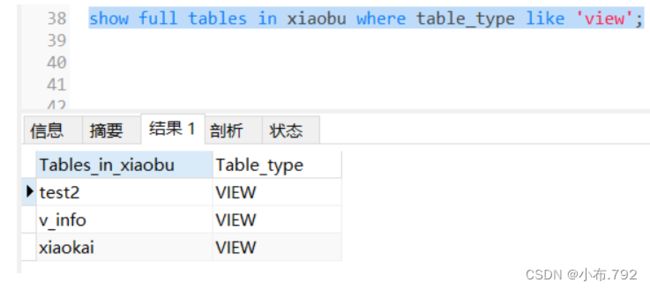
查看当前库的视图
show full tables in 库名 where table_type like 'view';删除视图
drop view test2info和test2
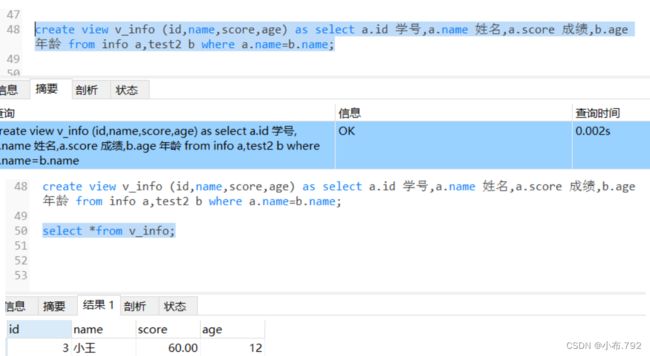
根据info的id,name score,加上test2的age?
create view v_info (id,name,score,age) as select a.id 学号,a.name 姓名,a.score 成绩,b.age 年龄 from info a,test2 b where a.name=b.name;源表的数据发生变化,视图表额数据同步更新
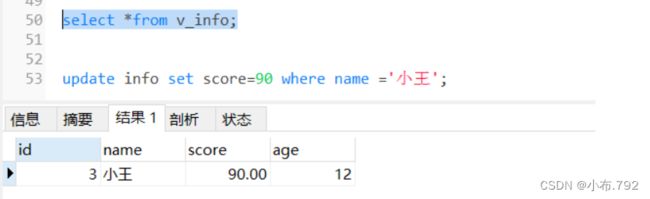
update info set score=90 where name ='小王';修改了视图表,原表也发生了变化(一般情况下我们是不会对视图表修改的)
update v_info set age=100 where name ='小王';视图表
原表
真表占了80%,视图适用于安全性要求比较高的场景,对外访问,基本上都是视图
null值和空值
null就是真空
空值 空气
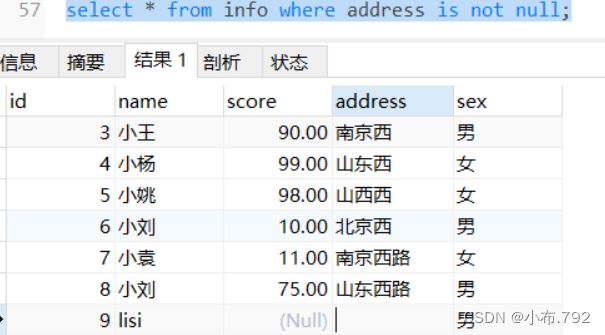
统计一下表里的空值
select * from info where address is not null;null是不被统计的,空值可以被统计的
连接查询
内连接:是把两张表或者多张表(三张),同时符合特定条件的数据记录的组合
一个或者多个列相同值才会有查询的结果
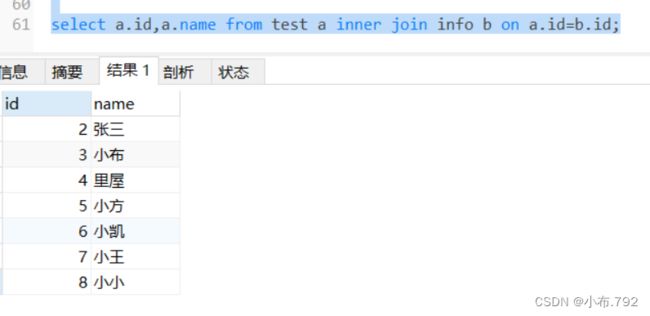
select a.id,a.name from test a inner join info b on a.id=b.id;左连接
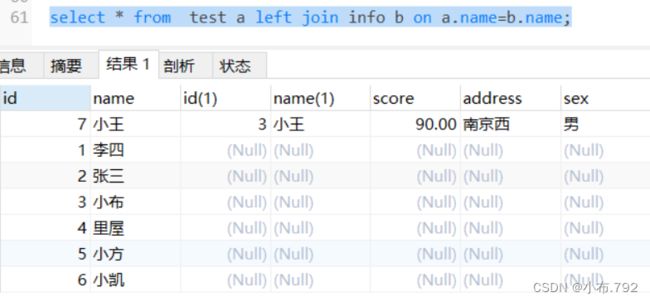
左外连接,在left join关键字来表示,在左连接当中,左侧表式基础表,接收左边的所有行,然后和右表(参考表)记录进行匹配
匹配坐标当中的所有行,以及右表中符合条件的行 ,不匹配
右连接
右外连接,right join以右侧表为寄出接收右侧表的所有记录,不匹配的记录的null值
select * from test a right join info on a.name=b.name;