立冬特辑-----链表OJ题优选合集~~
目录
前言
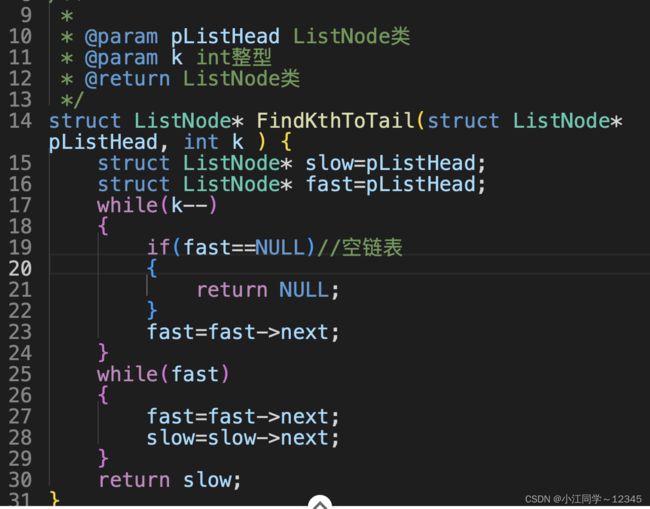
1.链表中倒数第k个结点
1.1 思路
1.2 代码
2. 链表的回文结构
2.1 思路
2.2 代码
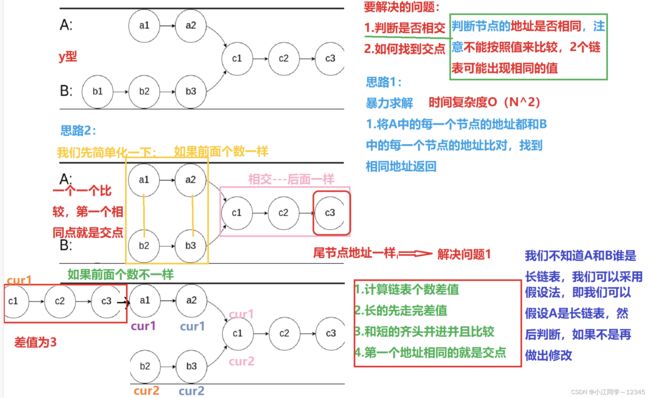
3.相交链表️
3.1 思路
3.2 代码
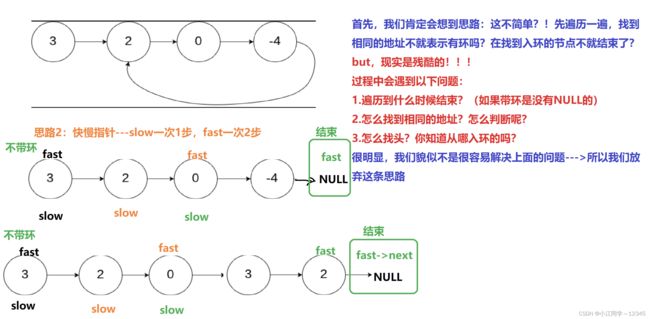
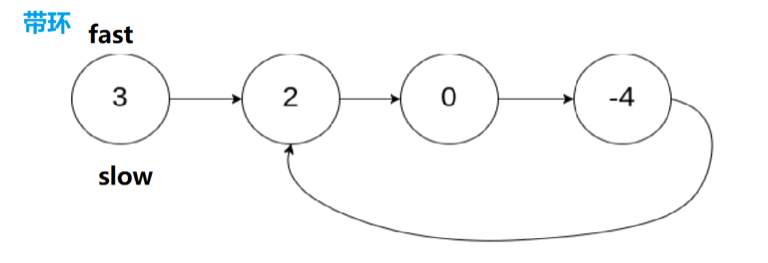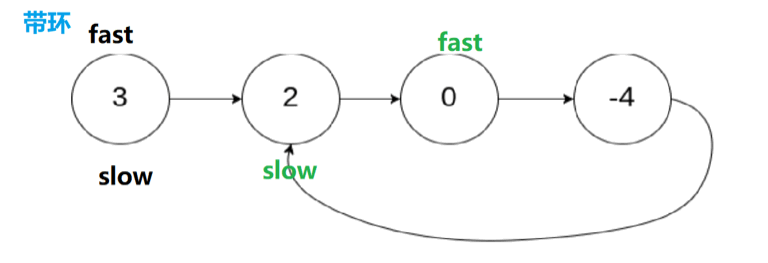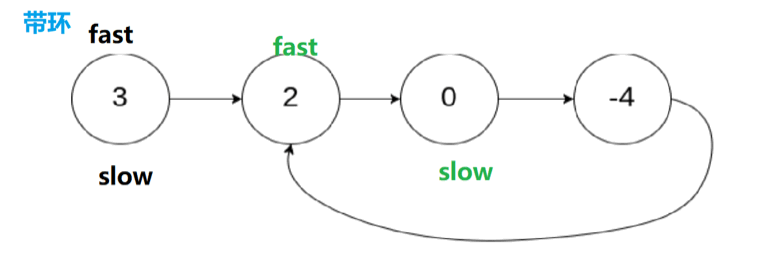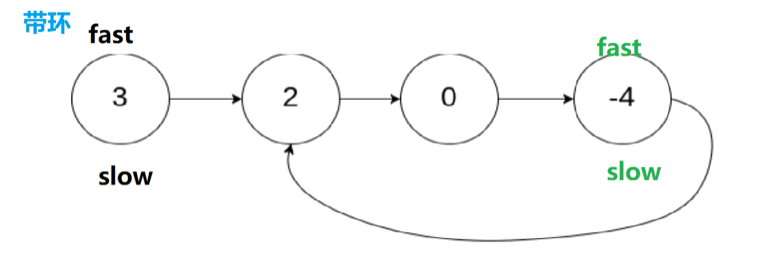
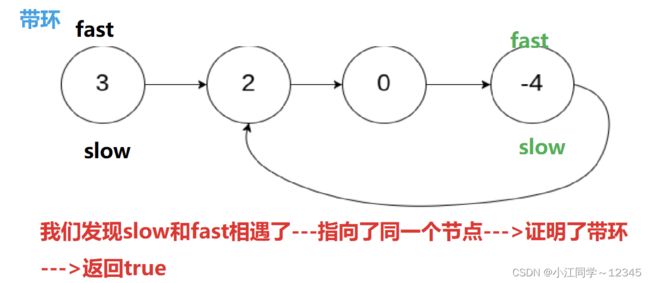
4.环形链表I️
4.1 思路
4.2 代码
4--->5过渡:拓展思考
5.环形链表II
5.1 思路
5.2 代码
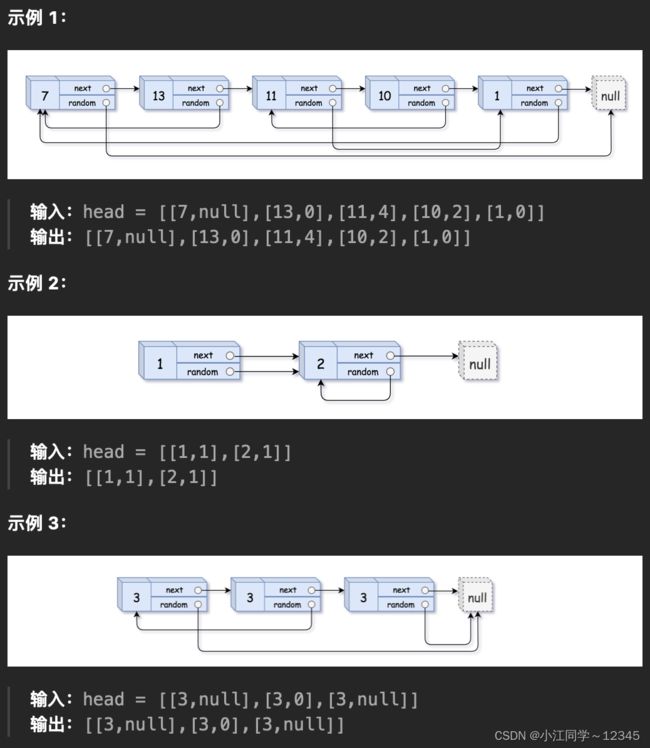
6.随机链表的复制
6.1 思路编辑
6.2 代码
后语
前言
之前,我们已经将链表部分的知识了解学习的差不多了,那么没有题目来练练手算个什么事⁉️必需给大家安排上,小江优选---保质又保量‼️
1.链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网
1.1 思路
忘记之前的题目的同学,可以看看这篇博客:
学习笔记---看完就会的单链表的应用~~-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读119次,点赞36次,收藏16次。小链表的尾节点指向大链表的第一个节点(不是指向哨兵位)https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79184587/article/details/134049599
1.2 代码
2. 链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
2.1 思路
2.2 代码
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
if (A == NULL) {
return NULL;//空链表
}
ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3,*cur1,*cur2;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = A;
n3 = A->next;
while (n2) {
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3) {
n3 = n3->next;//注意空指针
}
}
cur1=A,cur2=n1;//比较
while(cur1&&cur2)
{
if(cur1->val==cur2->val)
{
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
if (A == NULL) {
return NULL;//空链表
}
ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow=fast=A;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3,*cur1,*cur2;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = slow;
n3 = slow->next;
while (n2) {
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3) {
n3 = n3->next;//注意空指针
}
}
cur1=A,cur2=n1;//比较
while(cur1&&cur2)
{
if(cur1->val==cur2->val)
{
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};3.相交链表️
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
3.1 思路
3.2 代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {//遍历判断是否相交
struct ListNode* cur1=headA;
struct ListNode* cur2=headB;
int count1=1,count2=1;
//长度都少一,但相减之后不影响--->但是要想计数准确,我们也可以从1开始计数
//不能用cur1和cur2遍历,因为我们要找到尾节点的地址判断是否相交,否则到cur1和cur2都为NULL的时候,循环结束,尾节点的地址就找不到了
while(cur1->next)
{
count1++;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
while(cur2->next)
{
count2++;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
if(cur1!=cur2)
{
return NULL;
}//到这里,就是相交了-->计算差值
int D_value=abs(count1-count2);//假设法
struct ListNode* longlist=headA,* shortlist=headB;
if(count1next;
}
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
} 4.环形链表I️
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
4.1 思路
4.2 代码
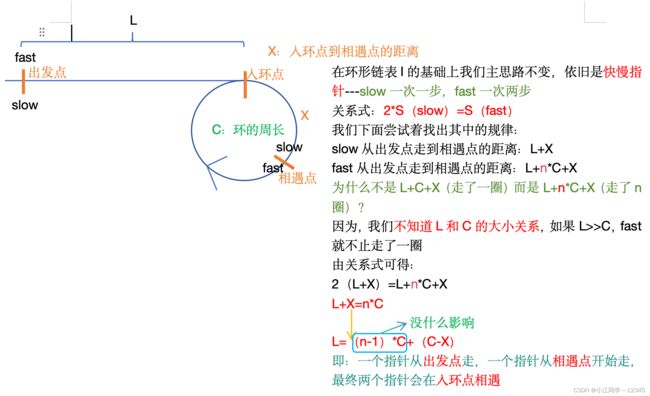
4--->5过渡:拓展思考
前提:带环链表
1.slow一次1步,fast一次2步,一定能相遇吗?
2.slow一次1步,fast一次3步,一定能相遇吗?
3.slow一次m步,fast一次n步,一定能相遇吗?
1.slow一次1步,fast一次2步,一定能相遇吗?
2.slow一次1步,fast一次3步,一定能相遇吗?
3.slow一次m步,fast一次n步,一定能相遇吗?
5.环形链表II
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
5.1 思路
5.2 代码
6.随机链表的复制
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
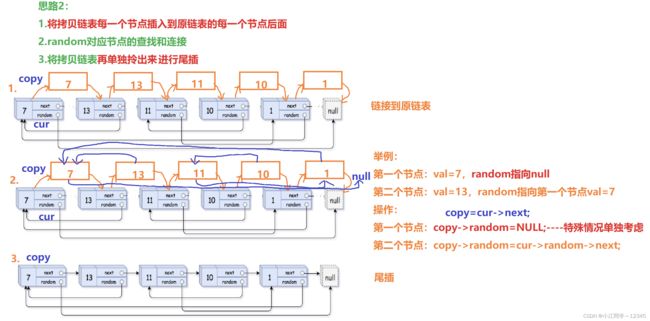
6.1 思路
6.2 代码
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct Node* cur=head;//插入到原链表
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=cur->next->next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=cur->next->next;
}
cur=head;
struct Node* newhead,* tail;
newhead=tail=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
struct Node* next=copy->next;
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead=tail=copy;
}
else
{
tail->next=copy;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur->next=next;
cur=cur->next;
}
return newhead;
}后语
本次的分享到这里就结束了!!!
PS:小江目前只是个新手小白。欢迎大家在评论区讨论哦!有问题也可以讨论的!
如果对你有帮助的话,记得点赞+收藏⭐️+关注➕