ThreadLocal原理、内存泄漏以及TransmittableThreadLocal说明
1、线程、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap关系
以下是Thread类的部分全局变量
//普通的线程本地变量表(key:ThreadLocal,value:需要保存的变量),只支持在当前线程上下文中获取set过的值
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
//可以在父子线程中传递值的线程本地变量(key:InheritableThreadLocal,value:需要保存的变量),其原理会在后面解释
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
Thread -> ThreadLocal -> ThreadLocalMap
每个线程都会有一个本地变量表,这个表就是ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类,会在初始化ThreadLocal完成,并且set值的时候初始化,获取在get的时候初始化(此时会返回一个null值)
以下是
ThreadLocal调用set方法的代码块
public void set(T value) {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//拿到当前的全局变量 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
//设置值,取当前ThreadLocal的 hashcode % table.size()
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//取当前ThreadLocal的 hashcode % Entry数组的大小
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
//******注意:这里直接覆盖原始值,不会解决hash冲突******
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
以下是
ThreadLocal调用get方法的代码块
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//取当前ThreadLocal的 hashcode % table.size(),得到Entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
//和set方法逻辑类似,只是多了一个initialValue操作
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
//
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
2 、可以在父子线程传递变量的 ThreaLocal —— InheritableThreadLocal
2.1 继承关系
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
//实现父类的抽象方法
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
//重写父类的方法
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
//重写父类的方法
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
2.2 大概描述
- 线程在启动创建的时候,会检查父线程inheritableThreadLocals(ThreadLocalMap)是否为空,如果不为空,说明在父线程里面创建了可以在父子线程传递的线程本地变量
- 此时子线程在初始化的时候,会去初始化自己的inheritableThreadLocals
- 子线程拿到父线程的inheritableThreadLocals(ThreadLocalMap)循环遍历将不为空的Entry塞到当前线程中
- 父子线程完成变量传递
2.3 源码分析
new Thread(() -> {}).start();
public Thread(Runnable target) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize) {
init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true);
}
//****** 注意inheritThreadLocals变量,默认为true -> 默认需要初始化inheritableThreadLocals变量(即可以在父子线程传递变量的ThreadLocal)
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
/* Determine if it's an applet or not */
/* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
what to do. */
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
/* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter
use the parent thread group. */
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
/* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
explicitly passed in. */
g.checkAccess();
/*
* Do we have the required permissions?
*/
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
// **** 检查父线程inheritableThreadLocals(ThreadLocalMap)是否为空 ****
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
/* Set thread ID */
tid = nextThreadID();
}
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
//拿到父线程的Entry数组(实际存储value的地方)
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
//初始化和父线程一样大小的Entry数组
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
//找出不为null的Entry
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();
if (key != null) {
//此时key为InheritableThreadLocal,实现了ThreadLocal中定义的抽象方法 childValue
Object value = key.childValue(e.value);
//封装一个父类有相同key 和 value Entry
Entry c = new Entry(key, value);
int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
while (table[h] != null)
//一直从下标 h 开始寻找第一个空的节点,用这种方法解决hash冲突
h = nextIndex(h, len);
//赋值到自己(子线程)变量表中
table[h] = c;
size++;
}
}
}
}
3 分析ThreadLocalMap key 内存泄漏问题
3.1 强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用的关系
- 强引用是使用最普遍的引用。如果一个对象具有强引用,那垃圾回收器绝不会回收它。当内存空间不足,Java虚拟机宁愿抛出OutOfMemoryError错误,使程序异常终止,也不会靠随意回收具有强引用的对象来解决内存不足的问题。
- 如果一个对象只具有软引用,则内存空间足够,垃圾回收器就不会回收它;如果内存空间不足了,就会回收这些对象的内存。只要垃圾回收器没有回收它,该对象就可以被程序使用。软引用可用来实现内存敏感的高速缓存。
- 弱引用与软引用的区别在于:只具有弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。不过,由于垃圾回收器是一个优先级很低的线程,因此不一定会很快发现那些只具有弱引用的对象。
- “虚引用”顾名思义,就是形同虚设,与其他几种引用都不同,虚引用并不会决定对象的生命周期。如果一个对象仅持有虚引用,那么它就和没有任何引用一样,在任何时候都可能被垃圾回收器回收。
3.2 ThreadLocal内存泄漏问题
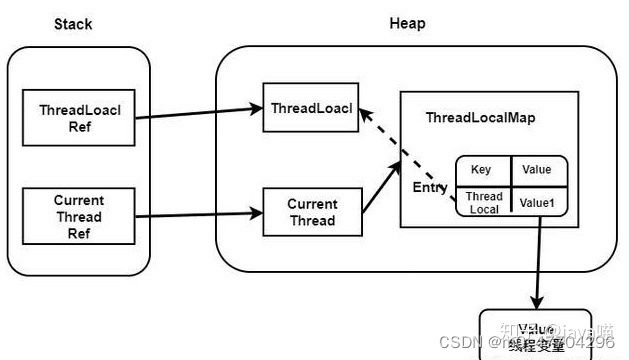
每一个Thread维护一个ThreadLocalMap,key为使用弱引用的ThreadLocal实例,value为线程变量的副本。这些对象之间的引用关系如下:
什么时候出现内存泄漏
从上图中可以看出,hreadLocalMap使用ThreadLocal的弱引用作为key,如果一个ThreadLocal不存在外部强引用时,Key(ThreadLocal)势必会被GC回收,这样就会导致ThreadLocalMap中key为null, 而value还存在着强引用,只有thead线程退出以后,value的强引用链条才会断掉。但如果当前线程再迟迟不结束的话,这些key为null的Entry的value就会一直存在一条强引用链:
Thread Ref -> Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value
永远无法回收,造成内存泄漏。获取线程存活时间很长,导致ThreadLocalMap熬过yangGC进入老年代,容易引起fullGC。
为什么ThreadLocalMap的key使用弱引用的ThreaLocal,不使用强引用
-
如果使用强引用的话,如果当前线程不结束,ThreadLocal会一直被ThreadLocalMap引用,导致内存泄漏
-
相反使用弱引用的话,如果ThreadLocal没有强引用指向它,那么不管线程有没有结束,会在下次GC的时候回收ThreadLocal对象。
当key为null,在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set(),get(),remove()方法的时候会被清除value值。