Springboot自动装配工作原理-注解自动装配(注解,自定义starter启动器)
Springboot自动装配工作原理-注解自动装配(注解,自定义starter启动器)
- Springboot自动装配工作原理
-
- 1 自动装配的基础
-
- 1.1 spring注解式BD
- 1.2 注解形式
- 1.3 注解形式实现
-
- Configration + ComponentScan + Controller、Service、Component……(类上)注意scan的默 认包路径
- Configration + Bean(方法上)
- Configration + Import (其他Configration上)
- Configration + Import (直接指定Class)
- Configration + ImportResource (其他xml文件)//几乎没用
- Configration + Import (ImportSelector)
- 2 自动装配源码分析
-
- 2.1 自动装配的入口在哪里
- 2.2 自动装配核心元注解源码
-
- 2.2.1 自动配置包源码剖析
- 2.2.2 自动导入源码剖析
- 3 starter的秘密
-
- 3.1 初识starter
-
- 3.1.1 springboot之前
- 3.1.2 了解starter
- 3.1.3 了解自动装配
- 3.2 如何自定义starter启动器
-
- 3.2.1 starter启动器有什么作用
- 3.2.2 开始自定义starter启动器
- 3.2.3 测试自定义启动器
- 总结
Springboot自动装配工作原理
1 自动装配的基础
1.1 spring注解式BD
回顾一下,springboot其实使用了一个Annotation开头的 应用上下文对象
1.2 注解形式
xml是spring最原始最基本的bean定义方式。
3.x 后,支持注解来启动bean容器
spring注解的启动方式(【重要】!springboot自动装配就是基于这个基础特性来的):
Configration + ComponentScan + Controller、Service、Component……(类上)注意scan的默 认包路径
Configration + Bean(方法上)
Configration + Import (其他Configration上)
Configration + Import (直接指定Class)
Configration + ImportResource (其他xml文件)//几乎没用
Configration + Import (ImportSelector)
甚至,你可以自定义注解EnableXXX,将上面组合起来!
再想想我们的springboot里一堆Enable……是不是很像???
注解式源码 :
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
refresh() - super.refresh - obtainFreshBeanFactory - refreshBeanFactory -
loadBeanDefinitions - scanner.scan
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor: 后置处理器处理import等详细逻辑
1.3 注解形式实现
Configration + ComponentScan + Controller、Service、Component……(类上)注意scan的默 认包路径
如果只是加@ComponentScan只会扫当前目录和子包
@Configuration
//指定扫描的包
@ComponentScan({"anno"})
public class ParentScan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ParentScan.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
Configration + Bean(方法上)
指定bean加载
@Configuration
public class BeanScan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanScan.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
@Bean
Service1 service1(){
return new Service1();
}
@Bean
Service2 service2(){
return new Service2();
}
}
Configration + Import (其他Configration上)
可以引用别人的注入的bean
Configuration
@Import(ParentScan.class)
public class ImportConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ImportConfig.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
Configration + Import (直接指定Class)
@Configuration
@Import({Service1.class,Service2.class})
public class ImportBean {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ImportBean.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
Configration + ImportResource (其他xml文件)//几乎没用
@Configuration
@ImportResource({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ImportRes {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ImportRes.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="anno.pkg1.Service1">
bean>
<bean class="anno.pkg2.Service2">
bean>
beans>
Configration + Import (ImportSelector)
首先mySelector
public class MySelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{
Service1.class.getName(),
Service2.class.getName()
};
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(MySelector.class)
public class ImportSelector {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ImportSelector.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
还有一种通过枚举类来导入
@Configuration
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(MySelector.class)
public @interface EnableMySelector {
}
@EnableMySelector
public class MyEnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyEnable.class);
Service1 service1 = context.getBean(Service1.class);
service1.go();
Service2 service2 = context.getBean(Service2.class);
service2.go();
}
}
2 自动装配源码分析
2.1 自动装配的入口在哪里
要谈自动装配我们需要从项目的初始注解入手:@SpringBootApplication
//标识启动类,它是一个复合注解,标识使用自动装配、通过扫描注解注入bean
@SpringBootApplication
public class Hibernate52Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Hibernate52Application.class, args);
}
}
进入到@SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//该注解只能声明在一个类前
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
@Documented//表明这个注解应该被 javadoc工具记录. 默认情况下,javadoc是不包括注解的
@Inherited//表示该注解会被子类继
@SpringBootConfiguration//继承自@Configuration,二者功能也一致,标注当前类是配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration//自动装配
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
上面的代码实现自动装配的注解为:@EnableAutoConfiguration
需要重点关注点的核心注解如下

2.2 自动装配核心元注解源码
进入@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//该注解只能声明在一个类前
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Documented// 表明这个注解应该被 javadoc工具记录. 默认情况下,javadoc是不包括注解的
@Inherited//表示该注解会被子类继
@AutoConfigurationPackage//自动配置包, 作用:将main包下的所组件注册到容器中
//@Import的作用就是导入一个类到IOC容器
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)//核心AutoConfigurationImportSelector的方法selectImports
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
在这个注解下我们需要关注两个注解:@AutoConfigurationPackage、
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
2.2.1 自动配置包源码剖析
@AutoConfigurationPackage
进入到元注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)//进入内部类Registrar
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
我们进入到内部类Registrar.class
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames()返回一个主包名称
//这个包就是Spring Boot主配置类所在的包,metadata,返回主配置类
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
这是AutoConfigurationPackage的一个静态内部类
里面的方法registerBeanDefinitions指定@ComponentScan的扫描路径,此处打断点启动项目我们可以发现这个为项目的顶级包名。
进入到register方法
//packageNames名称:org.springframework.boot.tests.hibernate52
public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String... packageNames) {
//如果存在这个bean定义
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN)) {
BasePackagesBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (BasePackagesBeanDefinition) registry.getBeanDefinition(BEAN);
beanDefinition.addBasePackages(packageNames);
} else {
//不存在就注册(在这个package路径下的org.springframework.boot.tests.hibernate52)
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN, new BasePackagesBeanDefinition(packageNames));
}
}
确保了将项目目录下所有的bean注入到容器
2.2.2 自动导入源码剖析
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}
核心
接下来我们看看引入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector,进入到当前类
重点关注getAutoConfigurationEntry这个方法
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Documented// 表明这个注解应该被 javadoc工具记录. 默认情况下,javadoc是不包括注解的
@Inherited//表示该注解会被子类继
@AutoConfigurationPackage//自动配置包, 作用:将main包下的所组件注册到容器中
//@Import的作用就是导入一个类到IOC容器
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)//核心AutoConfigurationImportSelector的方法selectImports
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
// getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法返回所有带有@Configuration注解的类的全类名,
// Spring Boot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取到这个数组,
// 将数组中的类作为自动配置类导入到容器中
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
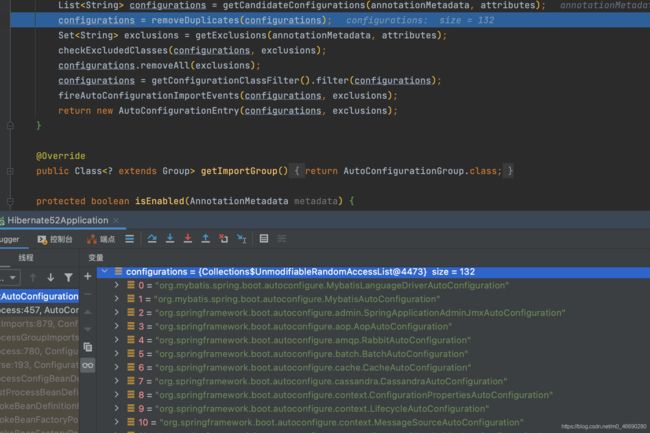
// 发现configurations的结果是所有的xxxAtuoConfiguration类,配置类一共124个
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
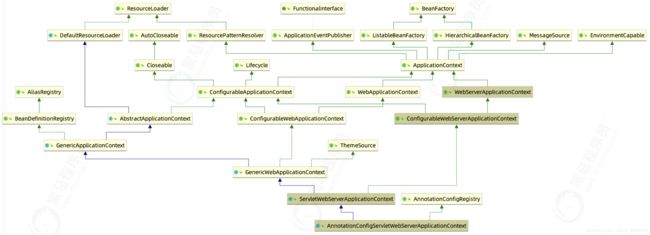
继承关系如下

可以看出,AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类实现了 ImportSelector(DeferredImportSelector父接口)接口,也就实现了这个接口中的 selectImports方法,该方法主要用于获取所有符合条件的类的
全限定类名,这些类需要被加载到 IoC 容器中。
继续进入到selectImports方法
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
// <1>.判断自动装配开关是否打开
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
//<2>.获取所有需要装配的bean
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
这里我们需要重点关注一下getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法,这个方法主要负责加载自动配置类的。
该方法调用链如下
// getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法返回所有带有@Configuration注解的类的全类名,
// Spring Boot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取到这个数组,
// 将数组中的类作为自动配置类导入到容器中
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 发现configurations的结果是所有的xxxAtuoConfiguration类,配置类一共124个
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
此处是去获取真正自动配置类的集合
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 打开spring-boot-autoconfigure/META-INF/spring.factories,
// 132个
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
继续进入到(Spring-core包下的方法)
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
我们可以发现spring-boot会去META-INF/spring.factories找
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的value.这个的具体位置如图

打开spring.factories

自动配置的类,如下
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfig
uration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfig
uration,\
......................略
部分截图
从20行到151行;合计130个
注意
在代码中加载的时候并不是全部加载
需要根据bean的加载条件进行加载
最终小于等于130个
到此 我们已经知道了bean的配置过程,但是还没有看到springboot是如何读取yml或者properites配置文件的的属性来创建数据源的?
在DataSourceAutoConfiguration类里面,我们注意到使用了EnableConfigurationProperties这个注解。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(type = "io.r2dbc.spi.ConnectionFactory")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
@Import({ DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class, DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.class })
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
DataSourceProperties中封装了数据源的各个属性,且使用了注解ConfigurationProperties指定了配置文件的前缀。
总结
关于Bean加载
如果要让一个普通类交给Spring容器管理,通常有以下方法:
1、使用 @Configuration与@Bean 注解
2、使用@Controller @Service @Repository @Component 注解标注该类,然后启用@ComponentScan自动扫描
3、使用@Import 方法
Springboot中使用了@Import 方法
3 starter的秘密
3.1 初识starter
3.1.1 springboot之前
通常搭建一个基于spring的web应用,我们需要做以下工作:
1、pom文件中引入相关jar包,包括spring、springmvc、redis、mybaits、log4j、mysql-connectorjava 等等相关jar …
2、配置web.xml,Listener配置、Filter配置、Servlet配置、log4j配置、error配置 …
3、配置数据库连接、配置spring事务
4、配置视图解析器
5、开启注解、自动扫描功能
6、配置完成后部署tomcat、启动调试
…
搭个初始项目不一会就一个小时甚至半天过去了。而用springboot后,一切都变得很简便快速。
接下来,我们一起看看springboot的起步依赖和自动配置的原理
3.1.2 了解starter
打开根目下E:\ideaEnv\bootsourcecode\spring-boot-2.4.3\spring-boot-tests\spring-boot-smoketests\spring-boot-smoke-test-hibernate52下的build.gradle
dependencies {
// implementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client"))
implementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-starter-web"))
// implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
// testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.12'
testImplementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-starter-test"))
//引用自定义启动器(暂时注释,使用的使用在用,否则无法看到项目代码)
compile project (":test-spring-boot-starter")
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter
implementation group: 'org.mybatis.spring.boot', name: 'mybatis-spring-boot-starter', version: '2.1.4'
// testImplementation("org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient")
}
1、spring-boot-starter-web包自动帮我们引入了web模块开发需要的相关jar包,
2、如果你想使用mybatis作为你的 orm层
可以使用mybatis-spring-boot-starter帮我们引入了dao开发相关的jar包。

可以看出在这个mybatis-spring-boot-starter 中,并没有任何源码,只有一个pom文件,它的作用就是帮我们引入了相关jar包
3、注意:
spring-boot-starter-xxx是官方提供的starter,xxx-spring-boot-starter是第三方提供的starter
stater机制帮我们完成了项目起步所需要的的相关jar包。那问题又来了,传统的spring应用中不是要在application.xml中配置很多bean的吗,比如dataSource的配置,transactionManager的配置
springboot是如何帮我们完成这些bean的配置的?下面我们来分析这个过程
3.1.3 了解自动装配
以mybatis为例,在上面的截图中,我们发下mybatis-spring-boot-starter这个包帮我们引入了mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包,如下图:

找到mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure
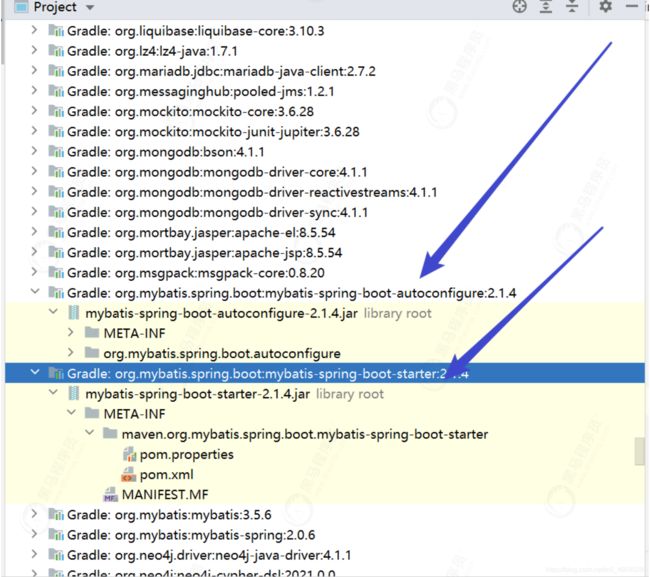
打开
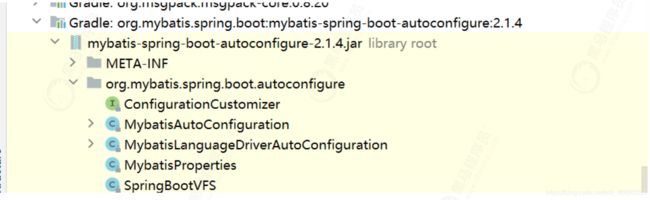
里面有MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类,打开这个类看看有什么东西。
截取部分源码
熟悉@Configuration&、@Bean这两个bean的同学或许已经知道了。这两个注解一起使用就可以创建一个基于java代码的配置类,可以用来替代相应的xml配置文件。
@Configuration注解的类可以看作是能生产让Spring IoC容器管理的Bean实例的工厂。
@Bean注解告诉Spring,一个带有@Bean的注解方法将返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册到spring容器中。
扩展知识点
关于自动配置的条件依赖
要完成Mybatis的自动配置,需要在类路径中存在SqlSessionFactory.class、
SqlSessionFactoryBean.class这两个类,需要存在DataSource这个bean且这个bean完成自动注册。
进入DataSourceAutoConfiguration这个类,可以看到这个类属于这个包:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc、

这个包又属于spring-boot-autoconfigure这个boot的子项目!

这个子项目帮我们引入了jdbc、kafka、logging、mail、mongo等包。很多包需要我们引入相应jar后自动配置才生效。

@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class })
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
}
这些是springboot特有的,常见的条件依赖注解有:
@ConditionalOnClass,某个class位于类路径上,才会实例化这个Bean。
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate表示当指定Bean在容器中只有一个,或者虽然有多个但是指定首选Bean
@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean进行属性值的配置
@AutoConfigureAfter,在某个bean完成自动配置后实例化这个bean。
其他的配置
@ConditionalOnBean,仅在当前上下文中存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean。
@ConditionalOnExpression,当表达式为true的时候,才会实例化这个Bean。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean,仅在当前上下文中不存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean。
@ConditionalOnMissingClass,某个class在类路径上不存在的时候,才会实例化这个Bean。
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication,不是web应用时才会实例化这个Bean。
@AutoConfigureBefore,在某个bean完成自动配置前实例化这个bean。
总结
所以,上面的MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类,自动帮我们生成了SqlSessionFactory这些Mybatis的重要实例并交给spring容器管理,从而完成bean的自动注册。
3.2 如何自定义starter启动器
3.2.1 starter启动器有什么作用
在我们的日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,我们经常将其放到一个特定的包下, 然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,麻烦至 极。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在 pom中引用依赖即可,Spring Boot为我们完成自动装配,这样就非常的方便。
一个Spring Boot 项目就是由一个一个 starter 组成的,一个 starter 代表该项目的 Spring Boot 启动依赖,除了官方已有的 starter,我们可以根据自己的需要自定义新的starter。
我们经常会看到或者使用到各种*-starter。比如下面几种:**
spring-boot-starter-web:嵌入Tomcat和web开发需要的相关jar包
spring-boot-starter-data-redis:redis数据库支持
mybatis-spring-boot-starter:第三方的mybatis集成的starter
spring-boot -starter-test:用于测试 Spring 引导应用程序
spring-boot-starter-AOP :这个 starter 用于使用 AspectJ 和 Spring AOP 进行面向方面的编程
Spring Boot starter机制 Spring Boot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制,能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,Spring Boot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置。starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。
Spring Boot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。Spring Boot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念
3.2.2 开始自定义starter启动器
按照Spring官方的建议,Starter的命名规则如下:
官方:spring-boot-starter-{moduleName}
第三方:{moduleName}-spring-boot-starter
启动器总览

1)自定义启动器moudle项目
新建
设置名称
设置build.gradle
plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'org.springframework.boot'
version '2.4.3'
repositories {
maven { url "https://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/repositories/central" }
maven { url "https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/spring?spm=a2c40.maven_devops2020_goldlog_.0.0.43643054RwkQD7" }
maven { url "https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/spring-plugin?spm=a2c40.maven_devops2020_goldlog_.0.0.43643054RwkQD7" }
//mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
// implementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-starter-web"))
// testImplementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-starter-test"))
// implementation(project(":spring-boot-project:spring-boot-starters:spring-boot-autoconfigure"))
compile (
"org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:2.4.3",
"org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-configuration-processor:2.4.3"
)
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
2) 创建starter启动器实体
这是一个典型JavaBean。然后通过 @ConfigurationProperties 注解指定这是一个配置类,并设置注解的 prefix 属性值指定配置项的前缀。
package com.test.starter.pojo;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NestedConfigurationProperty;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.test.starter")
public class Custom {
private String name = "Hello";
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private String description = "自定义starter测试";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
3)创建starter启动器接口
public interface CustomService {
/**
* 示例方法
*/
void print();
}
4)创建starter接口实现
创建一个类 CustomServiceImpl.class 实现上一步骤创建的接口 。
import com.test.starter.pojo.Custom;
import com.test.starter.service.CustomService;
public class CustomServiceImpl implements CustomService {
private Custom custom;
public CustomServiceImpl(Custom custom) {
this.custom=custom;
}
;
@Override
public void print() {
String message = String.format("你好!%s,%s!", custom.getName(), custom.getDescription());
System.out.println(message);
}
}
5)创建starter启动器配置类
创建一个自动化配置类 CustomAutoConfiguration.class:
通过 @Configuration 注解指明这是一个JavaConfig。
通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解启用上面定义的配置类,这样这个配置类才会被Spring容器自动装配
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Custom.class)
public class CustomAutoConfiguration {
/**
* 初始化自定义Starter的Bean
*/
@Bean
public CustomService customService(Custom custom) {
return new CustomServiceImpl(custom);
}
}
6)创建Spring.factories
在 src/main/resource/META-INF目录下创建一个配置文件 spring.factories,配置文件内容见下文。这个文件很重要,spring-core中的SpringFactoriesLoader通过检索这个文件中的内容,获取到指定的配置类。
# 自动初始化配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.test.starter.config.CustomAutoConfiguration
注意
如果这个配置类
com.test.starter.config.CustomAutoConfiguration
名称写错了,就会报错
3.2.3 测试自定义启动器
1) 正常情况下starter测试
使用现有的项目创建测试,改动的地方如下:
新增一个Controller内容如下
import com.test.starter.service.CustomService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class MystarterController {
@Autowired
CustomService service;
@RequestMapping("/starter")
public Object mystarter() {
service.print();
return "ok";
}
}
启动Hibernate52Application,访问 http://localhost:8080/demo/starter 使用默认配置时,测试结果如下
2)使用自定义配置测试
测试,使用自定义配置
在test的resources目录下,增加一个application.yml配置文件,文件配置如下:
com:
test:
starter:
name: Frank
description: 使用自定义配置的
总结
spring体系
ioc:beanFactory 模板模式 obtainBeanFactory,加载BD,getBean,doGetBean,createBean,doCreateBean
doCreateBean(){
实例化,设置3级缓存,赋值,后置处理器 (循环依赖)
}
aop:在赋值后,jdk动态代理+责任链
mvc :servlet DispatchServet10步
springboot : new +run(Annotation)
自动装配 SPI ,Configration+6种形式


