C语言函数大全-- _w 开头的函数(4)
_w 开头的函数(4)
- 1. _wstrtime
-
- 1.1 函数说明
- 1.2 演示示例
- 1.3 运行结果
- 2. _wstrtime_s
-
- 2.1 函数说明
- 2.2 演示示例
- 2.3 运行结果
- 3. _wsetlocale
-
- 3.1 函数说明
- 3.2 演示示例
- 3.3 运行结果
- 4. _wtmpnam
-
- 4.1 函数说明
- 4.2 演示示例
- 4.3 运行结果
- 5. _wtof
-
- 5.1 函数说明
- 5.2 演示示例
- 5.3 运行结果
- 6. _wtof_l
-
- 6.1 函数说明
- 6.2 演示示例
- 6.3 运行结果
- 7. _wtoi
-
- 7.1 函数说明
- 7.2 演示示例
- 7.3 运行结果
- 8. _wtoi_l
-
- 8.1 函数说明
- 8.2 演示示例
- 8.3 运行结果
- 9. _wtol
-
- 9.1 函数说明
- 9.2 演示示例
- 9.3 运行结果
- 10. _wtol_l
-
- 10.1 函数说明
- 10.2 演示示例
- 10.3 运行结果
- 11. _wsopen
-
- 11.1 函数说明
- 11.2 演示示例
- 11.3 运行结果
- 12. _wsopen_s
-
- 12.1 函数说明
- 12.2 演示示例
本篇介绍C语言函数大全-- _w 开头的函数(4)
1. _wstrtime
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
wchar_t *_wstrtime(wchar_t *buffer); |
用于获取当前系统时间并返回一个宽字符字符串表示,格式为 "HH:MM:SS"(小时:分钟:秒) |
参数:
- buffer : 一个指向
wchar_t类型数组的指针,用于存储表示当前系统时间的宽字符字符串。如果该参数为NULL,则_wstrtime函数会使用静态内部缓冲区来存储返回的时间字符串。
注意: 在多线程环境下,不应使用静态内部缓冲区,而应将
buffer参数传递给函数以避免竞争条件。
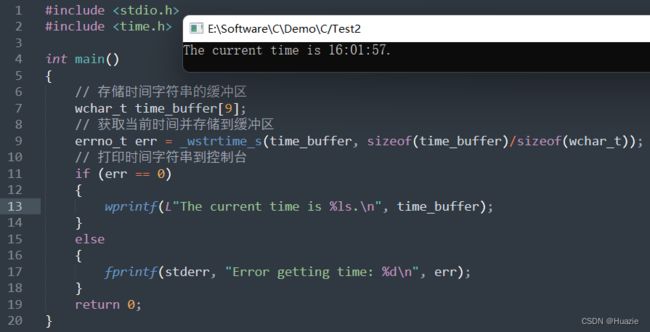
1.2 演示示例
#include 注意: 在不同平台上,本地化设置可能会影响
_wstrtime()函数的输出格式
1.3 运行结果
2. _wstrtime_s
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
errno_t _wstrtime_s(wchar_t *buffer, size_t sizeInWords); |
用于获取当前系统时间并返回一个宽字符字符串表示,格式为 "HH:MM:SS"(小时:分钟:秒)。相比于 _wstrtime 函数,_wstrtime_s 函数增加了一个额外的参数,用于指定缓冲区的大小,在多线程环境下更加安全可靠 |
参数:
- buffer : 一个指向 wchar_t 类型数组的指针,用于存储表示当前系统时间的宽字符字符串。如果该参数为
NULL,则_wstrtime_s()函数会使用静态内部缓冲区来存储返回的时间字符串。- sizeInWords : 指定了
buffer缓冲区的大小,以wchar_t单位计算。如果buffer参数不为NULL,则应将该参数设置为buffer的大小,以确保在写入时间字符串时不会发生缓冲区溢出。
2.2 演示示例
#include 2.3 运行结果
3. _wsetlocale
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
wchar_t* _wsetlocale(int category, const wchar_t* locale); |
用于设置当前线程的本地化环境 |
参数:
- category : 要设置的本地化类别,可以是如下值之一:
LC_ALL:设置所有本地化类别LC_COLLATE:设置字符串比较规则类别LC_CTYPE:设置字符分类和转换规则类别LC_MONETARY:设置货币格式类别LC_NUMERIC:设置数字格式类别LC_TIME:设置日期和时间格式类别- locale : 一个指向以
null结尾的宽字符字符串的指针,用于指定要使用的本地化信息。例如,"zh-CN"可以指定为中国大陆地区的本地化环境。如果该参数为NULL,则函数会根据系统默认设置来进行本地化。
返回值:
- 如果设置成功,则返回一个指向以
null结尾的宽字符字符串的指针,表示当前设置的本地化环境;- 如果设置失败,则返回
NULL。
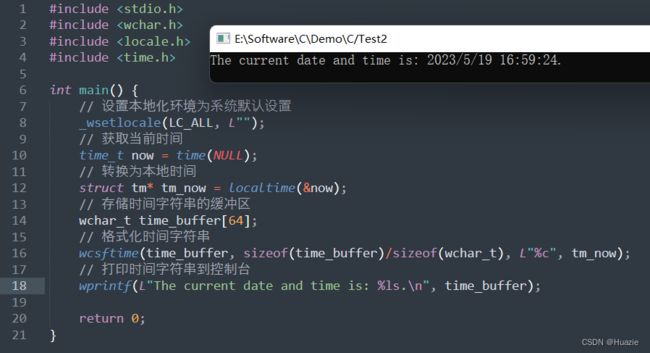
3.2 演示示例
#include 在上面的示例代码中,
- 首先,我们调用
_wsetlocale()函数将本地化环境设置为系统默认设置; - 接着,使用
time()函数获取当前时间now; - 然后,再使用
localtime()函数将now转换为本地时间; - 再接着,定义一个
wchar_t类型的数组作为存储格式化时间字符串的缓冲区; - 再然后,使用
wcsftime()函数将当前日期和时间格式化为指定的宽字符格式%c,并将结果存储到缓冲区中; - 最后,使用
wprintf()函数打印格式化后的时间字符串到控制台。
3.3 运行结果
4. _wtmpnam
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
wchar_t *_wtmpnam(wchar_t *s); |
用于生成一个唯一的临时文件名 |
参数:
- s : 一个指向
wchar_t类型字符数组的指针s,用于存储生成的唯一文件名。该数组必须至少具有L_tmpnam个元素
返回值:
- 如果成功生成临时文件时,则返回指向生成的唯一文件名的
wchar_t类型的指针;- 如果出现错误,则返回
NULL。
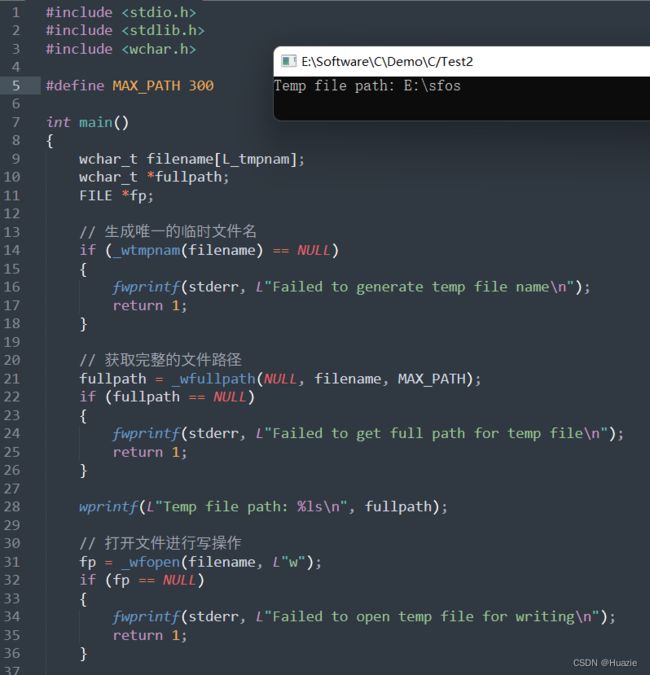
4.2 演示示例
#include 4.3 运行结果
5. _wtof
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double _wtof(const wchar_t *str); |
将一个宽字符串转换为浮点数 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
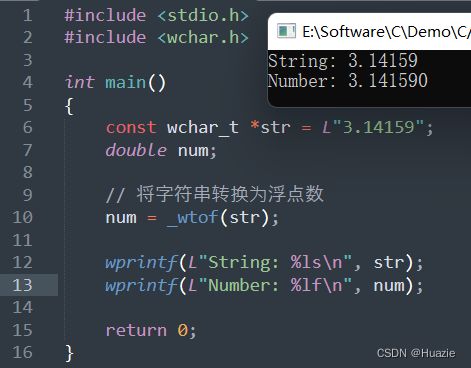
5.2 演示示例
#include 5.3 运行结果
6. _wtof_l
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
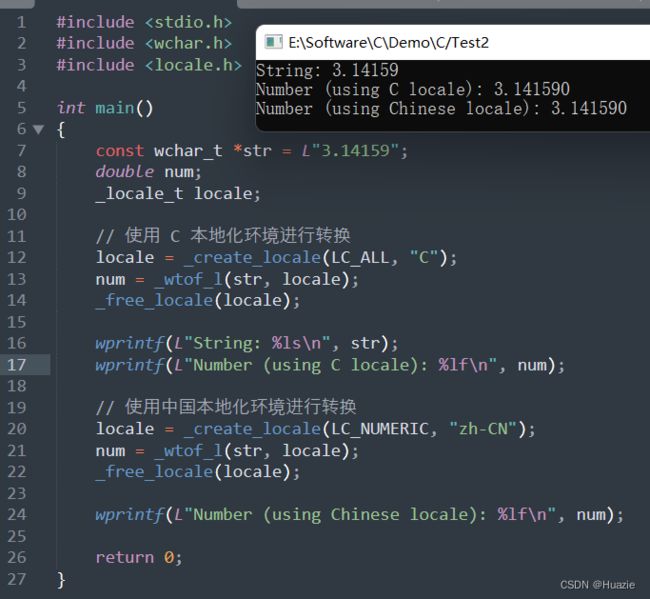
double _wtof_l(const wchar_t *str, _locale_t locale); |
用于将一个宽字符串转换为浮点数,并使用不同的本地化环境 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
- locale : 要使用的本地化环境。如果传递
NULL指针,则使用当前本地化环境
6.2 演示示例
#include 6.3 运行结果
7. _wtoi
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
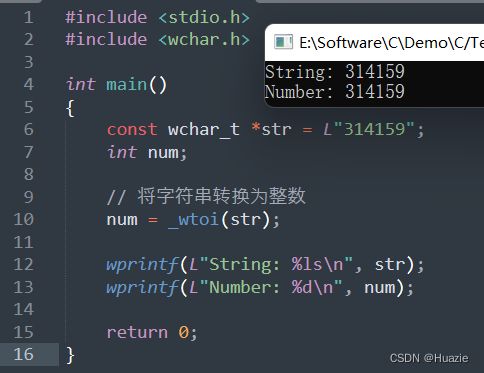
int _wtoi(const wchar_t *str); |
用于将一个宽字符串转换为整数 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
7.2 演示示例
#include 7.3 运行结果
8. _wtoi_l
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
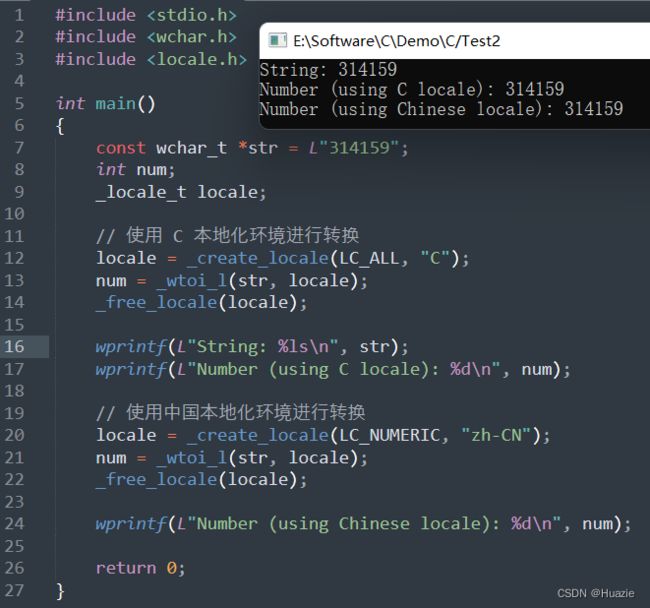
int _wtoi_l(const wchar_t *str, _locale_t locale); |
用于将一个宽字符串转换为整数,并使用不同的本地化环境 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
- locale : 要使用的本地化环境。如果传递
NULL指针,则使用当前本地化环境
8.2 演示示例
#include 8.3 运行结果
9. _wtol
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
long _wtol(const wchar_t *str); |
用于将一个宽字符串转换为长整形 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
9.2 演示示例
#include 9.3 运行结果
10. _wtol_l
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
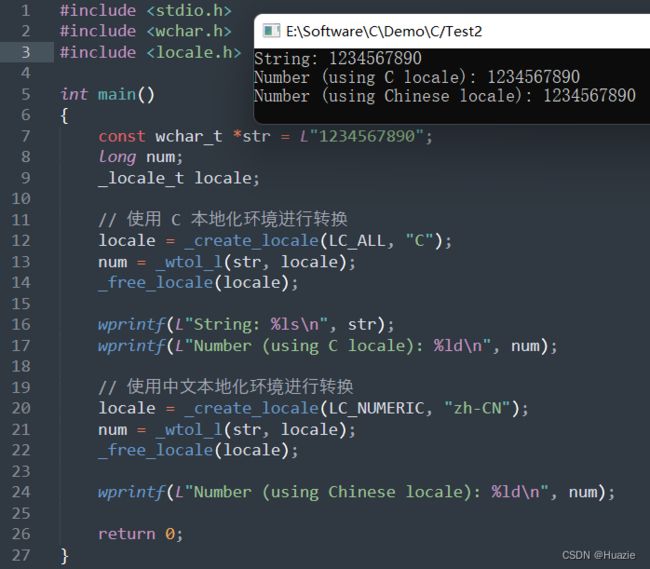
long _wtol_l(const wchar_t *str, _locale_t locale); |
用于将一个宽字符串转换为长整形,并使用不同的本地化环境 |
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
- locale : 要使用的本地化环境。如果传递
NULL指针,则使用当前本地化环境
10.2 演示示例
#include 10.3 运行结果
11. _wsopen
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int _wsopen(const wchar_t *filename, int oflag, int shflag, int pmode); |
用于打开指定文件 |
参数:
- filename : 要打开的文件名
- oflag : 打开文件的方式,可以是如下值之一或组合使用:
_O_RDONLY:以只读方式打开文件_O_WRONLY:以只写方式打开文件_O_RDWR:以读写方式打开文件_O_CREAT:如果文件不存在,则创建该文件_O_TRUNC:如果文件已存在,则截断该文件_O_EXCL:与_O_CREAT配合使用,确保创建的文件是原来不存在的- shflag : 共享方式,仅在
oflag中包括_O_CREAT标志时有效。可以是如下值之一:
_SH_DENYRW:拒绝其他程序读取或写入打开的文件_SH_DENYWR:拒绝其他程序写入打开的文件_SH_DENYRD:拒绝其他程序读取打开的文_SH_SHARE_DENYRW:允许其他程序只读打开打开的文件_SH_SHARE_DENYWR:允许其他程序只写打开的文件_SH_SHARE_DENYRD:允许其他程序读取打开的文件- pmode : 权限模式,仅在
oflag中包括_O_CREAT标志时有效。该参数指定新文件访问权限的位掩码
11.2 演示示例
#include 11.3 运行结果
12. _wsopen_s
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
errno_t _wsopen_s(int *pfh, const wchar_t *filename, int oflag, int shflag, int pmode); |
打开指定文件的安全版本,它避免了一些漏洞和错误,提高了程序的安全性 |
参数:
- pfh : 存储打开文件的句柄
- filename : 要打开的文件名或路径
- oflag : 打开文件的方式和访问模式,可以使用
_O_RDONLY、_O_WRONLY、_O_RDWR、_O_CREAT、_O_TRUNC等常量进行组合- shflag : 共享模式,可以使用
_SH_DENYRW、_SH_DENYWR、_SH_DENYRD等常量进行组合- pmode : 权限标志,例如
_S_IREAD和_S_IWRITE
12.2 演示示例
#include