Vuex模块概念
一、核心概念 - module
1.目标
掌握核心概念 module 模块的创建
2.问题
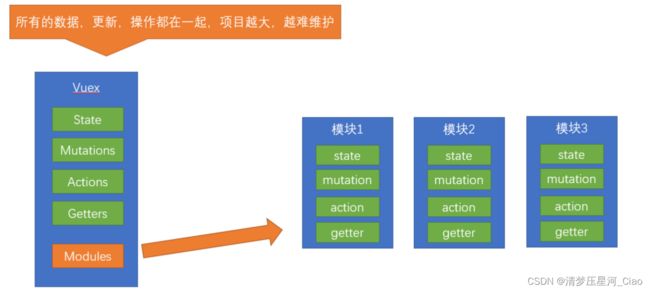
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
这句话的意思是,如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护
由此,又有了Vuex的模块化
3.模块定义 - 准备 state
定义两个模块 user 和 setting
user中管理用户的信息状态 userInfo modules/user.js
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
}
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
setting中管理项目应用的 主题色 theme,描述 desc, modules/setting.js
const state = {
theme: 'dark'
desc: '描述真呀真不错'
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
在store/index.js文件中的modules配置项中,注册这两个模块
import user from './modules/user'
import setting from './modules/setting'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
user,
setting
}
})
使用模块中的数据, 可以直接通过模块名访问 $store.state.模块名.xxx => $store.state.setting.desc
也可以通过 mapState 映射
二、获取模块内的state数据
1.目标:
掌握模块中 state 的访问语法
尽管已经分模块了,但其实子模块的状态,还是会挂到根级别的 state 中,属性名就是模块名

2.使用模块中的数据
- 直接通过模块名访问 $store.state.模块名.xxx
- 通过 mapState 映射:
- 默认根级别的映射 mapState([ ‘xxx’ ])
- 子模块的映射 :mapState(‘模块名’, [‘xxx’]) - 需要开启命名空间 namespaced:true
modules/user.js
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
},
myMsg: '我的数据'
}
const mutations = {
updateMsg (state, msg) {
state.myMsg = msg
}
}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
3.代码示例
$store直接访问
$store.state.user.userInfo.name
mapState辅助函数访问
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),
三、获取模块内的getters数据
1.目标:
掌握模块中 getters 的访问语
2.语法:
使用模块中 getters 中的数据:
- 直接通过模块名访问
$store.getters['模块名/xxx '] - 通过 mapGetters 映射
- 默认根级别的映射
mapGetters([ 'xxx' ]) - 子模块的映射
mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx'])- 需要开启命名空间
- 默认根级别的映射
3.代码演示
modules/user.js
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}
Son1.vue 直接访问getters
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}div>
Son2.vue 通过命名空间访问
computed:{
...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])
}
四、获取模块内的mutations方法
1.目标:
掌握模块中 mutation 的调用语法
2.注意:
默认模块中的 mutation 和 actions 会被挂载到全局,需要开启命名空间,才会挂载到子模块。
3.调用方式:
- 直接通过 store 调用 $store.commit('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
- 通过 mapMutations 映射
- 默认根级别的映射 mapMutations([ ‘xxx’ ])
- 子模块的映射 mapMutations(‘模块名’, [‘xxx’]) - 需要开启命名空间
4.代码实现
modules/user.js
const mutations = {
setUser (state, newUserInfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserInfo
}
}
modules/setting.js
const mutations = {
setTheme (state, newTheme) {
state.theme = newTheme
}
}
Son1.vue
export default {
methods: {
updateUser () {
// $store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 额外传参)
this.$store.commit('user/setUser', {
name: 'xiaowang',
age: 25
})
},
updateTheme () {
this.$store.commit('setting/setTheme', 'pink')
}
}
}
Son2.vue
methods:{
// 分模块的映射
...mapMutations('setting', ['setTheme']),
...mapMutations('user', ['setUser']),
}
五、获取模块内的actions方法
1.目标:
掌握模块中 action 的调用语法 (同理 - 直接类比 mutation 即可)
2.注意:
默认模块中的 mutation 和 actions 会被挂载到全局,需要开启命名空间,才会挂载到子模块。
3.调用语法:
- 直接通过 store 调用 $store.dispatch('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
- 通过 mapActions 映射
- 默认根级别的映射 mapActions([ ‘xxx’ ])
- 子模块的映射 mapActions(‘模块名’, [‘xxx’]) - 需要开启命名空间
4.代码实现
modules/user.js
const actions = {
setUserSecond (context, newUserInfo) {
// 将异步在action中进行封装
setTimeout(() => {
// 调用mutation context上下文,默认提交的就是自己模块的action和mutation
context.commit('setUser', newUserInfo)
}, 1000)
}
}
Son1.vue 直接通过store调用
methods:{
updateUser2 () {
// 调用action dispatch
this.$store.dispatch('user/setUserSecond', {
name: 'xiaohong',
age: 28
})
},
}
Son2.vue mapActions映射
<button @click="setUserSecond({ name: 'xiaoli', age: 80 })">一秒后更新信息</button>
methods:{
...mapActions('user', ['setUserSecond'])
}
六、Vuex模块化的使用小结
1.直接使用
- state --> $store.state.模块名.数据项名
- getters --> $store.getters[‘模块名/属性名’]
- mutations --> $store.commit(‘模块名/方法名’, 其他参数)
- actions --> $store.dispatch(‘模块名/方法名’, 其他参数)
2.借助辅助方法使用
1.import { mapXxxx, mapXxx } from ‘vuex’
computed、methods: {
// …mapState、…mapGetters放computed中;
// …mapMutations、…mapActions放methods中;
…mapXxxx(‘模块名’, [‘数据项|方法’]),
…mapXxxx(‘模块名’, { 新的名字: 原来的名字 }),
}
2.组件中直接使用 属性 {{ age }} 或 方法 @click="updateAge(2)"