青少年python大赛知识点学习5--字典
python中的字典,与我们使用的新华字典有点像。索引与对象,新华字典存的是每个字的相关内容,python中的字典是一个容器类型的数据结构,通过key进行索引。
1.什么是字典
- 字典是python内置的重要数据之一,与列表一样是一个可变序列。
- 以键值对(key:value)的方式存储数据,字典是一个无序的序列,列表是一个有序序列。
- 用{}来定义字典.
- 字典是Python语言中唯一的映射类型。字典对象是可变的,它是一个容器类型,能存储任意个数的Python对象,其中也可包括其他容器类型。
2.字典的创建
字典中的key是非常关健的数据,而且在程序中需要通过key来调用访问value值,因此字典中的key不能重复。两种创建方法:
1.使用{}创建
创建时,{}中应包含多个key_value对,key与value 之间用英文冒号隔开,多个key-value对以英文逗号隔开。小学生巧记:字典为“逗大猫”({,:})。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2023年11月05日 10时26分
# @Email : [email protected]
# @Author : Chenfengyi
# @File : 字典.py
# @notice :
treeword = {} # 空字典
print(treeword)
twoword = {'桌子': 'desk', '书': 'book'} # key与value均为字符串
print(twoword)
dict3 = {(1, 5): '合格', (1, 3): '优秀', 10: '李明'} # key为元组,整数,value均为字符串,
print(dict3)
dict3 = {2: '合格', (1, 3): 500, 10: '李明'}
print(dict3)
2.使用dict()函数创建
使用dict()函数创建字典时,可以传入多个元组或列表参数作为key_value对。每个列表或元组将作为key_value对,所以只能包含两个元素,如下:
word=((1, 3), (1, 3))
d1=dict(word)
print(d1)
word=((1, 3), (5, 3))
d1=dict(word)
print(d1)
word=[(1, 'good'), (1, 'book')]
d1=dict(word)
print(d1)
word=[('好', 'good'), ('书', 'book')]
d1=dict(word)
print(d1)
dictempty=dict()
print(dictempty)
结果:
{1: 3}
{1: 3, 5: 3}
{1: 'book'}
{'好': 'good', '书': 'book'}
{}
3.字典的基本用法
注意,字典包含多个k-v对,而key是字典的关健数据,所以对字典的操作都是基于key的
通过key访问值
通过key添加值
cj={'语文':85,'数学':105,'英语':98}
print(cj)
print(cj['英语'])
print(cj['美术'])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "F:/le_python/csdn/字典增删改查.py", line 11, in
print(cj['美术'])
KeyError: '美术'
{'语文': 85, '数学': 105, '英语': 98}
98
通过key修改值
通过key删除值
cj={'语文':85,'数学':105,'英语':98}
print(cj)
print(cj['英语'])
if '美术' not in cj:
cj['美术'] = 99
print('没用美术成绩')
else:
print(cj['美术'])
print(cj)
del cj['美术']
print(cj)
结果:
{'语文': 85, '数学': 105, '英语': 98}
98
没用美术成绩
{'语文': 85, '数学': 105, '英语': 98, '美术': 99}
{'语文': 85, '数学': 105, '英语': 98}
进程已结束,退出代码 0通过key确定key-value对是否存在
cj={'语文':85,'数学':105,'英语':98}
print(cj)
print(cj['英语'])
if '美术' not in cj:
print('没用美术成绩')
else:
print(cj['美术'])
结果:
{'语文': 85, '数学': 105, '英语': 98}
98
没用美术成绩字典相当于索引是任意不可变的类型列表,而列表相当于key只能是整数的字典,因此如果程序中要使用的字典的key都是整数类型,则可以考虑能否换成列表。
列表不充许对不存在的索引赋值,而字典可以。
4.字典的常用方法
print(dir({}))
print(dir(dict))
lb=dir({})
b=[]
for a in lb:
if '_' not in a:
b.append(a)
print(b)
结果:
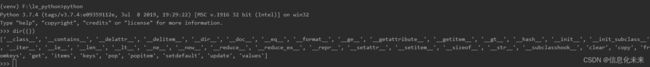
['__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values']
['__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values']
['clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values']
常用方法:
'clear':清空字典
'copy':复制
'fromkeys':使用多个给定的多个key创建字典,key对应的寄默认值为none也可指定默认值
cj=dict.fromkeys(['数学','语文'])
print(cj)
cj=dict.fromkeys(('数学','语文'))
print(cj)
cj=dict.fromkeys(('数学','语文'),80)
print(cj)
{'数学': None, '语文': None}
{'数学': None, '语文': None}
{'数学': 80, '语文': 80}'items'
'keys',
'values'
cj=dict.fromkeys(['数学','语文'])
print(cj)
cj=dict.fromkeys(('数学','语文'))
print(cj)
cj=dict.fromkeys(('数学','语文'),80)
print(cj)
print('items',cj.items)
print('keys',cj.keys)
print('values',cj.values)
print('items',list(cj.items()))
print('keys',list(cj.keys()))
print('values',list(cj.values()))
结果:
{'数学': None, '语文': None}
{'数学': None, '语文': None}
{'数学': 80, '语文': 80}
items
keys
values
items [('数学', 80), ('语文', 80)]
keys ['数学', '语文']
values [80, 80] 'get':根据key获得value值,相当于[]语法的增强版,使用[]获得不存在的key时会引发keyerro错误,get()会返回none,不引起错误。
'pop',
'popitem',
'setdefault',
'update'
有空自已试试。