asp.net core mvc之模型绑定、特性约束模型绑定、模型验证(服务器/客户端/远程)
一、不用模型绑定
数据类型都是string
1、UserController.cs
public class UserController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Register()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult DoRegister()
{
//不用模型绑定 以前的方法取表单数据或Url的参数
//数据类型都是string
string s1 = HttpContext.Request.Form["name"];
string s2 = HttpContext.Request.Query["id"];
return View();
}
}2、Register.cshtml
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "注册";
}
二、简单数据类型绑定
可以指定数据类型,比如id 我们可以指定int
表单数据的name 一定要和参数的名称一致
public IActionResult DoRegister(string name,string password,string comfirmpassword,int id)
三、复杂数据类型绑定
把数据绑定到一个实体类型的属性
1、创建UserInfo实体
public class UserInfo
{
private int id;
private string name;
private string password;
private string comfirmpassword;
public int Id { get => id; set => id = value; }
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }
public string Password { get => password; set => password = value; }
public string Comfirmpassword { get => comfirmpassword; set => comfirmpassword = value; }
}2、UserController.cs控制器修改
public IActionResult DoRegister(UserInfo userInfo)四、特性约束模型绑定
1、UserInfo.cs 模型
//增加这个标注 则这个属性不会被绑定
[BindNever]
public int Id { get => id; set => id = value; }
//增加这个标注 则这个属性必须被绑定,如果没绑定 控制器中 ModelState.IsValid==false
//将 用户名输入框注释,可测试这个标注
[BindRequired]
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }2、Register.cshtml 视图,将 用户名 输入框注释掉
3、UserController.cs 控制器
public IActionResult DoRegister(UserInfo userInfo)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid==false)
{
string message=ModelState.Root.Children[0].Errors[0].ErrorMessage;
}
return View();
}五、模型验证 - 服务器端
模型 UserInfo.cs
[StringLength(maximumLength:15,MinimumLength =6)]//字符最小长度6,最大长度15
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }
[Required] //必填
public string Password { get => password; set => password = value; }
[Compare("Password")] //比较验证
public string Comfirmpassword { get => comfirmpassword; set => comfirmpassword = value; }其他验证
[Required];必填的属性。
[Compare]:验证模型中的两个性是否匹配
[StringLength]:验证字符串属性的最大长度
[RegularExpression]:验证数据是否与指定的正则表达式匹配
[EmailAddress]:验证属性是否为电子邮件格式
[Phone]:验证属性是否为电话号码格式
[Range]:验证属性值是否在给定范围内
[Url]:验证属性是否为网址格式
六、模型验证 - 客户端
客户端验证是通过js挡住普通用户,危险用户可以能会把js去掉。所以客户端验证是不安全的。
客户端验证可以减轻服务器端的压力。
1、在 Register.cshtml 视图中,添加 js文件。js导入顺序不能颠倒
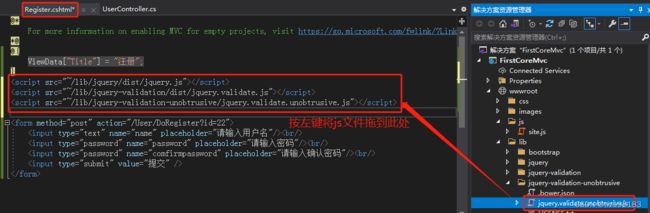 2、在 Register.cshtml 视图,指定强视图
2、在 Register.cshtml 视图,指定强视图
@model FirstCoreMvc.Models.UserInfo3、在 Register.cshtml 视图,使用 bootstrap框架 ,完整代码如下:
@model FirstCoreMvc.Models.UserInfo
@*指明视图使用那一个实体*@
4、UserInfo.cs 模型
[Required(ErrorMessage = "用户名必填")] //必填
[StringLength(maximumLength: 15, MinimumLength = 6,ErrorMessage ="用户名长度必须6-15字符")]
[Display(Name = "用户名")]
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }
[Required(ErrorMessage ="密码必填")] //必填
[Display(Name = "密码")]
public string Password { get => password; set => password = value; }
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessage ="{0}和{1}必须一样")] //比较验证
[Display(Name = "确认密码")]
public string Comfirmpassword { get => comfirmpassword; set => comfirmpassword = value; }效果:
七、远程验证
有些验证需要用到数据库里的数据。如:验证用户名是否已经注册了。
1、UserInfo.cs 模型
在Name属性添加 [Remote("方法","控制器")] 标注
[Remote("VerifyName","User")]
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }2、UserController 控制器添加 VerifyName 方法
public IActionResult VerifyName(string name)
{
if (name == "aaaaaa")
{
return Json(data: $"{name}已经被注册");
}
else
{
return Json(data: true);
}
}