链表OJ(四)链表排序合集
目录
合并两个排序的链表
合并k个已排序的链表
单链表的排序
链表的奇偶重排
链表的奇偶重排扩展
合并两个排序的链表
描述
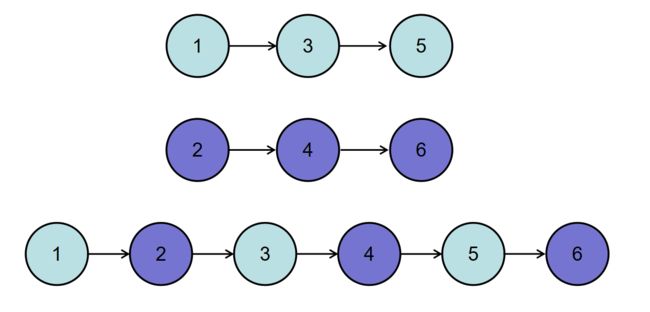
输入两个递增的链表,单个链表的长度为n,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
数据范围: 0≤n≤10000≤n≤1000,−1000≤节点值≤1000−1000≤节点值≤1000
要求:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)如输入{1,3,5},{2,4,6}时,合并后的链表为{1,2,3,4,5,6},所以对应的输出为{1,2,3,4,5,6},转换过程如下图所示:
或输入{-1,2,4},{1,3,4}时,合并后的链表为{-1,1,2,3,4,4},所以对应的输出为{-1,1,2,3,4,4},转换过程如下图所示:
示例1
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p = newhead;
ListNode* l1 = pHead1, *l2 = pHead2;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val <= l2->val) // 创建一个头结点,让头结点依次按序接入各个结点
{
p->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
p->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
p->next = l1 ? l1 : l2; // 记得循环跳出后对剩余结点的接入
return newhead->next;
}
};
合并k个已排序的链表
描述
合并 k 个升序的链表并将结果作为一个升序的链表返回其头节点。
数据范围:节点总数 0≤n≤50000≤n≤5000,每个节点的val满足 ∣val∣<=1000∣val∣<=1000
要求:时间复杂度 O(nlogn)O(nlogn)
使用优先级队列,存储依次存储各个链表,然后根据链表首部元素的大小进行建堆,
每次从堆中取出堆顶链表,将堆顶链表pop取出,得到头结点数据后,链表后移重新入队
class Com
{
public:
bool operator()(ListNode* left, ListNode* right)
{
return left->val > right->val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector &lists) {
if(lists.empty())return nullptr;
priority_queue, Com> q; // 创建一个优先级队列,按照大于的比较方式存储
for(auto &e : lists)
{
if(e!=nullptr) // 对每个不空的结点进行入队列
q.push(e);
}
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);
newhead->next = nullptr;
ListNode* pre = newhead;
while(!q.empty())
{
ListNode* cur = q.top(); // cur标记当前堆顶结点
q.pop();
pre->next = cur; // 将它插入返回链表中
cur = cur->next; // 当前结点后移一步
if(cur)
q.push(cur); // 如果不为空就重新入队列
pre = pre->next;
}
return newhead->next;
}
}; 单链表的排序
描述
给定一个节点数为n的无序单链表,对其按升序排序。
数据范围:0
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(nlogn)O(nlogn)
使用优先级队列,存储结点
class Com
{
public:
bool operator()(const ListNode* left, const ListNode* right)
{
return left->val > right->val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortInList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
priority_queue, Com> q;
while(head)
{
q.push(head); // 将每一个结点入队列
head = head->next;
}
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p = newhead;
while(!q.empty())
{
ListNode* cur = q.top(); // 将堆顶结点依次取出置入新头结点后面
q.pop();
p->next = cur;
p = p->next;
}
p->next = nullptr;
return newhead->next;
}
}; 下面是使用按值存储并还原,这是因为上面的办法使用时我没有最后将p的next指向nullptr,导致p的屁股后面跟了一长串,这一长串都是一堆数据。
而上面的k个链表合并,他们每一个链表最终都走到了末尾空的位置。
class Com { public: bool operator()(const long long left, const long long right) { return left > right; } }; class Solution { public: ListNode* sortInList(ListNode* head) { // write code here // 使用long long类型 priority_queue, Com> q; while(head) { q.push(head->val); // 存储值的优先级队列 head = head->next; } ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0); ListNode* p = newhead; while(!q.empty()) { ListNode* cur = new ListNode(q.top()); // 用值将链表结点还原 q.pop(); p->next = cur; // 插入newhead后面即可 p = p->next; } return newhead->next; } };
链表的奇偶重排
描述
给定一个单链表,请设定一个函数,将链表的奇数位节点和偶数位节点分别放在一起,重排后输出。
注意是节点的编号而非节点的数值。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
if(head==nullptr)return nullptr;
ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head->next;
ListNode* link = fast;
while(fast && fast->next) // 注意这里fast 与 fast->next的判空
{
slow->next = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
fast->next = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
/* 俩种写法都可以
slow->next = slow->next->next;
fast->next = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
*/
}
slow->next = link;
return head;
}
};链表的奇偶重排扩展
class Com
{
public:
bool operator()(const ListNode* left, const ListNode* right)
{
return left->val > right->val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
priority_queue, Com> q1;
priority_queue, Com> q2;
for(int i = 0; head; i++)
{
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(head->val);
if(i%2==0)
q1.push(newNode);
else
q2.push(newNode);
head = head->next;
}
ListNode* newhead1 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p1 = newhead1;
ListNode* newhead2 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p2 = newhead2;
while(!q1.empty())
{
p1->next = q1.top();
q1.pop();
p1 = p1->next;
}
while(!q2.empty())
{
p2->next = q2.top();
q2.pop();
p2 = p2->next;
}
p1->next = newhead2->next;
p2->next = nullptr;
return newhead1->next;
}
};