@SpringbootApplication注释是什么意思?
什么是springboot?
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Spring Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
我们以前编写项目用到的框架基本上是SSM/SSH等等,搭建项目的时候你会发现你需要配置一大堆配置文件,比如:spring配置文件、mybatis配置文件、bean装配等等,这些都会耗费程序员大量的时间,然后就有团队注意到这个问题了,如果这些配置文件都能省略,直接业务开发,那岂不是爽歪歪?于是springboot就出来,它能就简化90%的配置文件,实现自动装配。
搭建一个springbbot项目
1.新建项目
工具:idea
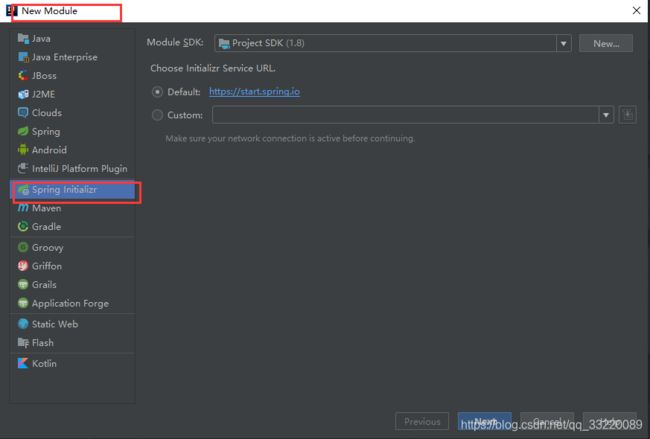
新建项目的时候选择Spring Initializr
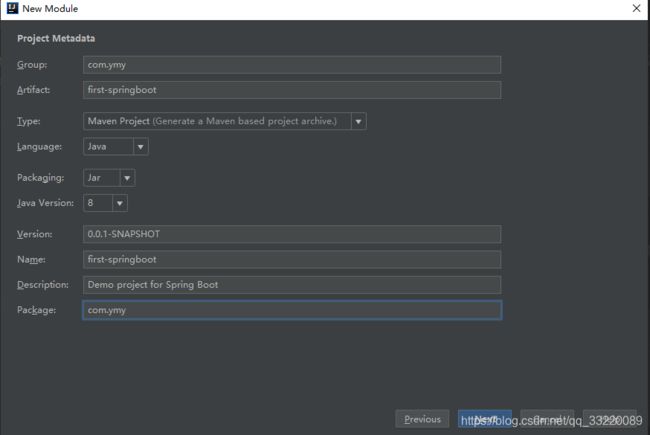
这里按照自己的要求填写即可,下一步
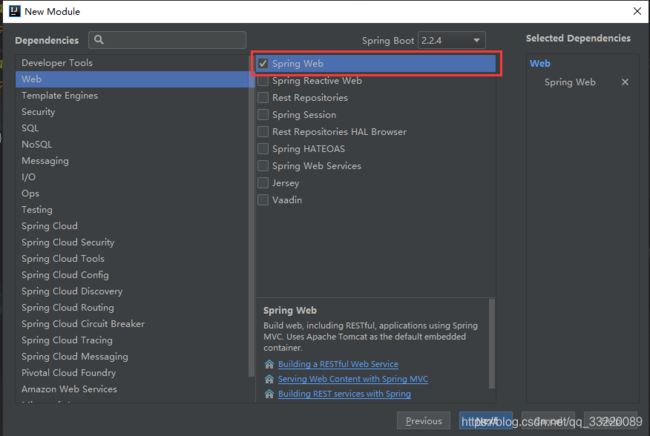
引入你需要的依赖,我这里引入了spring web,web项目要运行,它必不可少,点击next,后面是路径和名字的配置,可以自己填写,最后点击finsh,springboot项目就建好了。
请看新建项目的pom文件:
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.6.RELEASE
com.ymy
first-springboot
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
first-springboot
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
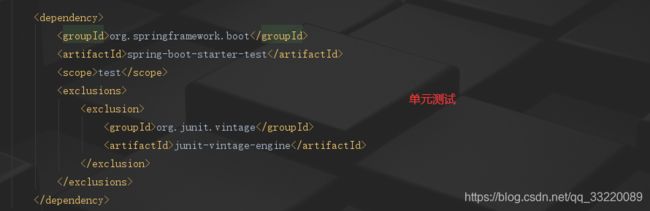
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
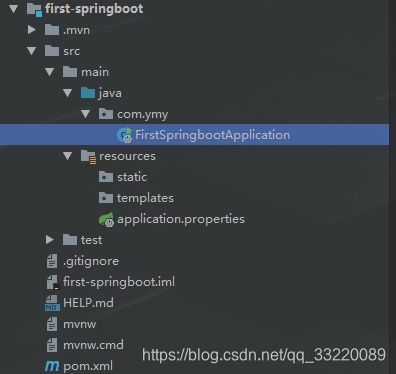
我们再来看一下项目的整个结构:
这里我们写一个测试controller:TestController
package com.ymy.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping(value = "/test")
public String test(){
return "HELLO-BUG!!!";
}
}
代码很简单,就是一个普通的get请求,那现在如何启动项目呢?
2.启动项目
找到FirstSpringbootApplication这个类,你会发现这个类里面有一个main函数,没错,运行main函数即可。
package com.ymy;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class FirstSpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FirstSpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
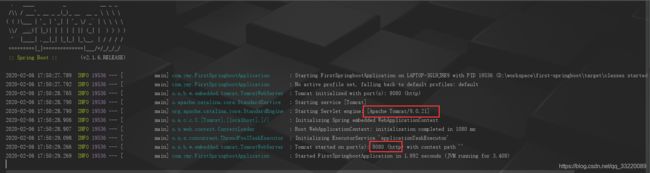
这里还需要说明一点,我到目前为止并没有指定项目的端口号,那我启动的时候会不会报错呢?我们来看:
我们并没有指定tomcat和端口,为什么执行main函数的时候会加载这两个?这里都是springboot默认给我配置的,再不配置的情况下默认使用toamcat与端口8080,你可以将tomcat改成jetty。
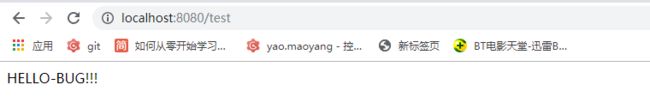
下面我们来测试一下,浏览器输入:localhost:8080/test
到此,springboot项目就算搭建成功了,不知道你有没有发现在启动类中有这么一个注解:@SpringBootApplication,知道他代表者什么吗?
@SpringBootApplication
不知道你们有没有接触过springboot1.5之前的版本,如果接触过的话,应该会对这三个注解很熟:@SpringBootConfiguration、@ComponentScan、@Configuration,这三个注解构成了springboot启动的必要条件。
1.@SpringBootConfiguration:负责激活springboot自动装配机制。
2.@ComponentScan:激活@Component扫描。
3.@Configuration:声明被标注为配置类。
这三个注解让我们省去了大量的配置文件,但是在springboot1.5之后的版本基本上就看不到他们了,代替他们的是:@SpringBootApplication,它实现了上面三个注解实现的所有功能,我们一起来看一下这个神奇的注解:
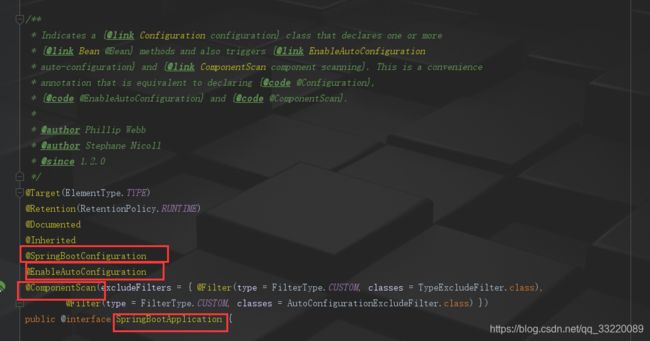
这是 @SpringBootApplication注解的源码,注意我标记出来的三个注解,其中有两个是前面讲到的三个注解中的两个相同,那还有一个@Configuration注解在哪里实现的?注意看@SpringBootConfiguration这个注解:
藏得有点深,但最终还是引用了 @Configuration注解,所以@SpringBootApplication注解等同于@SpringBootConfiguration、@ComponentScan、@Configuration。
但是,有一点需要注意一下,那就是@SpringBootApplication中的@ComponentScan并非使用了默认值,它添加了排除的FilterType实现:TypeExcludeFilter与AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter,第一个是spring boot1.4引入的用于查找BeanFactory中已经注册的TypeExcludeFilter Bean,作为代理对象。
TypeExcludeFilter源码:
/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.context;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
/**
* Provides exclusion {@link TypeFilter TypeFilters} that are loaded from the
* {@link BeanFactory} and automatically applied to {@code SpringBootApplication}
* scanning. Can also be used directly with {@code @ComponentScan} as follows:
*
* @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class))
*
*
* Implementations should provide a subclass registered with {@link BeanFactory} and
* override the {@link #match(MetadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory)} method. They should
* also implement a valid {@link #hashCode() hashCode} and {@link #equals(Object) equals}
* methods so that they can be used as part of Spring test's application context caches.
*
* Note that {@code TypeExcludeFilters} are initialized very early in the application
* lifecycle, they should generally not have dependencies on any other beans. They are
* primarily used internally to support {@code spring-boot-test}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.4.0
*/
public class TypeExcludeFilter implements TypeFilter, BeanFactoryAware {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory && getClass() == TypeExcludeFilter.class) {
Collection delegates = ((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory)
.getBeansOfType(TypeExcludeFilter.class).values();
for (TypeExcludeFilter delegate : delegates) {
if (delegate.match(metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
throw new IllegalStateException("TypeExcludeFilter " + getClass() + " has not implemented equals");
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
throw new IllegalStateException("TypeExcludeFilter " + getClass() + " has not implemented hashCode");
}
}
而springboot1.5开始支持用于排除其他同时标注 @Configuration和@EnableAutoConfiguration的类。
AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
/**
* A {@link TypeFilter} implementation that matches registered auto-configuration classes.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.5.0
*/
public class AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter implements TypeFilter, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private volatile List autoConfigurations;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException {
return isConfiguration(metadataReader) && isAutoConfiguration(metadataReader);
}
private boolean isConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata().isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName());
}
private boolean isAutoConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return getAutoConfigurations().contains(metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName());
}
protected List getAutoConfigurations() {
if (this.autoConfigurations == null) {
this.autoConfigurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
}
return this.autoConfigurations;
}
}