Ansible-大总结(六)
文章目录
-
- Ansible
-
- Ansible的安装
- Ineventory主机清单
-
- 基于密钥连接
- Ad-Hoc
-
- 常用模块
- 帮助手册doc
- bash模块
- yum模块
- 文件管理模块
-
- copy文件拷贝模块
- file文件创建模块
- get_url文件下载模块
- 启停服务模块
- group组模块
- user模块
- crond定时任务模块
- mount挂载模块7 nfs 8客户端挂载
- 防火墙管理模块
- Ansible-Playbook
-
- PlayBook部署httpd小练习
- PlayBook实战
-
- 实战一
- 实战二:2
- Ansible跑起wordpress
- ansible变量
-
- 变量的优先级
- 定义变量
- 变量注册register
- facts变量
-
- setup模块
- 关闭facts
- 常用变量信息参数
- playbook控制
-
- Playbook条件语句
-
- 示例
- 添加yum仓库模块
- playbook循环语句
- handlers
- Playbook任务标签
- playbook文件复用
- Playbook忽略错误
- Playbook错误处理
- Ansible加密模块
- Jinja2模板
-
- Jinja2基本使用
- 配置keepalived配置文件
- mysql剧本模块
- Roles
-
- 解压模块
- 数据库模块
- 配置phpmyadmin
Ansible
ansible所需要掌握的内容
Ansible基础架构(被控端、控制端、inwentory、ad-hoc、playbook)
Inventory主机清单
Ad-Hoc
Playbook
变量
判断语句
异常处理
include包含
tag标记
handlers触发器
jinja模块
role角色
galaxy
ansible加密模块
Ansible自动化管理大纲
什么是Ansible
Ansible是一个IT 自动化的配置管理工具,自动化主要体现在Ansible集成了丰富的模块及丰富的功能的组,可以通过一个命令行
完成一系列的操作。进而能减少我们重复性的工作和维护成本,以提高工作的效率。
同类型软件对比
1.puppet 学习难,安装ruby环境难,没有远程执行功能
2.ansible 轻量级,大规模环境下只通过ssh会很慢,串行的
3.saltstack 一般选择salt会使用C/S结构的模式,salt-master和salt-minion,并行的,大规模批量操作的情况下,
会比Ansible速度快一些,底层使用的是zero-MQ消协队列
自动化运维时代
Ansible的功能及优点
1.远程执行
批量执行远程命令,可以对多台主机进行远程操作
2.配置管理
批量配置软件服务,可以进行自动化方式配置,服务的统一配置管理,和启停
3.事件驱动
通过Ansible的模块,对服务进行不同的事件驱动
比如:
1)修改配置后重启
2)只修改配置文件,不重启
3)修改配置文件后,重新加载
4)远程启停服务管理
4.管理公有云
通过API接口的方式管理公有云,不过这方面做的不如saltstack.
saltstack本身可以通过saltcloud管理各大云厂商的云平台。
5.二次开发
因为语法是Python,所以便于运维进行二次开发。
6.任务编排
可以通过playbook的方式来统一管理服务,并且可以使用一条命令,实现一套架构的部署
7.跨平台,跨系统
几乎不受到平台和系统的限制,比如安装apache和启动服务
在Ubuntu上安装apache服务名字叫apache2
在CentOS上安装apache服务名字叫httpd
在CentOS6上启动服务器使用命令:/etc/init.d/nginx start
在CentOS7上启动服务器使用命令:systemctl start nginx
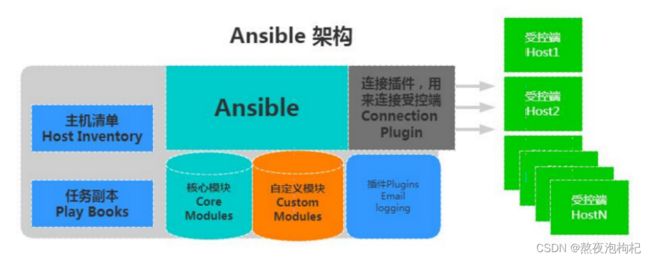
Ansible的架构
1、连接插件connection plugins用于连接主机 用来连接被管理端
2、核心模块core modules连接主机实现操作, 它依赖于具体的模块来做具体的事情
3、自定义模块custom modules根据自己的需求编写具体的模块
4、插件plugins完成模块功能的补充
5、剧本playbookansible的配置文件,将多个任务定义在剧本中,由ansible自动执行
6、主机清单inventor定义ansible需要操作主机的范围
最重要的一点是 ansible是模块化的 它所有的操作都依赖于模块
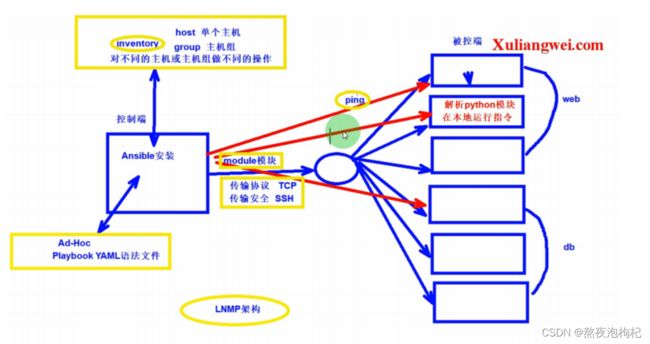
Ansible的执行流程
1.Ansible读取playbook剧本,剧本中会记录对哪些主机执行哪些任务。
2.首先Ansible通过主机清单找到要执行的主机,然后调用具体的模块。
3.其次Ansible会通过连接插件连接对应的主机并推送对应的任务列表。
4.最后被管理的主机会将Ansible发送过来的任务解析为本地Shell命令执行。
ANsible使用场景
Ansible基础架构(被控端、控制端、inventory、ad-hoc、playbook)
Ansible的安装
搭建环境
10.0.0.61 172.16.1.61 Ansible控制端 oldboy
10.0.0.7 172.16.1.7 Ansible被控端
10.0.0.8 172.16.1.8 Ansible被控端
安装epel
1.先安装epel源(提供最新的ansible)
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
安装ansible
2.安装Ansible
yum install ansible -y
查看ansible的版本
3.查看ansible的版本
[root@m01 ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.7.7
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Apr 11 2018, 07:36:10) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-28)]
Ansible配置文件读取顺序
4.Ansible的配置文件,配置文件可以随意放,但有查找顺序
$ANSIBLE_CONFIG #从变量下查找
ansible.cfg #当前目录下面查找
.ansible.cfg #当前用户的家目录下查找
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[root@m01 ~]# cat /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
#inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #主机列表配置文件
#library = /usr/share/my_modules/ #库文件存放目录
#remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #临时py文件存放在远程主机目录
#local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #本机的临时执行目录
#forks = 5 #默认并发数
#sudo_user = root #默认sudo用户
#ask_sudo_pass = True #每次执行是否询问sudo的ssh密码
#ask_pass = True #每次执行是否询问ssh密码
#remote_port = 22 #远程主机端口
host_key_checking = False #跳过检查主机指纹
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log #ansible日志
[privilege_escalation] #如果是普通用户则需要配置提权
#become=True
#become_method=sudo
#become_user=root
#become_ask_pass=False
Ineventory主机清单
1.场景一、基于密码连接
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
#方式一、主机+端口+密码
[webservers]
172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
172.16.1.8 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
#方式二、主机+端口+密码
[webservers]
web[1:2].oldboy.com ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
#方式三、主机+端口+密码
[webservers]
web[1:2].oldboy.com
[webservers:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
注意
如果控制端和被控制端第一次通讯,需要先添加指纹信息,那如果机器特别多少的情况下怎么办?
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
#host_key_checking = False 打开注释,默认false他就不用认证了.
#但是我们一般使用的是推送公钥的办法。
基于密钥连接
我们真正需要使用的方式
需要先创建公钥和私钥,并下发公钥至被控端
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-keygen
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
-----------------------------------------------------------
[root@m01 ~]# cat hosts
#方式一、主机+端口+密钥
[webservers]
172.16.1.7
172.16.1.8
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m ping -i ./hosts
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
-----------------------------------------------------------
[root@m01 ~]# cat hosts
#方式二、别名+主机+端口+密钥
[webservers]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=22
web02 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.8
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m ping -i ./hosts
web02 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
web01 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
--------------------------------------------------
场景三、主机组使用方式
#1.在inventory表里面定义两个组
root@m01 ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[lbservers]
172.16.1.5
172.16.1.6
[webservers]
172.16.1.7
172.16.1.8
#2.servers组包括两个子组[lbservers,webserver]
[servers:children]
lbservers #这里为组的名字
webserver #这里为组的名字
列出当前某个组有多少台主机
[root@m01 ~]# ansible lbservers -m ping -i ./hosts --list-hosts
hosts (1):
web01
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m ping -i ./hosts --list-hosts
hosts (1):
web02
[root@m01 ~]# ansible servers -m ping -i ./hosts --list-hosts
hosts (2):
web01
web02
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m ping -i ./hosts --list-hosts
hosts (3):
web03
web02
web01
Ad-Hoc
1.什么是ad-hoc
ad-hoc简而言之就是“临时名列“,执行完即结束,并不会保存,
2.ad-hoc模式使用场景:
比如在多台机器上查看某个进程启动,或拷贝指定文件到本地,等等。
3.ad-hoc模式的命令使用,ansible 'zlx' -m command -a 'df -h',含义如下图
常用模块
command # 执行shell命令(不支持管道等特殊字符)
shell # 执行shell命令
scripts # 执行shell脚本
yum_repository # 配置yum仓库
联网下载 get_url
安装 yum
配置 copy
启动 service、systemd
创建用户与组 user、group
授权 file
定时任务 crond
挂载 mount
firewalld firewall
selinux selinux
批量查看磁盘信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web_group -m command -a 'df -h' -i ./hosts
web02 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/sda3 18G 1.1G 17G 6% /
devtmpfs 981M 0 981M 0% /dev
tmpfs 992M 0 992M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 992M 9.5M 982M 1% /run
tmpfs 992M 0 992M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 124M 891M 13% /boot
tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0
web01 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/sda3 18G 1.1G 17G 6% /
devtmpfs 981M 0 981M 0% /dev
tmpfs 992M 0 992M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 992M 9.5M 982M 1% /run
tmpfs 992M 0 992M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 124M 891M 13% /boot
tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0
#批量查看内存信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web_group -m command -a 'free -m' -i ./hosts
web01 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1982 143 1688 9 150 1668
Swap: 1023 0 1023
web02 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1982 142 1684 9 155 1666
Swap: 1023 0 1023
帮助手册doc
6.使用过程中需要先了解ansible-doc帮助手册
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -l # 查看所有模块说明
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc copy # 表示指定模块方法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -s copy # 表示指定模块参数
bash模块
7.command默认执行bash命令模块,模块不支持重定向或管道
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -a "hostname"
8.shell模块,如果需要一些管道操作,则使用shell
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "ifconfig|grep eth0" -f 50
9.script脚本模块
[root@m01 ~]# cat yum.sh
#!/usr/bin/bash
yum install -y iftop
#在本地运行模块,等同于在远程执行,不需要将脚本文件进行推送目标主机执行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m script -a "/server/scripts/yum.sh"
yum模块
10.yum安装软件模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m yum -a "name=httpd state=installed"
name
httpd #指定要安装的软件包名称
file:// #指定从本地哪个目录安装rpm
http:// #指定从哪个网站安装rpm包
state #指定使用yum的方法
present #安装软件包
absent #移除软件包
latest #安装最新软件包
list=ansible #列出当前仓库可用的软件包
disablerepo="epel,ol7_latest" #安装软件时,不从哪些仓库获取
download_only=true #仅下载软件包,不安装
download_dir=/root #存放路径
文件管理模块
copy文件拷贝模块
#1.拷贝文件文件至被控节点
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/test.txt"
#2.对远端已有文件进行备份,按照时间信息备份
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/test.txt backup=yes"
#3.向被控端主机写入数据,并且会覆盖远端文件内原有数据信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m copy -a "content='bgx' dest=/tmp/oldboy"
src #推送数据的源文件信息
dest #推送数据的目标路径
backup #对推送传输过去的文件,进行备份 只有文件发生改变的时候才会产生新备份
content #直接批量在被管理端文件中添加内容 他是覆盖式的,而不是追加,所以使用时一定要小心。
group #将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件属组信息
owner #将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件属主信息
mode #将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件权限信息
file文件创建模块
1.直接修改被控端的权限
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web01 -m file -a "path=/opt mode=0400" -i ./hosts
2.在被控端创建目录
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m file -a "path=/tmp/oldboy state=directory"
3.在被控端创建文件
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m file -a "path=/tmp/tt state=touch mode=555 owner=root group=root"
4.递归授权目录权限
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m file -a "path=/data owner=bgx group=bgx recurse=yes"
path #指定远程主机目录或文件
recurse #递归授权
state #状态
directory #在远端创建目录
touch #在远端创建文件
link #创建链接文件
absent #表示删除文件或目录
mode #设置文件或目录权限
owner #设置文件或目录属主
group #设置文件或目录属组
get_url文件下载模块
1.通过get_url下载文件或者软件
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m get_url -a "url=http,https dest=/opt mode=0777" -i ./hosts
2.下载一个文件前先进行md5校验,通过则下载,不通过则失败
ansible webservers -m get_url -a "url=http,https dest=/opt mode=0777 checksum=md5:76eb3af80ffd" -i ./hosts
url #文件在网络上的具体位置
dest #下载到被控端的哪个目录下
checksum #校验(md5 sha256)
启停服务模块
ansible管理服务的启动与停止,使用service、systemd
#1.启动crond服务,并加入开机自启
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=started enabled=yes"
#2.停止crond服务,并删除开机自启
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=stopped enabled=no"
#3.重启crond服务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=restarted"
#4.重载crond服务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=reloaded"
name # 定义要启动服务的名称
state # 指定服务状态
started #启动服务
stopped #停止服务
restarted #重启服务
reloaded #重载服务
enabled #开机自启
group组模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m group -a "name=oldgirl gid=888"
name #指定创建的组名
gid #指定组的gid
state:
absent #移除远端主机的组
present #创建远端主机的组(默认)
user模块
1.创建用户指定uid和gid,不创建家目录也不允许登陆
[root@m01 ~]# ansible oldboy -m user -a "name=oldgirl uid=888 group=888 shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=no"
2.删除用户
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m user -a "name=tmd state=absent" -i ./hosts
3.给新创建的用户生成ssh密钥对
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m user -a "name=oo uid=6677 group=adm generate_ssh_key=yes ssh_key_bits=2048
ssh_key_file=.ssh/id_rsa" -i ./hosts
4.将明文密码进行hash加密,然后进行用户创建
[root@m01 ~]# ansible localhost -m debug -a "msg={{ '123456' | password_hash('sha512', 'salt') }}"
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"msg": "$6$salt$MktMKPZJ6t59GfxcJU20DwcwQzfMvOlHFVZiOVD71w.igcOo1R7vBYR65JquIQ/7siC7VRpmteKvZmfSkNc69."
}
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m user -a 'name=xlw password=$6$salt$MktMKPZJ6t59GfxcJU20DwcwQzfMvOlHFVZ
iOVD71w.igcOo1R7vBYR65JquIQ/7siC7VRpmteKvZmfSkNc69. create_home=yes shell=/bin/bash' -i ./hosts
uid #指定用户的uid
group #指定用户组名称
groups #指定附加组名称
password #给用户添加密码(记得单引号)
shell #指定用户登录shell
create_home #是否创建家目录
crond定时任务模块
# 正常使用crond服务(默认没写的时间都算*表示)
[root@m01 ~]# crontab -l
* * * * * /bin/sh /server/scripts/yum.sh
# 使用ansible添加一条定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m cron -a "minute=* hour=* day=* month=* weekday=* job='/bin/sh test.sh'"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m cron -a "job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh'"
# 设置定时任务注释信息,防止重复,name设定
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m cron -a "name='cron01' job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh'"
# 删除相应定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m cron -a "name='ansible cron02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh test.sh' state=absent"
# 注释相应定时任务,使定时任务失效
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible oldboy -m cron -a "name='ansible cron01' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh test.sh' disabled=yes"
mount挂载模块7 nfs 8客户端挂载
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web01 -m yum -a 'name=nfs-utils state=present' -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web01 -m file -a 'path=/data state=directory' -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web01 -m copy -a 'content="/data 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,no_all_squash)" dest=/etc/exports' -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web01 -m systemd -a "name=nfs state=started enabled=yes" -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web02 -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=present"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web02 -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=mounted"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web02 -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=unmounted"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web02 -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=absent"
present # 开机挂载,仅将挂载配置写入/etc/fstab
mounted # 挂载设备,并将配置写入/etc/fstab
unmounted # 卸载设备,不会清除/etc/fstab写入的配置
absent # 卸载设备,会清理/etc/fstab写入的配置
防火墙管理模块
Selinux模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m selinux -a "state=disabled" -i ./hosts
firewalld模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m systemd -a "name=firewalld state=started" -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m firewalld -a "service=http immediate=yes permanent=yes state=enabled" -i ./hosts
[root@m01 ~]# ansible webservers -m firewalld -a "port=8080-8090/tcp immediate=yes permanent=yes state=enabled" -i ./hosts
service #指定开放或关闭的服务名称
port #指定开放或关闭的端口
masquerade #开启地址伪装
immediate #临时生效
permanent #是否添加永久生效
state #开启或是关闭
zone #指定配置某个区域
rich_rule #配置富规则
source #指定来源IP
Ansible-Playbook
什么是PlayBook
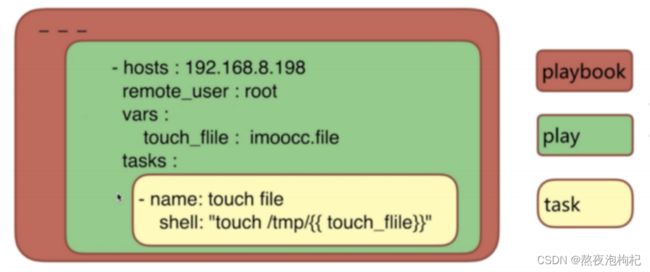
PlayBook即”剧本”,”兵书”之意,PlayBook是由以下部分组成的
- host(play:) 定义的是主机的角色。(主角还是配角,找哪个明星)
task: 定义的是具体执行的任务。(角色的台词和动作)
playbook: 由一个或多个play(角色)组成,一个play(角色)可以包含多个task(台词,动作,大腕每集拍什么)。
简单理解为: 使用不同的模块完成一件事情
在Ansible中”剧本文件”是以yml结尾的文件。
在SaltStack中”剧本文件”是以sls结尾的文件。
但是语法,使用的都是yaml语法
PlayBook与ad-hoc
1.PlayBook功能比ad-hoc更全,是对ad-hoc的一种编排.
2.PlayBook能很好的控制先后执行顺序, 以及依赖关系.
3.PlayBook语法展现更加的直观.
4.playbook可以持久使用,ad-hoc无法持久使用.
YAML语法
| 语法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 缩进 | YAML使用固定的缩进风格表示层级结构,每个缩进由两个空格组成, 不能使用TAB |
| 冒号 | 以冒号结尾的除外,其他所有冒号后面所有必须有空格 |
| 短横线 | 表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格,多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一列表 |
yum:
name: vsftpd
state: present
yum:
name:
- httpd
- nginx
- php-fpm
state: present
PlayBook部署httpd小练习
编写httpd剧本
#创建目录剧本存放目录
[root@m01 ~]# mkdir httpd
#编辑Inventory
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8
需求一:编写安装httpd剧本
[root@m01 ~]# vim /root/httpd/httpd.yml
---
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#检查语法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check httpd/httpd.yml
playbook: httpd/httpd.yml
#测试安装
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook -C httpd/httpd.yml
PLAY [web_group] *******************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************************************************
ok: [web02]
ok: [web01]
TASK [Install httpd Server] ************************************************************************************************
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************
web01 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
web02 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
需求二:安装完httpd服务并启动加入开机自启
[root@m01 ~]# vim /root/httpd/httpd.yml
---
- hosts: web_group
#安装httpd
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#启动httpd
- name: Start Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
#测试安装和启动
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook -C httpd/httpd.yml
PLAY [web_group]
************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************************
ok: [web02]
ok: [web01]
TASK [Install httpd Server] ************************************************************************
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
TASK [Start Httpd Server] ************************************************************************
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************
web01 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
web02 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
需求三:编写网站页面并启动
- hosts: web_group
#安装httpd
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#配置网站
- name: Config Httpd Server
copy:
content: oldboy_web_page
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
#启动httpd
- name: Start Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
#执行
[root@m01 httpd]# ansible-playbook /root/httpd/httpd.yml
需求四:开启防火墙端口
- hosts: web_group
#安装httpd
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#配置网站
- name: Config Httpd Server
copy:
content: oldboy_web_page
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
#启动httpd
- name: Start Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
#启动防火墙
- name: Start Firewalld Server
systemd:
name: firewalld
state: started
enabled: yes
#开启防火墙的80端口
- name: Config Firewalld Server
firewalld:
service: http
immediate: yes
permanent: yes
state: enabled
打开浏览器访问网站:
http://10.0.0.7
http://10.0.0.8
需求五:不同的主机配置不同的网站
---
- hosts: web_group
#安装httpd
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#启动httpd
- name: Start Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
#启动防火墙
- name: Start Firewalld Server
systemd:
name: firewalld
state: started
enabled: yes
#开启防火墙的80端口
- name: Config Firewalld Server
firewalld:
service: http
immediate: yes
permanent: yes
state: enabled
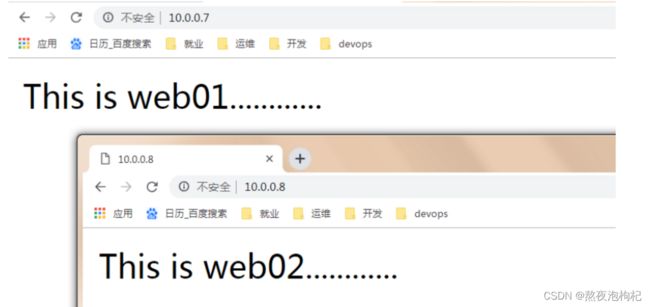
#单独配置web01页面
- hosts: web01
tasks:
- name: Config Httpd Server
copy:
content: oldboy_web01_page
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
#单独配置web02页面
- hosts: web02
tasks:
- name: Config Httpd Server
copy:
content: oldboy_web02_page
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
[root@m01 httpd]# ansible-playbook /root/httpd/httpd.yml
打开浏览器访问网站:
http://10.0.0.7
http://10.0.0.8
PlayBook实战
实战一
配置环境
| 主机名 | 公网ip | 私网ip | 服务 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m01 | 10.0.0.61 | 172.16.1.61 | Ansible | 控制端 |
| backup | 10.0.0.41 | 172.16.1.41 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
| web01 | 10.0.0.7 | 172.16.1.7 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
| web02 | 10.0.0.8 | 72.16.1.8 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
准备配置文件
#创建rsync剧本存放目录
[root@m01 ~]# mkdir rsyncd
#编辑Inventory
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[web_group]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8
[backup_group]
backup ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.41
#准备rsync配置文件
[root@m01 rsyncd]# vim /root/rsyncd/rsyncd.j2
uid = www
gid = www
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections = 200
timeout = 600
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
#####################################
[backup]
comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup!
path = /backup
playbook
#编写剧本
[root@m01 ~]# vim /root/rsyncd/rsyncd.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
#安装rsync
- name: Install Rsyncd Server
yum:
name: rsync
state: present
#创建www组
- name: Create www Group
group:
name: www
gid: 666
#创建www用户
- name: Create www User
user:
name: www
group: www
uid: 666
create_home: false
shell: /sbin/nologin
- hosts: backup_group
tasks:
#推送rsync配置文件
- name: Scp Rsync Config
copy:
src: ./rsyncd.j2
dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
#创建密码文件并授权
- name: Create Passwd File
copy:
content: 'rsync_backup:123'
dest: /etc/rsync.passwd
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0600
#创建/backup目录
- name: Create backup Directory
file:
path: /backup
state: directory
mode: 0755
owner: www
group: www
recurse: yes
#启动rsync服务
- name: Start Rsyncd Server
systemd:
name: rsyncd
state: started
#检测语法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check /root/rsyncd/rsyncd.yml
playbook: /root/rsyncd/rsyncd.yml
#测试
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook -C /root/rsyncd/rsyncd.yml
PLAY [all] ************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************
ok: [backup]
ok: [web02]
ok: [web01]
TASK [Install Rsyncd Server]*******************************************************
changed: [backup]
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
TASK [Scp Rsync Config]************************************************************
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
changed: [backup]
TASK [Create www Group] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [backup]
changed: [web01]
changed: [web02]
TASK [Create www User] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [web02]
changed: [web01]
changed: [backup]
TASK [Create backup Directory] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [web01]
changed: [backup]
changed: [web02]
TASK [Start Rsyncd Server] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [web01]
changed: [web02]
changed: [backup]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
backup : ok=7 changed=6 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
web01 : ok=7 changed=6 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
web02 : ok=7 changed=6 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
扩展需求:
1.给客户端推送脚本
2.加入crontab做备份
完成刚开始学架构阶段的rsync的实战案例
实战二:2
部署NFS服务,NFS服务端,敞开大门提供挂载点给web01和web02
| 主机名 | 公网ip | 私网ip | 服务 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m01 | 10.0.0.61 | 172.16.1.61 | Ansible | 控制端 |
| backup | 10.0.0.41 | 172.16.1.41 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
| web01 | 10.0.0.7 | 172.16.1.7 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
| web02 | 10.0.0.8 | 72.16.1.8 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
环境部署
#编辑Ansible Inventory
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8
[backup]
backup ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.41
[nfs]
nfs ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.31
[nfs_all:children]
web_group
nfs_group
#创建项目存放目录
[root@m01 ~]# mkdir nfs
#准备nfs配置文件
[root@m01 ~]# cat /root/nfs/nfs.j2
/data 10.0.0.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666)
playbook
[root@m01 ~]# vim /root/nfs/nfs.yml
- hosts: nfs_all
tasks:
#安装nfs
- name: Install nfs-utils
yum:
name: nfs-utils
state: present
#创建www组
- name: Create www Group
group:
name: www
gid: 666
#创建www用户
- name: Create www User
user:
name: www
group: www
uid: 666
create_home: false
shell: /sbin/nologin
- hosts: nfs
tasks:
#推送配置文件
- name: Scp NFS Server
copy:
src: ./nfs.j2
dest: /etc/exports
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
#创建挂载目录并授权
- name: Create data Directory
file:
path: /data
state: directory
owner: www
group: www
mode: 0755
recurse: yes
#启动nfs-server
- name: Start NFS Server
systemd:
name: nfs-server
state: started
enabled: yes
#web01和web02挂载目录
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Mount NFS Server
mount:
path: /opt
src: 10.0.0.31:/data
fstype: nfs
opts: defaults
state: mounted
#检查语法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check /root/nfs/nfs.yml
playbook: /root/nfs/nfs.yml
#执行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook /root/nfs/nfs.yml
Ansible跑起wordpress
部署需求:
1.使用yum安装httpd、php、php-mysql、php-pdo、mariadb
2.启动httpd、mariadb服务
3.下载wordpress代码
4.部署到httpd站点目录
1.环境准备
| 主机名 | 公网ip | 私网ip | 服务 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m01 | 10.0.0.61 | 172.16.1.61 | Ansible | 控制端 |
| web01 | 10.0.0.7 | 172.16.1.7 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
| web02 | 10.0.0.8 | 72.16.1.8 | rsync服务端 | 被控端 |
因为这只是一个练习,所以我们将apache mariadb php全部都写在一个yml文件中,并且放在一个目录下,
注意:在生产中,我们是不会这么做的,我们需要每一个服务单独拎出来,解耦。
#创建项目目录
[root@m01 ~]# cd lamp/
#编辑Inventory
[root@m01 lamp]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8
[backup]
backup ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.41
[backup_all:children]
web
backup
[nfs]
nfs ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.31
[nfs_all:children]
web_group
nfs_group
playbook
- hosts: web01
vars: #变量
package: #变量名
- httpd
- mariadb-server #安装需要全名
- php #安装需要卸载原有文件
- php-mysql
- php-pdo
- MySQL-python
tasks:
- name: Istall Httpd Mariadb Php Server
yum:
name: "{{ package }}"
state: present
- name: Stop Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: stopped
- name: Started Httpd
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Started Mariadb
systemd:
name: mariadb
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Install Wordpress
unarchive: #解压模块
src: /root/wordpress/wordpress-5.0.3.tar.gz
dest: /var/www/html/
copy: yes #解压并复制,这里必须开启
- name: Change Mode Httpd
file:
path: /var/www/html/
owner: apache
group: apache
recurse: yes
- name: Create Database user
mysql_user:
name: autumn
password: autumn123.com
priv: '*.*:ALL'
state: present
host: localhost
- name: Create Database wordpress
mysql_db:
login_user: autumn
login_password: autumn123.com
login_host: localhost
login_port: 3306
name: wordpress
state: present
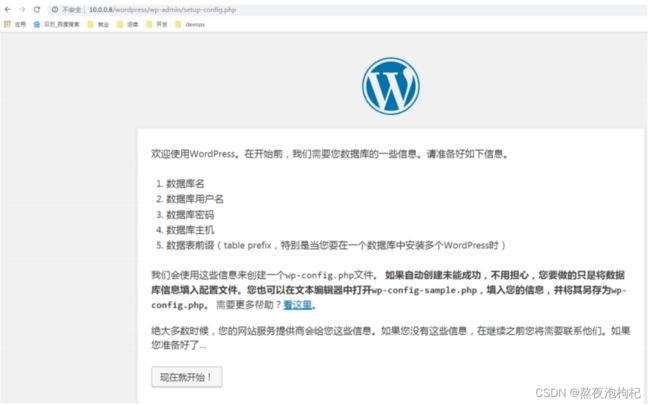
打开浏览器访问:
http://10.0.0.7/wordpress/wp-admin/setup-config.php
http://10.0.0.8/wordpress/wp-admin/setup-config.php
ansible变量
概述
变量提供了便捷的方式来管理ansible项目中的动态值。比如zabbix-3.4.15,可能后期会反复的使用这个版本的值,那么如果将
此值设置为变量,后续使用和修改将变得非常方便,这样可以简化项目的创建和维护
定义变量分为如下三种方式
1.通过命令行进行变量定义 #使用-e参数,优先级是最高的
2.在play文件中进行定义变量 #使用vars_file或者vars定义变量
3.通过inventory在主机组或单个主机中设置变量 #通过host_vars或者group_vars定义变量
变量的优先级
如果定义的变量出现重复,且造成冲突,优先级如下:
命令行变量--->play中的vars_files--->play中的vars变量-->host_vars中定义的变量--->group_vars/组--->group_vars/all
[root@m01 wget]# ansible-playbook wget.yml -e "webserver=zarafa-devel" #命令行变量.优先级第一名
[root@m01 project1]# cat p5.yml
- hosts: webservers
# vars: #play中vars变量 优先级第三
# filename: play_vars
# vars_files: #play中var_files变量,优先级第二
# - ./vars.yml
tasks:
[root@m01 project1]# cat host_vars/webserver #优先级第四
[root@m01 project1]# cat group_vars/webserver #优先级第五
[root@m01 project1]# cat group_vars/all #优先级第六
定义变量
playbook变量
playbook变量可以通过多种方式进行定义,最简单的方式就是在playbook的开头通过vars进行定义
#方法一:
- hosts: web_group
vars:
packages:
- httpd
- mariadb-server
- php
- php-mysql
- php-pdo
tasks:
- name: Install httpd mariadb php Server
yum:
name: "{{ packages }}"
#方法二:
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- web_server: httpd
- db_server: mariadb-server
- php_server: php,php-mysql,php-pdo
tasks:
- name: Install httpd mariadb php Server
yum:
name:
- "{{ web_server }}"
- "{{ db_server }}"
- "{{ php_server }}"
这种在playbook中使用vars定义变量,有一个缺陷,就是其他的playbook无法使用该变量。
使用vars_file定义变量
#定义阶段
[root@m01 project1]# cat vars.yml
web_package: httpd
ftp_package: vsftpd
[root@m01 project1]# cat p2.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars_files: ./vars.yml
tasks:
- name: Installed Packages
yum:
name:
- "{{ web_package }}"
- "{{ ftp_package }}"
state: present
在inventory中定义变量,主机变量优先级高于主机组变量(不推荐使用)
[root@m01 project1]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.8
[webservers:vars]
filename=group_vars
[root@m01 project1]# cat p3.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Create File
file: path=/tmp/{{ filename }} state=touch
创建host_vars和group_vars目录,使用变量
[root@m01 project1]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7
web02 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.8
# host_vars目录下必须存放和inventory清单文件中定义的组名一致
[root@m01 project1]# cat host_vars/web01
web_package: zlib-static
ftp_package: zmap
# group_vars目录下必须存放和inventory清单文件中定义的组名一致,如下
[root@m01 project1]# cat group_vars/webservers
web_package: httpd
ftp_package: vsftpd
[root@m01 project1]# cat group_vars/all
注意:系统提供了特殊的组,all,也就说在group_vars目录下创建一个all文件,定义变量对所有的主机都生效
[root@m01 project1]# cat host_vars/web01
web_package: zlib-static
ftp_package: zmap
[root@m01 project1]# cat group_vars/webservers
web_package: httpd
ftp_package: vsftpd
[root@m01 project1]# cat p4.yml
- hosts: webservers
#- hosts: otherservers
tasks:
- name: Installed Packages
yum:
name:
- "{{ web_package }}"
- "{{ ftp_package }}"
state: present
[root@m01 project1]# ansible-playbook p4.yml
PLAY [webservers] *****************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************
ok: [web02]
ok: [web01]
TASK [Installed Packages] ***********************************************************************
ok: [web02]
changed: [web01]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************
web01 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
web02 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
变量注册register
当ansible的模块运行之后,其实会有一些result结果,就像是执行脚本,我们有的时候需要脚本给我们return返回值,
我们才知道是否可以执行成功,但是,默认情况下,ansible的result并不会显示出来,所以,我们可以把这些返回值"存储"到变量中,
这样我们就能通过'调用'对应的变量名,从而获取到这些result,这种将模块的返回值,写入到变量中的方法被称为变量注册
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Get Network Port Status
shell: netstat -lntp
register: net_port #定义变量(netstat -lntp)
- name: OutPut Network Port Status
debug: #debug模块
msg: "{{ net_port.stdout_lines }}" #这里.stdout_lines是指仅仅只输出shell命令中netstat -lntup中的.stdout_lines包含的值
#debug :调试模块,用于在调试中输出信息 常用参数:
msg:调试输出的消息var:将某个任务执行的输出作为变量传递给debug模块,
debug会直接将其打印输出 verbosity:debug的级别(默认是0级,全部显示)
变量也支持层级定义,使用".“可能会有问题,建议使用”[]"代替。
[root@m01 project1]# cat vars1.yml
rainbow:
web:
web_package: httpd
db_package: mariadb
code:
web:
filename: code_web_filename
[root@m01 project1]# cat p8.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars_files: ./vars1.yml
tasks:
- name: Install Package
yum: name= "{{ rainbow['web']['web_package'] }}"
- name: create filename
file:
path: /tmp/{{ code.web.filename }}
state: touch
facts变量
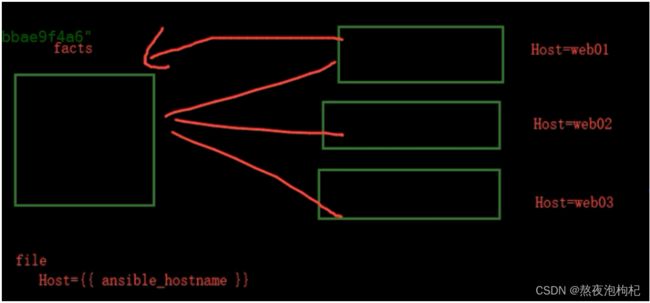
Ansible facts是在被管理主机上通过ansible自动采集发现的变量。facts包含每台特定主机信息。
比如:被控制的主机、IP地址、系统版本、CPU数据、内存状态、磁盘状态等等。
fact使用场景
1.通过facts检查CPU,来生成对应的Nginx配置文件,
2.通过facts检查主机名信息,来生成不同的Zabbix配置文件。
3.通过facts检查的内存情况来自定义mysql的配置文件
setup模块
命令行取变量用setup模块
使用setup模块可以取到主机所有的硬件信息及变量名(静态信息)
[root@m01 vars]# ansible web01 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_fqdn'
[root@m01 vars]# ansible web01 -m setup -a "filter="ansible_fqdn"
取变量示例
[root@m01 debug]# vim debug.yml
- name: OutPut Variables Ansible Facts
debug:
msg: >
this default IPv4 address"{{ansible_fqdn}}"is"{{ansible_eth1.ipv4.address }}"
使用ansible facts安装zabbix-agent
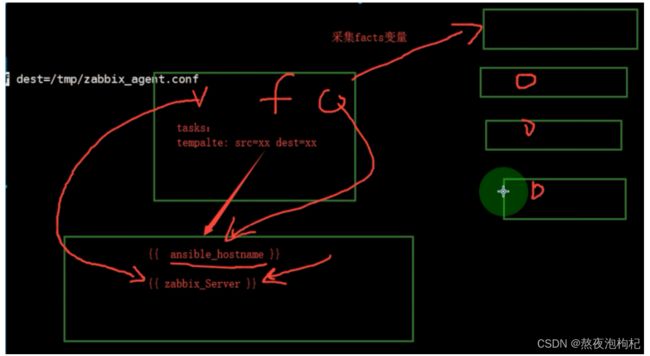
copy模块不支持解析变量
template模块支持解析变量,其他功能根本copy模块一样
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf
Server= {{ zabbix_server }} # 定义变量playbook里的变量
Hostname={{ ansible_hostname }} # 读取facts的变量
#facts(setup模块)
他们其实是同样的原理和功能,setup模块的原理就是facts
[root@m01 zabbix]# vim zabbix.yml
- hosts: web01
#gather_facts: no #关闭信息采集
vars:
- zabbix_server: 172.16.1.71 #
tasks:
- name: Copy zabbix configure
template: #如果使用copy模块不能解析变量
src: /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf
dest: /tmp/zabbix_agentd.conf
facts自定义安装memcached
我们在这里要学会用使用变量百分之比的值给被控端配置文件
playbook安装一个memcached
[root@m01 ~]# yum install memcached -y
[root@m01 project1]# cat memcached.j2 #配置文件内容
PORT="11211"
USER="memcached"
MAXCONN="1024"
CACHESIZE="{{ ansible_memtotal_mb //2 }}" #设置变量并且除以2
OPTIONS=""
[root@m01 project1]# cat p11.yml #编写剧本
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Installed Memcached
yum: name=memcached state=present
- name: Configure Memcached
template: src=./memcached.j2 dest=/etc/sysconfig/memcached
- name: Start Memcached
service: name=memcached state=started enabled=yes
关闭facts
[root@m01 ~]# vim facts.yml
- hosts: web_group
gather_facts: no #关闭信息采集
tasks:
# 在这里我们要知道,如果关闭了facts变量,我们就无法在当前的剧本使用facts里的变量的值了
常用变量信息参数
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses:仅显示ipv4的信息。
ansible_devices:仅显示磁盘设备信息。
ansible_distribution:显示是什么系统,例:centos,suse等。
ansible_distribution_major_version:显示是系统主版本。
ansible_distribution_version:仅显示系统版本。
ansible_machine:显示系统类型,例:32位,还是64位。
ansible_eth0:仅显示eth0的信息。
ansible_hostname:仅显示主机名。
ansible_kernel:仅显示内核版本。
ansible_lvm:显示lvm相关信息。
ansible_memtotal_mb:显示系统总内存。
ansible_memfree_mb:显示可用系统内存。
ansible_memory_mb:详细显示内存情况。
ansible_swaptotal_mb:显示总的swap内存。
ansible_swapfree_mb:显示swap内存的可用内存。
ansible_mounts:显示系统磁盘挂载情况。
ansible_processor:显示cpu个数(具体显示每个cpu的型号)。
ansible_processor_vcpus:显示cpu个数(只显示总的个数)。
playbook控制
-------task任务处理相关流程与控制参数
when 判断
item 循环
handlers 触发器(需要task使用notify通知)
tags 标签(调试使用)
include_tasks 包含task任务
ignore_errors 忽略错误
错误处理
force_handlers #扩展
changed_when false 抑制改变的状态为ok(获取系统的状态信息时)
-------重要(检查服务的配置是否正常,正常则不处理,不正常则中断)
register: httpd_check
changed_when:
- httpd_check.stdout.find('OK')
- false
Playbook条件语句
判断在Ansible任务中的使用频率非常高。比如yum模块可以检测软件包是否已经安装,而这个过程中我们不用做太多的人工干预。
但是部分任务需要进行判断,比如:web服务器角色都需要使用nginx仓库,但是其他的服务器角色并不需要,此时就会用到when判断。
比如:CentOS和Ubuntu系统都需要安装httpd服务,那么久需要使用when判断主机系统,然后调用不同的模块执行。
示例
根据不同操作系统,安装相同的软件包
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- name: Install httpd Server
apt: name=httpd2 state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu"
按照不同的主机名称进行判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_fqdn == "web02"
按照不同的IP地址进行判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "10.0.0.7"
按照获取客户端的某参数值得大小判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
host_mem: "{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- "{{ host_mem }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_memtotal_mb|int < "2000"
添加yum仓库模块
所有为web主机名的添加nginx仓库,其余的都跳过添加
1.如何添加yum仓库
2.如何判断,判断什么内容
---
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Add Nginx Repos
yum_repository: #模块
name: nginx_tet #它代表/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx_tet.repo
description: Nginx YUM repo #描述 (不加会报错)
baseurl: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck: no #把效验本地给关掉
when: (ansible_hostname is match ("web*")) or (ansible_hostname is match ("lb*")) #根据官方的写法
列表方式判断 and关系 并且关系
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
host_mem: "{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }}"
host_ver: "{{ ansible_distribution }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- "{{ host_mem }}"
- "{{ host_ver }}"
- name: Reboot Server
file:
path: /root/web01.txt
state: touch
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_fqdn == "web01"
修改Nginx配置文件 把Nginx从ansible服务器拷贝到web服务器
拷贝过去需要启动或者重启 如果Nginx配置文件不对 不让加载
如何判断Nginx文件配置是否正确?
1. 安装Nginx
2. 拷贝文件到Nginx.conf 判断文件是否正确 ngixn -t 变量注册接收结果
3. 启动
4. 重新加载 在重新加载的地方进行when判断
[root@m01 when]# cat nginx.yml
- hosts: web02
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: scp configure Nginx
copy:
src: ./nginx.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- name: Check Nginx Configure
command: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
register: result
ignore_errors: yes # 忽略错误继续执行
- name: print result
debug:
msg: "{{ result.rc }}"
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc == 0 # 判断nginx -t执行结果 是否为0 通过变量注册获取的
-----------------------------
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc is match "0"
判断http是否存活
- hosts: web02
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: scp configure Nginx
copy:
src: ./nginx.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- name: Check Nginx Configure
command: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
register: result
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Check HTTP Server
command: systemctl is-active httpd
register: result_http
ignore_errors: yes
- name: print result
debug: var=result_http
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc == 0
playbook循环语句
有时候我们写playbook的时候发现了很多tasks都要反复引用某个模块,比如一次启动10个服务,或者一次拷贝10个文件,
如果按照传统的写法最少要写10次,这样会显得很臃肿,如果使用循环的方式来编写playbook,这样可以减少重复使用某个模块.
==实践案例一 ==
弃用的写法,因为有可能会提示warn
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Started Server
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}" #官方定义的
state: started
with_items: #定义的循环的服务内容
loop: #或者这么使用
- httpd
- mariadb
#在这里httpd和mariadb对被控端重复循环
这种循环写法是官方推荐的写法
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml #但是他这里只属于yum模块的命令
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Started Server
yum:
name: "{{ packages }}"
state: present
vars:
packages:
- httpd
- mariadb
实践案例三:使用字典的方式创建用户和批量拷贝文件
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: add user
user:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
groups: "{{ item.groups}}"
state: present
with_items: 或者使用loop
- { name: 'testuser1', groups: 'adm' }
- { name: 'testuser2', groups: 'root' }
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Copy Rsync configure and Rsync passwd
copy: src={{ item.src }} dest={{ item.dest }} mode={{ item.mode }}
loop:
- { src: "./rsyncd.conf", dest: "/etc/rsyncd.conf", mode: "0644" }
- { src: "./rsync.passwd", dest: "/tmp/rsync.passwd", mode: "0600" }
handlers
handlers注意事项
1.无论多少个task通知了相同的handlers,handlers仅会在所有tasks结束后运行一次。
2.只有task发生改变了才会通知handlers,没有改变则不会触发handlers
3.不能使用handlers替代tasks
[root@m01 project2]# cat han.yml
- hosts: web
#force-handlers: yes #强制执行handlers,在这里使用的次数比较少
vars:
- http_port: 8083
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: #在这里我们要注意notify是模块层
- Restart Httpd Server #与handlers的- name对应,必须一致
- Restart PHP Server #与handlers的- name对应,必须一致
- name: start httpd server #这里必须启动服务器来,handlers无法替代tasks起来启动服务。
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers: #handlers是模块层
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
- name: Restart PHP Server
systemd: name=php-fpm state=restarted
#handlers是同过notify监听服务是否发生改变来出发的,如果服务没发生改变,handlers是无法触发的。
Playbook任务标签
默认情况下,Ansible在执行的一个playbook时,会执行playbook中定义的所有任务。Ansible的标签(Tags)功能可以给
单独任务甚至整个playbook打上标签,然后利用这些标签来指定要运行的playbook中的个别任务,或不执行指定的任务。
1.打标签的方式有几种,比如:
对一个task打一个标签、对一个task打多个标签、对多个task打一个标签
2.对task打完标签应该如何使用
-t: 执行指定的tag标签任务
--skip-tags:执行--skip-tags之外的标签任务
可以通过–list-tags查看yml剧本中的标签数
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --list-tags
可以用-t参数对指定tags执行命令
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t tags(定义的标签)
这里-t也执行单独运行多个tags标签
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t tags1,tags2
可以用–skip-tags对指定tags排除
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --skip-tags tags(定义的标签)
同时--skip-tags也可以排除多个tags标签
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --skip-tags tags1,tags2
示例
[root@m01 project2]# cat tag.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
- http_port: 8083
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
tags:
- install_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
tags:
- confiure_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
tags: service_httpd
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
由于生产场景里的playbook过于臃肿,其中如果某个task出了错误,
我们测试可能需要全部再执行一次,需要浪费很多的时间,非常不方便,如果我们对单独的tasks指定tags,对单个的tags进行调试,我们会方便很多
playbook文件复用
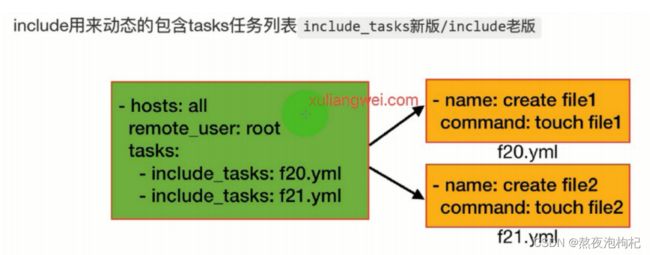
include(import_playbook)
#这种方式已经弃用,现在使用的是import_playbook,它包括的是任务文件.
include_tasks
#这种方式,include包含的是命令文件.
[root@m01 project2]# cat task.yml
- hosts: web
vars: #定义端口变量
- http_port: 801
tasks:
- include_tasks: task_install.yml #包含安装文件
- include_tasks: task_configure.yml #包含配置文件
- include_tasks: task_start.yml #包含启动文件
handlers: #触发器,一旦改变,重启服务使他生效
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_install.yml #安装文件的内容
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_configure.yml #配置文件的内容
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_start.yml #启动服务的文件
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
Playbook忽略错误
默认Playbook会检查tasks执行的返回状态,如果遇到错误则会立即终止playbook的后续执行,然而有时候playbook即使执行错误了也要让其继续执行
加入参数:ignore_errors:yes 忽略错误.
示例
[root@manager ~]# cat f9.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Ignore False
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors: yes
- name: touch new file
file: path=/tmp/bgx_ignore state=touch
Playbook错误处理
通常情况下,当task失败后,play将会终止,任何在前面已经被tasks notify的handlers都不会执行.
如果你在play中设置了force_handlers:yes参数,被通知的handlers就会强制执行.(有些特殊场景可能会使用到)
示例一
force_handlers: yes #强制调用handlers
[root@m01 project2]# cat tag.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
- http_port: 8083
force_handlers: yes #强制调用handlers
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
tags:
- install_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
tags:
- confiure_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
tags: service_httpd
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
示例二
changed_when: false #当文件状态没有被改变,我们可以用这个参数抑制changed状态的报告。
- hosts: web
vars:
- http_port: 8083
force_handlers: yes #强制调用handlers
tasks:
- name: Command
shell: netstat -lntp|grep httpd
registet: check_httpd
changed_when: false #当文件状态没有被改变,我们可以用这个参数抑制changed状态的报告。
- name: Debug
debug: msg={{ check_httpd.stdout_lines }}
示例三
在这里我们加上了判断,如果我们加上了判断,这里如果配置文件发生了错误,
将不会重启配置文件,这样就能在保证生产线的情况下让我有足够的时间排错
[root@m01 project2]# cat tag.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
- http_port: 8083
force_handlers: yes #强制调用handlers
tasks:
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: Check Httpd
shell: /usr/sbin/httpd -t #检测apache配置文件语法格式是否正确
registet: check_httpd
changed_when:
- check_httpd.stdout.find('OK')
- false
notify: Restart Httpd Server
- name: Srart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
判断失败示例
failed_when
命令不依赖返回状态码来判定是否执行失败,而是要查看命令返回内容来决定,比如返回内容中包括 failed 字符串,则判定为失败。示例如下:
- name: this command prints FAILED when it fails
command: /usr/bin/example-command -x -y -z
register: command_result
failed_when: "'FAILED' in command_result.stderr"
Ansible加密模块
ansible加密模块
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault --help
Usage: ansible-vault [create|decrypt|edit|encrypt|encrypt_string|rekey|view] [options] [vaultfile.yml]
加密一个文件
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault encrypt include.yml
查看一个文件
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault view include.yml
Vault password:
- import_playbook: han.yml
- import_playbook: when2.yml
修改加密的文件内容
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault edit include.yml
rekey 修改密码
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault rekey include.yml
Vault password:
New Vault password:
Confirm New Vault password:
Rekey successful
执行加密的playbook
[root@m01 project2]# echo "1" >pass
[root@m01 project2]# chmod 600 pass
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook include.yml --vault-password-file=pass
移除密码
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault decrypt include.yml
Vault password:
Jinja2模板
什么是jinja2
Jinja2是Python的全功能模板引擎
Jinja2模板与Ansible有什么关系
Ansible通常会使用Jinja2模板来修改被管理主机的配置文件,例如给10台远程主
机装上httpd服务,但是要求每个服务器的端口不一样,如何解决?
Ansible如果使用Jinja2模板
使用ansible的Jinja2模板,也就是template模板.该模块跟copy模块一样,都是将
文件复制到远端主机上去,但是区别在于template模块可以获取要复制的文件中变
量的值,而copy则是原封不动的把文件内容复制过去,不如:针对不同的主机定义不
同的变量,template会在将配置文件分发出去前读取变量Jinja2模块,然后分发到
不同的被管理主机上.
Jinja2基本使用
语法:
{{EXPR}}输出变量的值(会输出自定义变量的值或facts)
1)playbook文件使用template参数
2)模板文件里面变量使用(名称),比如{PORT}或者使用facts。
jinja模板逻辑关系
{% for i in EXPR %}...{% endfor%}作为循环表达式
{% if EXPR %}...{% elif EXPR %}...{% endif%}作为条件判断
{# COMMENT #}表示注释
jinja模板使用示例,使用facts变量的示例
1.编辑playbook
[root@m01 ~]# vim jinja2.yml
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Copy Template File
template:
src: ./motd.j2
dest: /etc/motd
2.准备motd.j2文件
[root@m01 ~]# vim motd.j2
Welcome to {{ ansible_fqdn }}
This system total mem is : {{ ansible_memtotal_mb }} MB
This system free mem is: {{ ansible_memfree_mb }} MB
3.执行playbook
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook jinja2.yml
#查看结果
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web_group -a 'cat /etc/motd'
web01 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Welcome to web01
This system total mem is : 1982 MB
This system free mem is: 1106 MB
web02 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Welcome to web02
This system total mem is : 1982 MB
This system free mem is: 1096 MB
jinja 模板逻辑关系
Nginx
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_nginx.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 80
- server_name: www.oldboyedu.com
tasks:
- name: Copy Nginx COnfigure
template:
src: ./oldboyedu.conf.j2 dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/oldboyedu_proxy.conf
[root@m01 project2]# cat oldboyedu.conf.j2
upstream {{ server_name }} {
{% for i in range(1,20) %}
server 172.16.1.{{i}}:{{http_port}};
{%endfor%}
}
server {
listen {{ http_port }};
server_name {{ server_name }};
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{ server_name }};
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}
配置keepalived配置文件
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_keepalived.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Copy Keepalived Configure
template:
src: ./kee.conf.j2
dest: /tmp/keepalived.conf
[root@m01 project2]# cat kee.conf.j2
global_defs {
router_id {{ ansible_hostname }}
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
{%if ansible_hostname =="web01" %}
state MASTER
priority 150
{%elif ansible_hostname == "web02" %}
state BACKUP
priority 100
{%endif%}
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 50
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3
}
}
mysql剧本模块
数据库模块
- name: Create Database User
mysql_user:
name: autumn #创建的用户
password: autumn123.com #创建用户的密码
priv: '*.*:ALL,GRANT' #授权用户
host: '%' #授权的网段
state: present #创建
- name: Create New Databases
mysql_db: #添加库信息
name:
- wordpress
- phpshe
login_user: root #登录的用户为root
login_port: 3306 #登录的端口
login_host #登录的网段
login_password #登录的密码
state: present #创建
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_mysql.yml
- hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
PORT: 13306
# PORT: false #相当于开关
tasks:
- name: Copy MySQL Configure
template: src=./my.cnf.j2 dest=/tmp/my.cnf
[root@m01 project2]# cat my.cnf.j2
{% if PORT %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:{{ PORT }}
{% else %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:3306
{%endif%}
Roles
概述
roles不管是Ansible还是saltstack,我在写一键部署的时候,都不可能把所有的步骤全部写入到
一个’剧本’文件当中,我们肯定需要把不同的工作模块,拆分开来,解耦,那么说到解耦,我们
就需要用到roles官方推荐,因为roles的目录结构层次更加清晰。
例如:我们之前推荐大家写一个base.yml里面写所有基础优化的项
目,其实把所有东西摞进去也是很鸡肋的,不如我们把这些功能全部拆分开,谁需要使用,就调用即可。
建议:每个roles最好只使用一个tasks这样方便我们去调用,能够很好的做到解耦。(SOA)
Ansible Roles目录结构
[root@m01 ~]# cd /etc/ansible/roles
[root@m01 roles]# mkdir {nfs,rsync,web}/{vars,tasks,template,handlers,files,meta} -p
[root@m01 roles]# tree
.
|── nfs
├── defaults #低优先级变量
├── files #存放文件
├── handlers #触发器文件
├── meta #依赖关系文件
├── tasks #工作任务文件
├── templates #jinja2模板文件
├── tests #测试文件
└── vars #变量文件
Ansible Roles依赖关系
roles允许你再使用roles时自动引入其他的roles。role依赖关系存储在roles目录中meta/main.yml文件中。
例如:推送wordpress并解压,前提条件,必须要安装nginx和php,把服务跑起来,才能运行wordpress的页面,此时我们就可以在wordpress的roles中定义依赖nginx和php的roles
[root@m01 roles]# cat wordpress/meta/main.yml
dependencies:
- role: web_server
when: ansible_hostname is match "web"
- role: php_server
when: ansible_hostname is match "web"
- role: mysql_server
when: ansible_hostname is match "db"
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/install.yml
- name: Install NFS-utils Server
yum:
name: nfs-utils
state: present
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/config.yml
- name: Configure Nfs-utils Server
template:
src: ./exports.j2
dest: /etc/exports
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
notify: Restart NFS Server
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/start.yml
- name: Start NFS Server
systemd:
name: nfs
state: started
enabled: yes
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs-client/tasks/main.yml
- name: Mount NFS Server
mount:
path: /opt src=172.16.1.7:/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state: mounted
[root@m01 roles]# cat site.yml
- hosts: web01
roles:
- nfs
- hosts: web02
roles:
- nfs-client
解压模块
- name: 解压压缩包
unarchive:
src: wordpress.tar.gz
dest: /code
owner: www
group: www
creates: /code/wordpress 如果存在就不解压
数据库模块
- name: 创建数据库表文件
mysql_db:
name:
- wordpress
- phpshe
login_user: root
login_port: 3306
state: present
- name: 创建数据库用户
mysql_user:
name: autumn
password: autumn123.com
priv: `*.*ALL,GRANT`
host: `%`
state: present
配置phpmyadmin
tasks目录
[root@m01 roles]# cat phpmyadmin/tasks/main.yml
- name: Configure PhpMyadmin
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
loop:
- { src: php.ini,dest: /etc/php.ini }
- { src: www.conf,dest: /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf }
notify: Restart PHP
- name: Create Code Dir
file:
path: /code
state: directory
- name: Configure PhpMyadmin Server
unarchive:
src: phpmyadmin.tar.gz
dest: /code
owner: www
group: www
creates: /code/myadmin
- name: Configure PhpMyadmin Conf
template:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
loop:
- { src: myadmin.oldboy.com.conf ,dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/myadmin.oldboy.com.conf }
- { src: nginx.conf,dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf }
notify: Restart Nginx
- name: Check Nginx
shell: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
register: result
- name: Start Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Start PHP-FPM
systemd:
name: php-fpm
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Create Dir
file:
path: /server/script
state: directory
recurse: yes
- name: Configure Push Script
template:
src: client_push_data.sh
dest: /server/script/client_push_data.sh
- name: Cron Push Script
cron:
name: "push backup"
minute: "*/5"
job: "sh /server/script/client_push_data.sh > /dev/null"
j2目录
[root@m01 roles]# ll phpmyadmin/templates/
total 12
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 793 Apr 19 16:37 client_push_data.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 275 Apr 20 17:38 myadmin.oldboy.com.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 639 Mar 27 15:31 nginx.conf
files目录
[root@m01 roles]# ll phpmyadmin/files
total 13584
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 62688 Apr 20 19:52 php.ini
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13822582 Apr 20 15:27 phpmyadmin.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17964 Apr 20 12:05 www.conf