第十八章总结 Swing程序设计
18.1 Swing概述
Swing 主要用来开发GUI(Graphical User Interface)程序,GUI是应用程序提供给用户操作的图形界面,包括窗口、菜单、按钮等图形界面元素,我们经常使用的QQ软件、360安全卫士等均为 GUI
第一代GUI框架AWT 程序。Java 语言为Swing程序的开发提供了丰富的类库,这些类分别被存储在java.awt和javax.swing
收率等不及一些其他流行术也逐渐被广大开发人包中。Swing 提供了丰富的组件,在开发Swing程序时,这些组件被广泛地应用。 Swing组件是完全由Java语言编写的组件。因为Java语言不依赖于本地平台(即“操作系统”),
所以Swing组件可以被应用于任何平台。基于“跨平台”这一特性,Swing组件被称作“轻量级组件”;
对象、接口事件等方面 反之,依赖于本地平台的组件被称作“重量级组件”,
在Swing包的层次结构和继承关系中,比较重要的类是Component类(组件)、Container类(容器类)和JComponent类(Swing组件父类)。Swing包的层次结构和继承关系如图18.1所示。
不会深入地讲解Swing
18.2 Swing常用窗体
18.2.1 JFrame
开发Swing程序的流程可以被简单地概括为首先通过继承java.swing.JFrame类创建一个窗体,然后向这个窗体中添加组件,最后为添加的组件设置监听事件。下面将详细讲解JFrame窗体的使用方法。 JFrame类的常用构造方法包括以下两种形式:
☑public JFrame):创建一个初始不可见、没有标题的窗体。
☑public JFrame(String title):创建一个不可见、具有标题的窗体。
例如,创建一个不可见、具有标题的窗体,关键代码如下:
JFrame jf = new JFrame("登录系统");
Container container = jf.getContentPane();
在创建窗体后,先调用getContentPane()方法将窗体转换为容器,再调用add()方法或者remove()方法向容器中添加组件或者删除容器中的组件。向容器中添加按钮,关键代码如下:
JButton okBtn = new JButton("确定")
container.add(okBtn);
删除容器中的按钮,关键代码如下:
container.remove(okBtn);
创建窗体后,要对窗体进行设置,如设置窗体的位置、大小、是否可见等。JFrame类提供的相应方法可实现上述设置操作,具体如下:
setBounds(intx, inty, int width, int leight):设置窗体左上角在屏幕中的坐标为(x,y),窗体的宽
度为 width,窗体的高度为height。
☑setLocation(int x,inty):设置窗体左上角在屏幕中的坐标为(x,y)。
☑setSize(intwidth,int height):设置窗体的宽度为width,高度为height。
☑setVisibale(boolean b):设置窗体是否可见。b为true时,表示可见:b为false时,表示不可见。☑setDefaultCloseOperation(int operation):设置窗体的关闭方式,默认值为DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE。
Java 语言提供了多种窗体的关闭方式,常用的有4种,如表18.2所示。
import java.awt.Container;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
public class JFreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
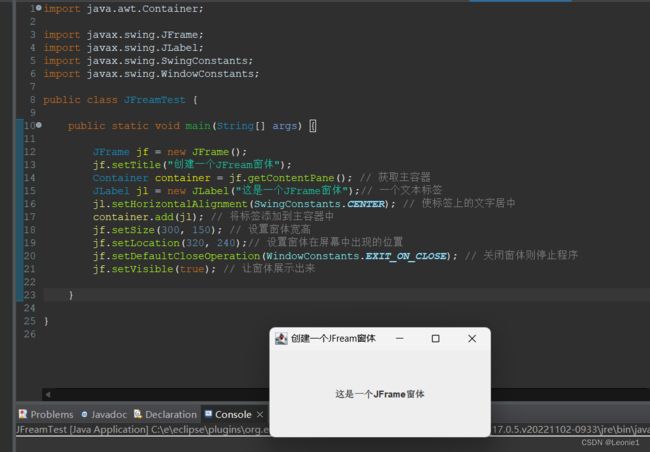
JFrame jf = new JFrame();
jf.setTitle("创建一个JFream窗体");
Container container = jf.getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
JLabel jl = new JLabel("这是一个JFrame窗体");// 一个文本标签
jl.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER); // 使标签上的文字居中
container.add(jl); // 将标签添加到主容器中
jf.setSize(300, 150); // 设置窗体宽高
jf.setLocation(320, 240);// 设置窗体在屏幕中出现的位置
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗体则停止程序
jf.setVisible(true); // 让窗体展示出来
}
} 18.2.2 JDialog对话框
18.2.2 JDialog对话框
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
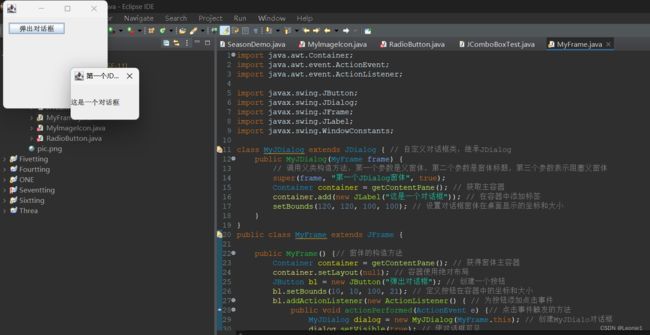
class MyJDialog extends JDialog { // 自定义对话框类,继承JDialog
public MyJDialog(MyFrame frame) {
// 调用父类构造方法,第一个参数是父窗体,第二个参数是窗体标题,第三个参数表示阻塞父窗体
super(frame, "第一个JDialog窗体", true);
Container container = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
container.add(new JLabel("这是一个对话框")); // 在容器中添加标签
setBounds(120, 120, 100, 100); // 设置对话框窗体在桌面显示的坐标和大小
}
}
public class MyFrame extends JFrame {
public MyFrame() {// 窗体的构造方法
Container container = getContentPane(); // 获得窗体主容器
container.setLayout(null); // 容器使用绝对布局
JButton bl = new JButton("弹出对话框"); // 创建一个按钮
bl.setBounds(10, 10, 100, 21); // 定义按钮在容器中的坐标和大小
bl.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 为按钮添加点击事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {// 点击事件触发的方法
MyJDialog dialog = new MyJDialog(MyFrame.this); // 创建MyJDialo对话框
dialog.setVisible(true); // 使对话框可见
}
});
container.add(bl); // 将按钮添加到容器中
setSize(200, 200); // 窗体的宽高
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗体则停止程序
setVisible(true); // 使窗体可见
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new MyFrame();
}
}
18.2.3 JOptionPane小型对话框
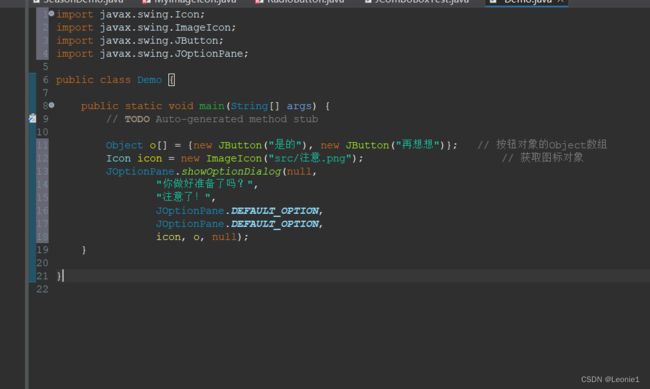
1.自定义对话框
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Object o[] = {new JButton("是的"), new JButton("再想想")}; // 按钮对象的Object数组
Icon icon = new ImageIcon("src/注意.png"); // 获取图标对象
JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null,
"你做好准备了吗?",
"注意了!",
JOptionPane.DEFAULT_OPTION,
JOptionPane.DEFAULT_OPTION,
icon, o, null);
}
}2.确认框
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int answer = JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,
"确定离开吗?",
"标题",
JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION);
}
}
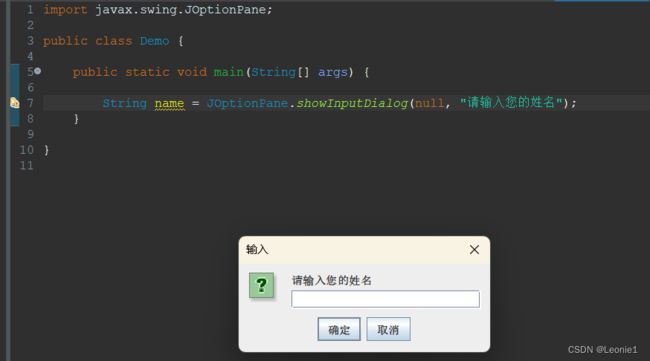
3.输入框
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "请输入您的姓名");
}
}
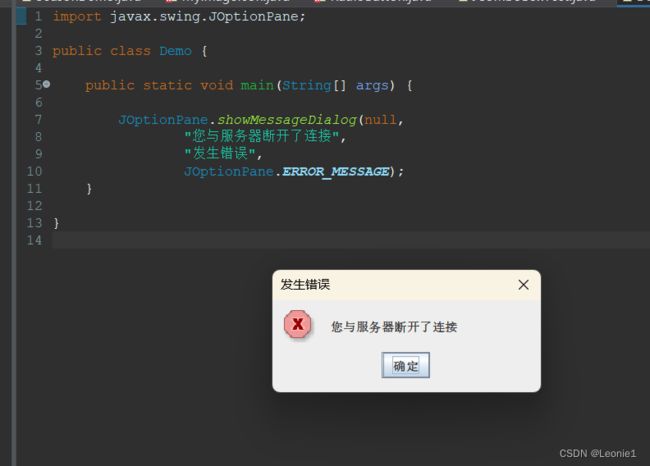
4.通知框
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"您与服务器断开了连接",
"发生错误",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
}
18.3常用布局管理器
18.3.1 null绝对布局
import java.awt.Container;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
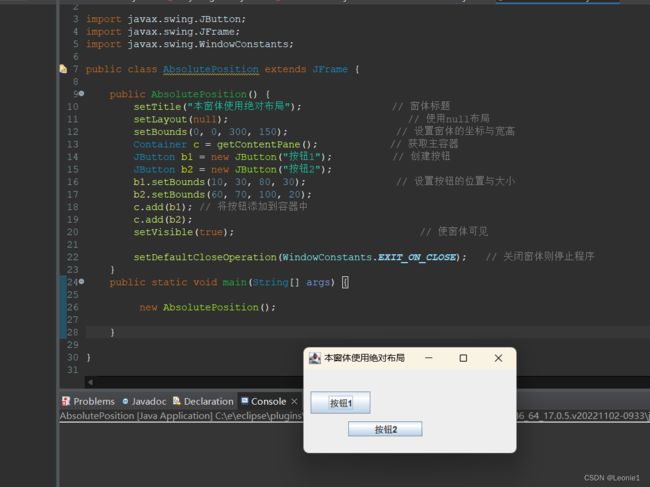
public class AbsolutePosition extends JFrame {
public AbsolutePosition() {
setTitle("本窗体使用绝对布局"); // 窗体标题
setLayout(null); // 使用null布局
setBounds(0, 0, 300, 150); // 设置窗体的坐标与宽高
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
JButton b1 = new JButton("按钮1"); // 创建按钮
JButton b2 = new JButton("按钮2");
b1.setBounds(10, 30, 80, 30); // 设置按钮的位置与大小
b2.setBounds(60, 70, 100, 20);
c.add(b1); // 将按钮添加到容器中
c.add(b2);
setVisible(true); // 使窗体可见
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗体则停止程序
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new AbsolutePosition();
}
}18.3.2 FlowLayout流布局管理器
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FlowLayoutPosition extends JFrame {
public FlowLayoutPosition() {
setTitle("本窗体使用流布局管理器"); // 设置窗体标题
Container c = getContentPane();
// 窗体使用流布局,组件右对齐,组件之间的水平间隔为10像素,垂直间隔10像素
setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT, 10, 10));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 在容器中循环添加10个按钮
c.add(new JButton("button" + i));
}
setSize(300, 200); // 设置窗体大小
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗体则停止程序
setVisible(true); // 设置窗体可见
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FlowLayoutPosition();
}
}
18.3.3 BorderLayout边界布局管理器
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
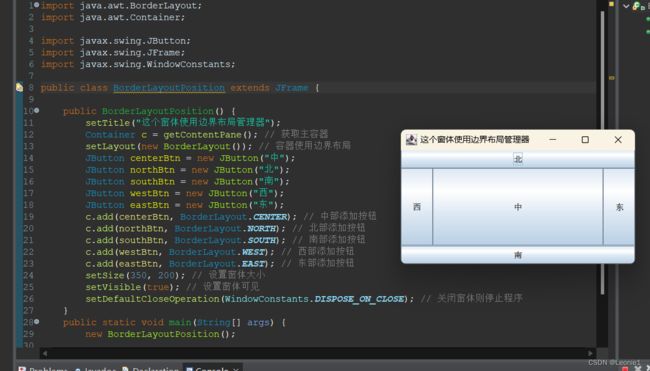
public class BorderLayoutPosition extends JFrame {
public BorderLayoutPosition() {
setTitle("这个窗体使用边界布局管理器");
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // 容器使用边界布局
JButton centerBtn = new JButton("中");
JButton northBtn = new JButton("北");
JButton southBtn = new JButton("南");
JButton westBtn = new JButton("西");
JButton eastBtn = new JButton("东");
c.add(centerBtn, BorderLayout.CENTER); // 中部添加按钮
c.add(northBtn, BorderLayout.NORTH); // 北部添加按钮
c.add(southBtn, BorderLayout.SOUTH); // 南部添加按钮
c.add(westBtn, BorderLayout.WEST); // 西部添加按钮
c.add(eastBtn, BorderLayout.EAST); // 东部添加按钮
setSize(350, 200); // 设置窗体大小
setVisible(true); // 设置窗体可见
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗体则停止程序
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BorderLayoutPosition();
}
}18.3.4 GridLayout网格布局管理器
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
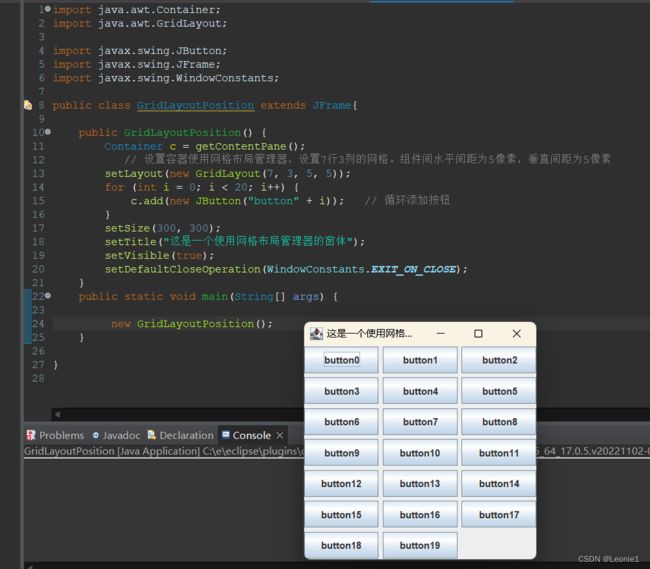
public class GridLayoutPosition extends JFrame {
public GridLayoutPosition() {
Container c = getContentPane();
// 设置容器使用网格布局管理器,设置7行3列的网格。组件间水平间距为5像素,垂直间距为5像素
setLayout(new GridLayout(7, 3, 5, 5));
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
c.add(new JButton("button" + i)); // 循环添加按钮
}
setSize(300, 300);
setTitle("这是一个使用网格布局管理器的窗体");
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new GridLayoutPosition();
}
}18.4 常用面板
18.4.1JPanbel面板
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.BorderFactory;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
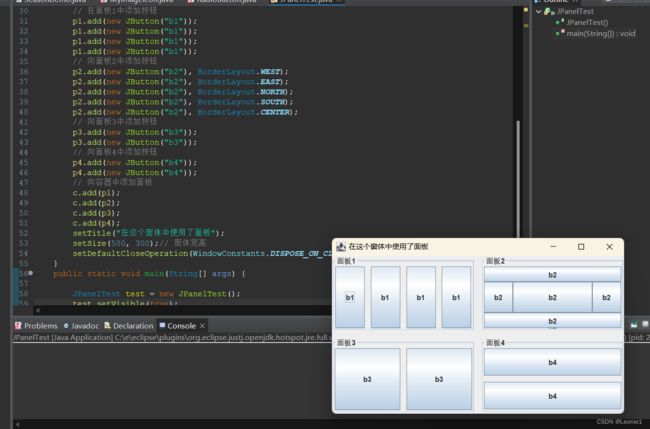
public class JPanelTest extends JFrame {
public JPanelTest() {
Container c = getContentPane();
// 将整个容器设置为2行2列的网格布局,组件水平间隔10像素,垂直间隔10像素
c.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2, 10, 10));
// 初始化一个面板,此面板使用1行4列的网格布局,组件水平间隔10像素,垂直间隔10像素
JPanel p1 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1, 4, 10, 10));
// 初始化一个面板,此面板使用边界布局
JPanel p2 = new JPanel(new BorderLayout());
// 初始化一个面板,此面板使用1行2列的网格布局,组件水平间隔10像素,垂直间隔10像素
JPanel p3 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1, 2, 10, 10));
// 初始化一个面板,此面板使用2行1列的网格布局,组件水平间隔10像素,垂直间隔10像素
JPanel p4 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(2, 1, 10, 10));
// 给每个面板都添加边框和标题,使用BorderFactory工厂类生成带标题的边框对象
p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("面板1"));
p2.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("面板2"));
p3.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("面板3"));
p4.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("面板4"));
// 在面板1中添加按钮
p1.add(new JButton("b1"));
p1.add(new JButton("b1"));
p1.add(new JButton("b1"));
p1.add(new JButton("b1"));
// 向面板2中添加按钮
p2.add(new JButton("b2"), BorderLayout.WEST);
p2.add(new JButton("b2"), BorderLayout.EAST);
p2.add(new JButton("b2"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
p2.add(new JButton("b2"), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
p2.add(new JButton("b2"), BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 向面板3中添加按钮
p3.add(new JButton("b3"));
p3.add(new JButton("b3"));
// 向面板4中添加按钮
p4.add(new JButton("b4"));
p4.add(new JButton("b4"));
// 向容器中添加面板
c.add(p1);
c.add(p2);
c.add(p3);
c.add(p4);
setTitle("在这个窗体中使用了面板");
setSize(500, 300);// 窗体宽高
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭动作
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JPanelTest test = new JPanelTest();
test.setVisible(true);
}
}18.4.2JScrollPane滚动面板
import java.awt.Container;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
public class JScrollPaneTest extends JFrame {
public JScrollPaneTest() {
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
// 创建文本区域组件,文本域默认大小为20行、50列
JTextArea ta = new JTextArea(20, 50);
// 创建JScrollPane滚动面板,并将文本域放到滚动面板中
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(ta);
c.add(sp); // 将该面板添加到主容器中
setTitle("带滚动条的文字编译器");
setSize(400, 200);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JScrollPaneTest test = new JScrollPaneTest();
test.setVisible(true);
}
}18.5 文字标签组件与图标
18.5.1JLabel标签
import java.awt.Container;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
public class JLabelTest extends JFrame {
public JLabelTest() {
Container container = getContentPane();
// 创建一个标签
JLabel jl = new JLabel("这是一个JFrame窗体");
container.add(jl); // 将标签添加到容器中
setSize(200, 100); // 设置窗体大小
// 设置窗体关闭模式
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true); // 使窗体可见
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new JLabelTest(); // 创建MyImageIcon对象
}
}18.5.2图标的使用
import java.awt.Container;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
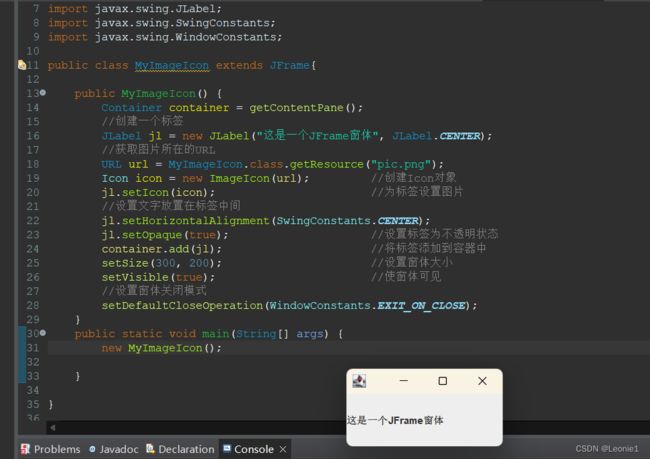
public class MyImageIcon extends JFrame {
public MyImageIcon() {
Container container = getContentPane();
//创建一个标签
JLabel jl = new JLabel("这是一个JFrame窗体", JLabel.CENTER);
//获取图片所在的URL
URL url = MyImageIcon.class.getResource("pic.png");
Icon icon = new ImageIcon(url); //创建Icon对象
jl.setIcon(icon); //为标签设置图片
//设置文字放置在标签中间
jl.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
jl.setOpaque(true); //设置标签为不透明状态
container.add(jl); //将标签添加到容器中
setSize(300, 200); //设置窗体大小
setVisible(true); //使窗体可见
//设置窗体关闭模式
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new MyImageIcon(); //创建MyImageIcon对象
}
}18.6 按钮组件
18.6.1JButton按钮
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
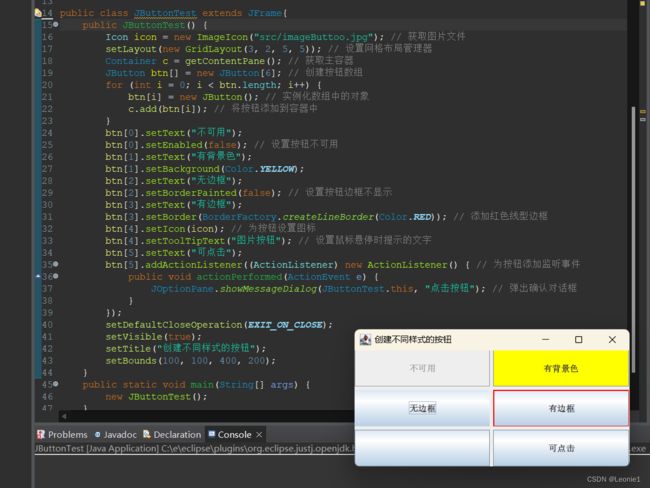
public class JButtonTest extends JFrame {
public JButtonTest() {
Icon icon = new ImageIcon("src/imageButtoo.jpg"); // 获取图片文件
setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2, 5, 5)); // 设置网格布局管理器
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
JButton btn[] = new JButton[6]; // 创建按钮数组
for (int i = 0; i < btn.length; i++) {
btn[i] = new JButton(); // 实例化数组中的对象
c.add(btn[i]); // 将按钮添加到容器中
}
btn[0].setText("不可用");
btn[0].setEnabled(false); // 设置按钮不可用
btn[1].setText("有背景色");
btn[1].setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
btn[2].setText("无边框");
btn[2].setBorderPainted(false); // 设置按钮边框不显示
btn[3].setText("有边框");
btn[3].setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.RED)); // 添加红色线型边框
btn[4].setIcon(icon); // 为按钮设置图标
btn[4].setToolTipText("图片按钮"); // 设置鼠标悬停时提示的文字
btn[5].setText("可点击");
btn[5].addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 为按钮添加监听事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(JButtonTest.this, "点击按钮"); // 弹出确认对话框
}
});
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
setTitle("创建不同样式的按钮");
setBounds(100, 100, 400, 200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonTest();
}
}18.6.2JRadioButton单选按钮
import javax.swing.*;
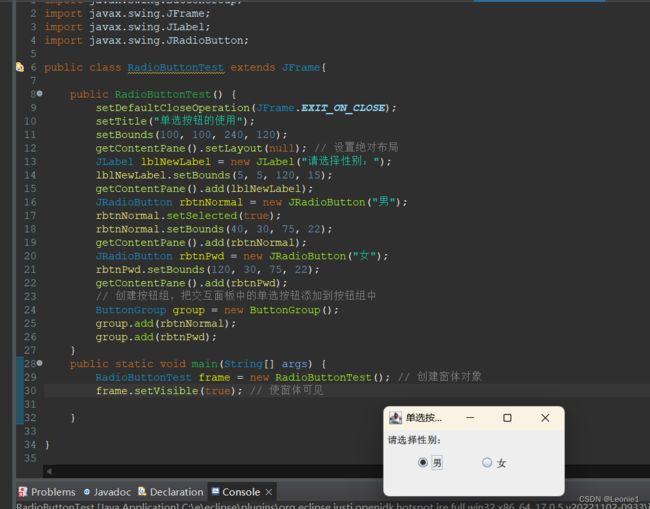
public class RadioButtonTest extends JFrame {
public RadioButtonTest() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setTitle("单选按钮的使用");
setBounds(100, 100, 240, 120);
getContentPane().setLayout(null); // 设置绝对布局
JLabel lblNewLabel = new JLabel("请选择性别:");
lblNewLabel.setBounds(5, 5, 120, 15);
getContentPane().add(lblNewLabel);
JRadioButton rbtnNormal = new JRadioButton("男");
rbtnNormal.setSelected(true);
rbtnNormal.setBounds(40, 30, 75, 22);
getContentPane().add(rbtnNormal);
JRadioButton rbtnPwd = new JRadioButton("女");
rbtnPwd.setBounds(120, 30, 75, 22);
getContentPane().add(rbtnPwd);
// 创建按钮组,把交互面板中的单选按钮添加到按钮组中
ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup();
group.add(rbtnNormal);
group.add(rbtnPwd);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RadioButtonTest frame = new RadioButtonTest(); // 创建窗体对象
frame.setVisible(true); // 使窗体可见
}
}
18.6.3JCheckBox复选框
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JCheckBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
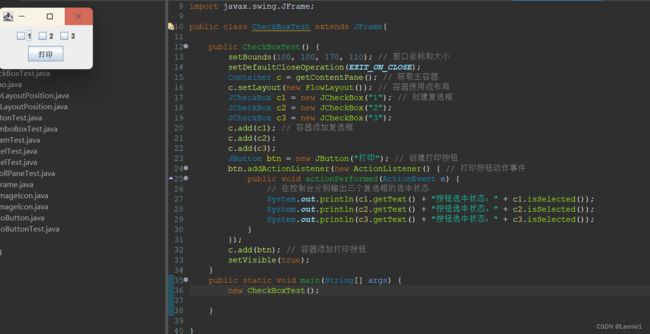
public class CheckBoxTest extends JFrame {
public CheckBoxTest() {
setBounds(100, 100, 170, 110); // 窗口坐标和大小
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取主容器
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); // 容器使用流布局
JCheckBox c1 = new JCheckBox("1"); // 创建复选框
JCheckBox c2 = new JCheckBox("2");
JCheckBox c3 = new JCheckBox("3");
c.add(c1); // 容器添加复选框
c.add(c2);
c.add(c3);
JButton btn = new JButton("打印"); // 创建打印按钮
btn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 打印按钮动作事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 在控制台分别输出三个复选框的选中状态
System.out.println(c1.getText() + "按钮选中状态:" + c1.isSelected());
System.out.println(c2.getText() + "按钮选中状态:" + c2.isSelected());
System.out.println(c3.getText() + "按钮选中状态:" + c3.isSelected());
}
});
c.add(btn); // 容器添加打印按钮
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new CheckBoxTest();
}
}18.7 列表组件
18.7.1JComboBox下拉列表框
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
public class JComboBoxTest extends JFrame {
public JComboBoxTest() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setTitle("下拉列表框的使用");
setBounds(100, 100, 317, 147);
getContentPane().setLayout(null); // 设置绝对布局
JLabel lblNewLabel = new JLabel("请选择证件:");
lblNewLabel.setBounds(28, 14, 80, 15);
getContentPane().add(lblNewLabel);
JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox(); // 创建一个下拉列表框
comboBox.setBounds(110, 11, 80, 21); // 设置坐标
comboBox.addItem("身份证"); // 为下拉列表中添加项
comboBox.addItem("军人证");
comboBox.addItem("学生证");
comboBox.addItem("工作证");
comboBox.setEditable(true);
getContentPane().add(comboBox); // 将下拉列表添加到容器中
JLabel lblResult = new JLabel("");
lblResult.setBounds(0, 57, 146, 15);
getContentPane().add(lblResult);
JButton btnNewButton = new JButton("确定");
btnNewButton.setBounds(200, 10, 67, 23);
getContentPane().add(btnNewButton);
btnNewButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 为按钮添加监听事件
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
// 获取下拉列表中的选中项
lblResult.setText("您选择的是:" + comboBox.getSelectedItem());
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JComboBoxTest frame = new JComboBoxTest(); // 创建窗体对象
frame.setVisible(true); // 使窗体可见
}
} 
18.7.2JList列表框
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JListTest extends JFrame {
public JListTest() {
Container cp = getContentPane(); // 获取窗体主容器
cp.setLayout(null); // 容器使用绝对布局
// 创建字符串数组,保存列表的中的数据
String[] contents = { "列表1", "列表2", "列表3", "列表4", "列表5", "列表6" };
JList jl = new JList<>(contents); // 创建列表,并将数据作为构造参数
JScrollPane js = new JScrollPane(jl); // 将列表放入滚动面板
js.setBounds(10, 10, 100, 109); // 设定滚动面板的坐标和大小
cp.add(js);
JTextArea area = new JTextArea(); // 创建文本域
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(area); // 将文本域放入滚动面板
scrollPane.setBounds(118, 10, 73, 80); // 设定滚动面板的坐标和大小
cp.add(scrollPane);
JButton btnNewButton = new JButton("确认"); // 创建确认按钮
btnNewButton.setBounds(120, 96, 71, 23); // 设定按钮的坐标和大小
cp.add(btnNewButton);
btnNewButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 添加按钮事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 获取列表中选中的元素,返回java.util.List类型
java.util.List values = jl.getSelectedValuesList();
area.setText(""); // 清空文本域
for (String value : values) {
area.append(value + "\n"); // 在文本域循环追加List中的元素值
}
}
});
setTitle("在这个窗体中使用了列表框");
setSize(217, 167);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new JListTest();
}
}
18.8 文本组件
18.8.1JTextField文本框
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
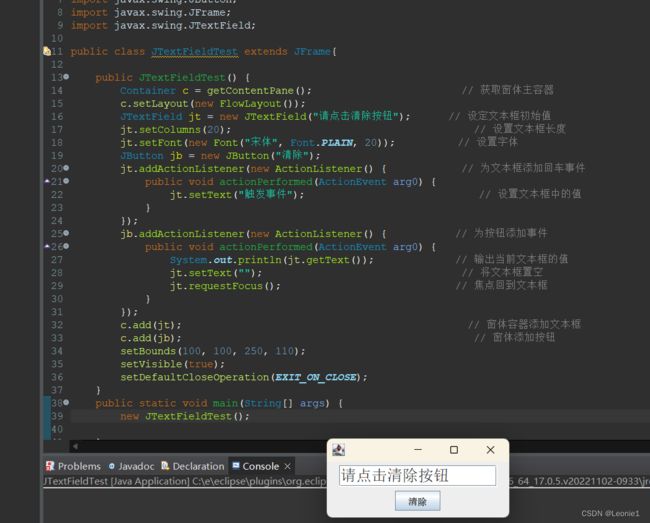
public class JTextFieldTest extends JFrame {
public JTextFieldTest() {
Container c = getContentPane(); // 获取窗体主容器
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JTextField jt = new JTextField("请点击清除按钮"); // 设定文本框初始值
jt.setColumns(20); // 设置文本框长度
jt.setFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 20)); // 设置字体
JButton jb = new JButton("清除");
jt.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 为文本框添加回车事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
jt.setText("触发事件"); // 设置文本框中的值
}
});
jb.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { // 为按钮添加事件
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
System.out.println(jt.getText()); // 输出当前文本框的值
jt.setText(""); // 将文本框置空
jt.requestFocus(); // 焦点回到文本框
}
});
c.add(jt); // 窗体容器添加文本框
c.add(jb); // 窗体添加按钮
setBounds(100, 100, 250, 110);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JTextFieldTest();
}
}18.8.2JPasswordField密码框
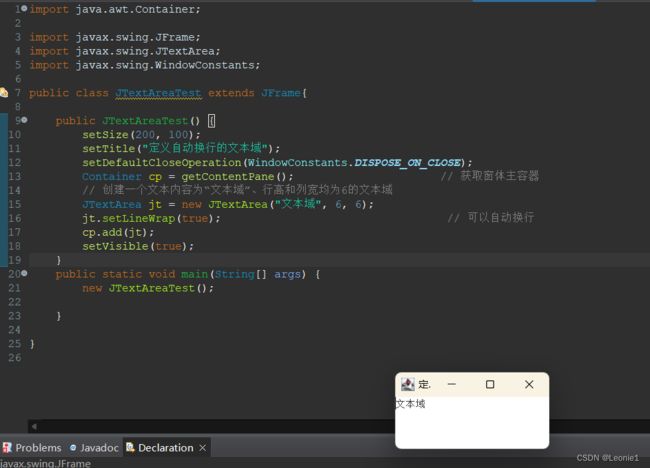
18.8.3JTextArea文本域
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JTextAreaTest extends JFrame {
public JTextAreaTest() {
setSize(200, 100);
setTitle("定义自动换行的文本域");
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
Container cp = getContentPane(); // 获取窗体主容器
// 创建一个文本内容为“文本域”、行高和列宽均为6的文本域
JTextArea jt = new JTextArea("文本域", 6, 6);
jt.setLineWrap(true); // 可以自动换行
cp.add(jt);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JTextAreaTest();
}
}
18.9 表格组件
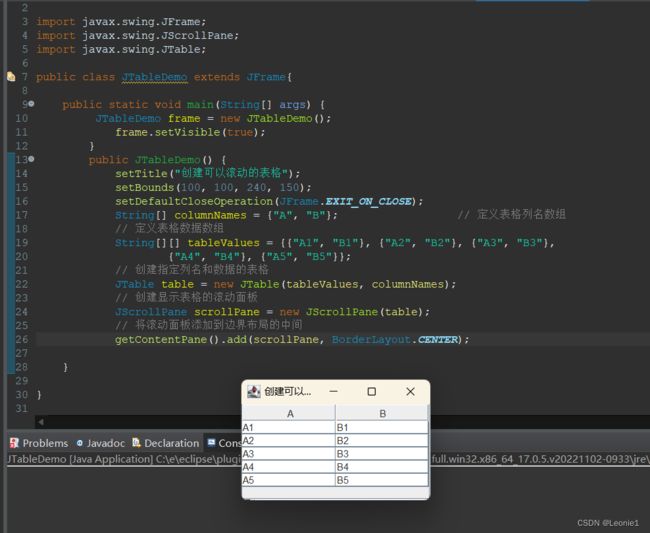
18.9.1创建表格
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JTableDemo extends JFrame {
public static void main(String args[]) {
JTableDemo frame = new JTableDemo();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public JTableDemo() {
setTitle("创建可以滚动的表格");
setBounds(100, 100, 240, 150);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
String[] columnNames = {"A", "B"}; // 定义表格列名数组
// 定义表格数据数组
String[][] tableValues = {{"A1", "B1"}, {"A2", "B2"}, {"A3", "B3"},
{"A4", "B4"}, {"A5", "B5"}};
// 创建指定列名和数据的表格
JTable table = new JTable(tableValues, columnNames);
// 创建显示表格的滚动面板
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(table);
// 将滚动面板添加到边界布局的中间
getContentPane().add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}18.9.2DefaultTableModel表格数据模型
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
public class SortingTable extends JFrame {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static void main(String args[]) {
SortingTable frame = new SortingTable();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public SortingTable() {
setTitle("表格模型与表格");
setBounds(100, 100, 240, 150);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
getContentPane().add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
String[] columnNames = {"A", "B"}; // 定义表格列名数组
// 定义表格数据数组
String[][] tableValues = {{"A1", "B1"}, {"A2", "B2"}, {"A3", "B3"}};
// 创建指定表格列名和表格数据的表格模型
DefaultTableModel tableModel = new DefaultTableModel(tableValues, columnNames);
JTable table = new JTable(tableModel); // 创建指定表格模型的表格
table.setRowSorter(new TableRowSorter<>(tableModel));
scrollPane.setViewportView(table);
}
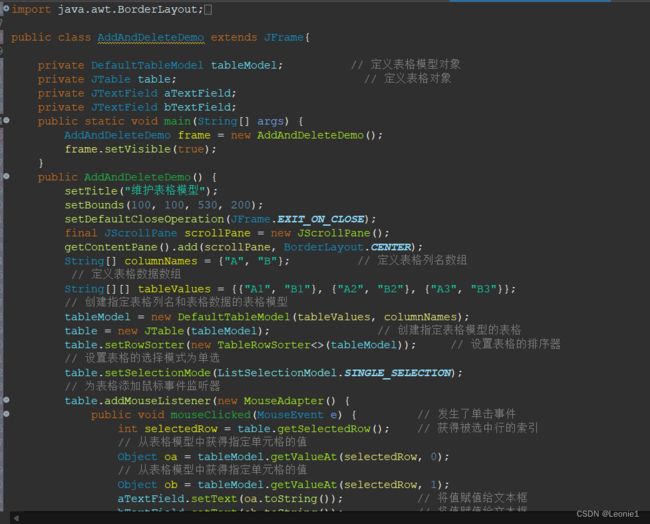
}18.9.3维护表格模型
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
public class AddAndDeleteDemo extends JFrame {
private DefaultTableModel tableModel; // 定义表格模型对象
private JTable table; // 定义表格对象
private JTextField aTextField;
private JTextField bTextField;
public static void main(String args[]) {
AddAndDeleteDemo frame = new AddAndDeleteDemo();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public AddAndDeleteDemo() {
setTitle("维护表格模型");
setBounds(100, 100, 530, 200);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
final JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
getContentPane().add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
String[] columnNames = {"A", "B"}; // 定义表格列名数组
// 定义表格数据数组
String[][] tableValues = {{"A1", "B1"}, {"A2", "B2"}, {"A3", "B3"}};
// 创建指定表格列名和表格数据的表格模型
tableModel = new DefaultTableModel(tableValues, columnNames);
table = new JTable(tableModel); // 创建指定表格模型的表格
table.setRowSorter(new TableRowSorter<>(tableModel)); // 设置表格的排序器
// 设置表格的选择模式为单选
table.setSelectionMode(ListSelectionModel.SINGLE_SELECTION);
// 为表格添加鼠标事件监听器
table.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) { // 发生了单击事件
int selectedRow = table.getSelectedRow(); // 获得被选中行的索引
// 从表格模型中获得指定单元格的值
Object oa = tableModel.getValueAt(selectedRow, 0);
// 从表格模型中获得指定单元格的值
Object ob = tableModel.getValueAt(selectedRow, 1);
aTextField.setText(oa.toString()); // 将值赋值给文本框
bTextField.setText(ob.toString()); // 将值赋值给文本框
}
});
scrollPane.setViewportView(table);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
panel.add(new JLabel("A:"));
aTextField = new JTextField("A4", 10);
panel.add(aTextField);
panel.add(new JLabel("B:"));
bTextField = new JTextField("B4", 10);
panel.add(bTextField);
JButton addButton = new JButton("添加");
addButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String[] rowValues = {aTextField.getText(),
bTextField.getText()}; // 创建表格行数组
tableModel.addRow(rowValues); // 向表格模型中添加一行
int rowCount = table.getRowCount() + 1;
aTextField.setText("A" + rowCount);
bTextField.setText("B" + rowCount);
}
});
panel.add(addButton);
JButton updButton = new JButton("修改");
updButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int selectedRow = table.getSelectedRow(); // 获得被选中行的索引
if (selectedRow != -1) { // 判断是否存在被选中行
// 修改表格模型当中的指定值
tableModel.setValueAt(aTextField.getText(), selectedRow, 0);
// 修改表格模型当中的指定值
tableModel.setValueAt(bTextField.getText(), selectedRow, 1);
}
}
});
panel.add(updButton);
JButton delButton = new JButton("删除");
delButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int selectedRow = table.getSelectedRow(); // 获得被选中行的索引
if (selectedRow != -1) // 判断是否存在被选中行
tableModel.removeRow(selectedRow); // 从表格模型当中删除指定行
}
});
panel.add(delButton);
}
}18.10 事件监听器
18.10.1ActionEvent动作事件
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.WindowConstants;
public class SimpleEvent extends JFrame {
private JButton jb = new JButton("我是按钮,点击我");
public SimpleEvent() {
setLayout(null);
setSize(200, 100);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
Container cp = getContentPane();
cp.add(jb);
jb.setBounds(10, 10, 150, 30);
jb.addActionListener(new jbAction());
setVisible(true);
}
class jbAction implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
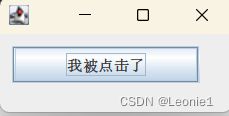
jb.setText("我被点击了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SimpleEvent();
}
}
18.10.2KeyEvent键盘事件
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.border.EmptyBorder;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Component;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import java.awt.Font;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.border.TitledBorder;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
/**
* 虚拟键盘(键盘的按下与释放)
*/
public class KeyBoard extends JFrame { // 创建“键盘”类继承JFrame
// 声明窗体中的成员组件
private JPanel contentPane;
private JTextField textField;
private JButton btnQ;
private JButton btnW;
private JButton btnE;
private JButton btnR;
private JButton btnT;
private JButton btnY;
private JButton btnU;
private JButton btnI;
private JButton btnO;
private JButton btnP;
private JButton btnA;
private JButton btnS;
private JButton btnD;
private JButton btnF;
private JButton btnG;
private JButton btnH;
private JButton btnJ;
private JButton btnK;
private JButton btnL;
private JButton btnZ;
private JButton btnX;
private JButton btnC;
private JButton btnV;
private JButton btnB;
private JButton btnN;
private JButton btnM;
Color green = Color.GREEN;// 定义Color对象,用来表示按下键的颜色
Color white = Color.WHITE;// 定义Color对象,用来表示释放键的颜色
ArrayList btns = new ArrayList();// 定义一个集合,用来存储所有的按键ID
// 自定义一个方法,用来将容器中的所有JButton组件添加到集合中
private void addButtons() {
for (Component cmp : contentPane.getComponents()) {// 遍历面板中的所有组件
if (cmp instanceof JButton) {// 判断组件的类型是否为JButton类型
btns.add((JButton) cmp);// 将JButton组件添加到集合中
}
}
}
/**
* 主方法
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() { // 使得Runnable中的的run()方法在the system EventQueue的指派线程中被调用
public void run() {
try {
KeyBoard frame = new KeyBoard(); // 创建KeyBoard对象
frame.setVisible(true); // 使frame可视
frame.addButtons();// 初始化存储所有按键的集合
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* 创建JFrame窗体
*/
public KeyBoard() { // KeyBoard的构造方法
setTitle("\u865A\u62DF\u952E\u76D8\uFF08\u6A21\u62DF\u952E\u76D8\u7684\u6309\u4E0B\u4E0E\u91CA\u653E\uFF09"); // 设置窗体题目
setResizable(false); // 不可改变窗体宽高
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 设置窗体关闭的方式
setBounds(100, 100, 560, 280); // 设置窗体的位置和宽高
/**
* 创建JPanel面板contentPane置于JFrame窗体中,并设置面板的背景色、边距和布局
*/
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
/**
* 创建按钮button置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnQ = new JButton("Q");
btnQ.setBackground(white);
btnQ.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnQ.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnQ.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnQ.setBounds(0, 60, 47, 45);
contentPane.add(btnQ);
/**
* 创建按钮button_2置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnW = new JButton("W");
btnW.setBackground(white);
btnW.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnW.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnW.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnW.setBounds(55, 60, 49, 45);
contentPane.add(btnW);
/**
* 创建按钮button_3置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnE = new JButton("E");
btnE.setBackground(white);
btnE.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnE.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnE.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnE.setBounds(110, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnE);
/**
* 创建按钮button_4置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnR = new JButton("R");
btnR.setBackground(white);
btnR.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnR.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnR.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnR.setBounds(165, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnR);
/**
* 创建按钮button_5置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnF = new JButton("F");
btnF.setBackground(white);
btnF.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnF.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnF.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnF.setBounds(195, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnF);
/**
* 创建按钮button_6置于面板contentPane中,设置按钮的背景色、位置、宽高以及按钮中的字体位置、内容、样式
*/
btnD = new JButton("D");
btnD.setBackground(white);
btnD.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnD.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnD.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnD.setBounds(137, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnD);
btnT = new JButton("T");
btnT.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnT.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnT.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnT.setBackground(white);
btnT.setBounds(220, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnT);
btnY = new JButton("Y");
btnY.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnY.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnY.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnY.setBackground(white);
btnY.setBounds(275, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnY);
btnU = new JButton("U");
btnU.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnU.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnU.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnU.setBackground(white);
btnU.setBounds(330, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnU);
btnI = new JButton("I");
btnI.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnI.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnI.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnI.setBackground(white);
btnI.setBounds(385, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnI);
btnO = new JButton("O");
btnO.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnO.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnO.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnO.setBackground(white);
btnO.setBounds(440, 60, 46, 45);
contentPane.add(btnO);
btnP = new JButton("P");
btnP.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnP.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnP.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnP.setBackground(white);
btnP.setBounds(495, 60, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnP);
btnA = new JButton("A");
btnA.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnA.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnA.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnA.setBackground(white);
btnA.setBounds(23, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnA);
btnS = new JButton("S");
btnS.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnS.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnS.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnS.setBackground(white);
btnS.setBounds(82, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnS);
btnG = new JButton("G");
btnG.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnG.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnG.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnG.setBackground(white);
btnG.setBounds(251, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnG);
btnH = new JButton("H");
btnH.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnH.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnH.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnH.setBackground(white);
btnH.setBounds(306, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnH);
btnJ = new JButton("J");
btnJ.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnJ.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnJ.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnJ.setBackground(white);
btnJ.setBounds(361, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnJ);
btnK = new JButton("K");
btnK.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnK.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnK.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnK.setBackground(white);
btnK.setBounds(416, 125, 47, 45);
contentPane.add(btnK);
btnL = new JButton("L");
btnL.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnL.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnL.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnL.setBackground(white);
btnL.setBounds(471, 125, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnL);
btnZ = new JButton("Z");
btnZ.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnZ.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnZ.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnZ.setBackground(white);
btnZ.setBounds(39, 190, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnZ);
btnX = new JButton("X");
btnX.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnX.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnX.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnX.setBackground(white);
btnX.setBounds(107, 190, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnX);
btnC = new JButton("C");
btnC.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnC.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnC.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnC.setBackground(white);
btnC.setBounds(178, 190, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnC);
btnV = new JButton("V");
btnV.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnV.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnV.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnV.setBackground(white);
btnV.setBounds(250, 190, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnV);
btnB = new JButton("B");
btnB.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnB.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnB.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnB.setBackground(white);
btnB.setBounds(315, 190, 45, 45);
contentPane.add(btnB);
btnN = new JButton("N");
btnN.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnN.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnN.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnN.setBackground(white);
btnN.setBounds(382, 190, 47, 45);
contentPane.add(btnN);
btnM = new JButton("M");
btnM.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
btnM.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.LEADING);
btnM.setFont(new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, 14));
btnM.setBackground(white);
btnM.setBounds(449, 190, 48, 45);
contentPane.add(btnM);
/**
* 创建面板panel置于面板contentPane中,设置面板panel的位置、宽高、TitledBorder、背景色以及布局方式(边界布局)
*/
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.setBorder(new TitledBorder(null, "文本显示区", TitledBorder.LEADING, TitledBorder.TOP, null, null));
panel.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
panel.setBounds(0, 0, 540, 45);
contentPane.add(panel);
panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout(0, 0));
/**
* 创建文本框textField置于面板panel的中间
*/
textField = new JTextField();
textField.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() { // 文本框添加键盘事件的监听
char word;
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) { // 按键被按下时被触发
word = e.getKeyChar();// 获取按下键表示的字符
for (int i = 0; i < btns.size(); i++) {// 遍历存储按键ID的ArrayList集合
// 判断按键是否与遍历到的按键的文本相同
if (String.valueOf(word).equalsIgnoreCase(btns.get(i).getText())) {
btns.get(i).setBackground(green);// 将指定按键颜色设置为绿色
}
}
}
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) { // 按键被释放时被触发
word = e.getKeyChar();// 获取释放键表示的字符
for (int i = 0; i < btns.size(); i++) {// 遍历存储按键ID的ArrayList集合
// 判断按键是否与遍历到的按键的文本相同
if (String.valueOf(word).equalsIgnoreCase(btns.get(i).getText())) {
btns.get(i).setBackground(white);// 将指定按键颜色设置为白色
}
}
}
});
panel.add(textField, BorderLayout.CENTER);
textField.setColumns(10);
}
} ......
18.10.3MouseEvent鼠标事件
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
public class MouseEventDemo extends JFrame { // 继承窗体类JFrame
public static void main(String args[]) {
MouseEventDemo frame = new MouseEventDemo();
frame.setVisible(true); // 设置窗体可见,默认为不可见
}
/**
* 判断按下的鼠标键,并输出相应提示
*
* @param e 鼠标事件
*/
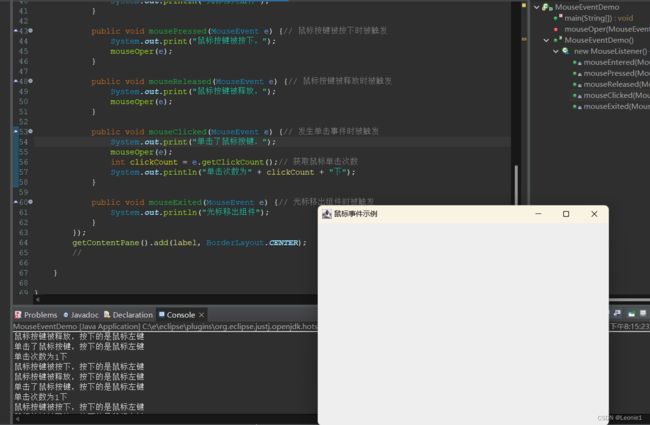
private void mouseOper(MouseEvent e) {
int i = e.getButton(); // 通过该值可以判断按下的是哪个键
if (i == MouseEvent.BUTTON1)
System.out.println("按下的是鼠标左键");
else if (i == MouseEvent.BUTTON2)
System.out.println("按下的是鼠标滚轮");
else if (i == MouseEvent.BUTTON3)
System.out.println("按下的是鼠标右键");
}
public MouseEventDemo() {
super(); // 继承父类的构造方法
setTitle("鼠标事件示例"); // 设置窗体的标题
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 375); // 设置窗体的显示位置及大小
// 设置窗体关闭按钮的动作为退出
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
final JLabel label = new JLabel();
label.addMouseListener(new MouseListener() {
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {// 光标移入组件时被触发
System.out.println("光标移入组件");
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {// 鼠标按键被按下时被触发
System.out.print("鼠标按键被按下,");
mouseOper(e);
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {// 鼠标按键被释放时被触发
System.out.print("鼠标按键被释放,");
mouseOper(e);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {// 发生单击事件时被触发
System.out.print("单击了鼠标按键,");
mouseOper(e);
int clickCount = e.getClickCount();// 获取鼠标单击次数
System.out.println("单击次数为" + clickCount + "下");
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {// 光标移出组件时被触发
System.out.println("光标移出组件");
}
});
getContentPane().add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);
//
}
}