Golang Template
golang提供了两个标准库用来处理模版text/template和html/template。我们使用html/template格式化html字符。
模版引擎
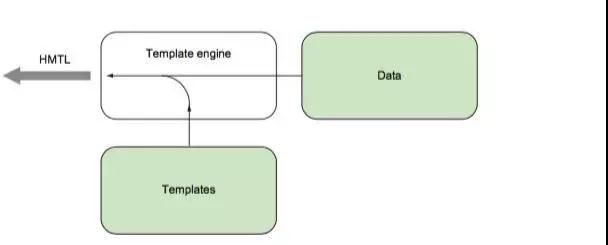
模版引擎很多,Python的jinja,nodejs的jade等都很好。所谓模版引擎,则将模版和数据进行渲染的输出格式化后的字符程序。对于go,执行这个流程大概需要三步:
·创建模版对象
·加载模版子串
·执行渲染模版
其中最后一步就是把加载的字符和数据进行格式化。其过程可以总结下图:
warming up
go提供的标准库html/template提供了很多处理模版的接口,我们的项目结构为:
templates文件夹有两个文件,分别为模版文件。layout.html文件如下:
!DOCTYPE html>
layout
This is layout
template data: {
{ . }}
我们可以使用ParseFiles方法加载模版,该方法会返回一个模版对象和错误,接下来就可以使用模版对象执行模版,注入数据对象。go提供了一些模版标签,称之为action,.也是一种action。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){
t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html")
fmt.Println(t.Name())
t.Execute(w, "Hello world")
}我们打印了t模板对象的Name方法,实际上,每一个模板,都有一个名字,如果不显示指定这个名字,go将会把文件名(包括扩展名当成名字)本例则是layout.html。访问之后可以看见返回的html字串:
☁ ~ curl -i http://127.0.0.1:8000/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 09 Dec 2016 09:04:36 GMT
Content-Length: 223
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
layout
This is layout
template data: Hello world
go不仅可以解析模版文件,也可以直接模版子串,这就是标准的处理,新建-加载-执行三部曲:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){
tmpl := `
Go Web Programming
{
{ . }}
`
t := template.New("layout.html")
t, _ = t.Parse(tmpl)
fmt.Println(t.Name())
t.Execute(w, "Hello World")
}实际开发中,最终的页面很可能是多个模板文件的嵌套结果。go的ParseFiles也支持加载多个模板文件,不过模板对象的名字则是第一个模板文件的文件名。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){
t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html", "templates/index.html")
fmt.Println(t.Name())
t.Execute(w, "Hello world")
}可见打印的还是 layout.html的名字,执行的模板的时候,并没有index.html的模板内容。此外,还有ParseGlob方法,可以通过glob通配符加载模板。
模版命名与嵌套
模版命名
模版对象是有名字的,可以在创建模版对象的时候显